
A parallel beam of sodium light of wavelength 5890 ${A^\circ }$ is incident on a thin glass plate of refractive index 1.5 such that the angle of refraction in the plate is ${60^\circ }$ . The smallest thickness of the plate which will make it dark by reflection:
A) $3926{A^\circ }$
B) $4353{A^\circ }$
C) $1396{A^\circ }$
D) $1921{A^\circ }$
Answer
524.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem one must have knowledge about the condition of maxima and minima or constructive or destructive interference. When one part of ray will be reflected and another will refract, it will create either constructive or destructive interference based on path difference.
Formula Used:
Formula for solving this question is \[2\mu t\cos r = \lambda \] where \[\mu \] , \[t\] , \[r\] , \[\lambda \] are refractive index, thickness of plate, angle of refraction and wavelength of ray.
Complete step by step answer:
To understand this question let’s deduce the expression from the very beginning.
Let’s consider a plane plate
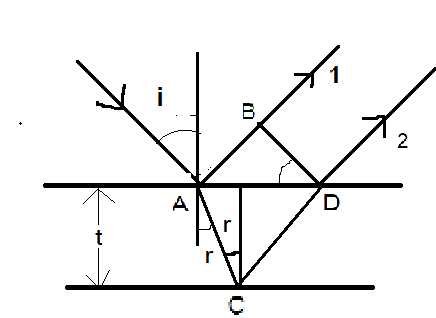
Let’s calculate the path difference $\Delta x = \mu (AC + CD) - AB$ . $\mu t$ is optical distance
So, $\Delta x = \dfrac{{\mu t}}{{\cos r}} + \dfrac{{\mu t}}{{\cos r}} - AB$
$\angle BDA = \angle i$
Because $[AB = AD\sin i = 2AE\sin i = 2d\tan r\sin i = 2d\tan r\mu \sin r]$
So, $\Delta x = \dfrac{{2\mu t}}{{\cos r}} - 2\mu t \times \tan r \times \sin r$
On further solving, $\Delta x = \dfrac{{2\mu t}}{{\cos r}}\left\{ {\dfrac{1}{{\cos r}} - \tan r \times \sin r} \right\} = 2\mu t.\cos r - - - (1)$ .
Till now we calculated the path difference generated due to difference in path length, but we need to consider the path difference that occurred due to reflection. Due to reflection there is a phase difference of 180 degrees and 360 degrees corresponds to $\lambda $ . So, 180 degrees will cause a path difference of $\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$ . So, adding $\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$ in equation (1).
So \[\Delta x = 2\mu t.\cos r + \dfrac{\lambda }{2} - - - (2)\] which is our final path difference
We know for destructive interference or dark spot path differences must be an odd multiple of wavelength.
So, \[2\mu t.\cos r + \dfrac{\lambda }{2} = (2n + 1)\dfrac{\lambda }{2}\] for n=1
\[ \Rightarrow 2\mu t\cos r = \lambda \]
Finally putting values given in the question
$\therefore t = \dfrac{\lambda }{{2\mu \cos r}} = \dfrac{{5890{A^\circ }}}{{2 \times 1.5 \times \cos {{60}^\circ }}} = 3926{A^\circ }$
$\therefore$ the correct option is A.
Note: In order to know more about interference, one should study about young’s double slit experiment and superposition of waves. This question was asked about bright spots. Then we need to apply conditions for constructive interference and the path difference will be even multiple of wavelength, and then we will solve accordingly.
Formula Used:
Formula for solving this question is \[2\mu t\cos r = \lambda \] where \[\mu \] , \[t\] , \[r\] , \[\lambda \] are refractive index, thickness of plate, angle of refraction and wavelength of ray.
Complete step by step answer:
To understand this question let’s deduce the expression from the very beginning.
Let’s consider a plane plate

Let’s calculate the path difference $\Delta x = \mu (AC + CD) - AB$ . $\mu t$ is optical distance
So, $\Delta x = \dfrac{{\mu t}}{{\cos r}} + \dfrac{{\mu t}}{{\cos r}} - AB$
$\angle BDA = \angle i$
Because $[AB = AD\sin i = 2AE\sin i = 2d\tan r\sin i = 2d\tan r\mu \sin r]$
So, $\Delta x = \dfrac{{2\mu t}}{{\cos r}} - 2\mu t \times \tan r \times \sin r$
On further solving, $\Delta x = \dfrac{{2\mu t}}{{\cos r}}\left\{ {\dfrac{1}{{\cos r}} - \tan r \times \sin r} \right\} = 2\mu t.\cos r - - - (1)$ .
Till now we calculated the path difference generated due to difference in path length, but we need to consider the path difference that occurred due to reflection. Due to reflection there is a phase difference of 180 degrees and 360 degrees corresponds to $\lambda $ . So, 180 degrees will cause a path difference of $\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$ . So, adding $\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$ in equation (1).
So \[\Delta x = 2\mu t.\cos r + \dfrac{\lambda }{2} - - - (2)\] which is our final path difference
We know for destructive interference or dark spot path differences must be an odd multiple of wavelength.
So, \[2\mu t.\cos r + \dfrac{\lambda }{2} = (2n + 1)\dfrac{\lambda }{2}\] for n=1
\[ \Rightarrow 2\mu t\cos r = \lambda \]
Finally putting values given in the question
$\therefore t = \dfrac{\lambda }{{2\mu \cos r}} = \dfrac{{5890{A^\circ }}}{{2 \times 1.5 \times \cos {{60}^\circ }}} = 3926{A^\circ }$
$\therefore$ the correct option is A.
Note: In order to know more about interference, one should study about young’s double slit experiment and superposition of waves. This question was asked about bright spots. Then we need to apply conditions for constructive interference and the path difference will be even multiple of wavelength, and then we will solve accordingly.
Recently Updated Pages
Differential Equations Explained: Guide for Students

Derivatives of Ammonia - Important Concepts and Tips for JEE

Degree of Dissociation in Chemistry: Concept, Formula & Examples

Cyclotron: Principles, Working & Uses Explained

Current Loop as a Magnetic Dipole: Concepts & Examples

Current and Potential Difference Explained Simply

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




