
A molecule of ammonia $(N{H_3})$ has:
A. Only single bonds
B. Only double bonds
C. Only triple bonds
D. Two double bonds and one single bond
Answer
534.6k+ views
Hint: Ammonia molecule has \[A{B_3}\] molecular geometry with a lone pair in which the three hydrogen atoms and an unshared pair of electrons are attached to the central nitrogen atom.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Ammonia is a colourless gas, consisting of hydrogen and nitrogen. It has a pungent smell and it is dangerous in its concentrated form. It behaves as a weak base as it forms salts with many acids. Ammonia is also called azane or nitrogen trihydride. It is a polar molecule due to the presence of lone pairs and readily forms hydrogen bonds.
Ammonia is a covalent atom because of the overlap of orbitals of three hydrogen atoms and three \[s{p^3}\] hybrid orbitals of nitrogen in the structure. The fourth \[s{p^3}\] hybrid orbital is denoted by a lone pair. The lone pair exerts an extra repulsion on the three-bonding hydrogen atoms and creates a slight compression to a ${107.3^\circ }$ bond angle. The H-N-H bond angle is ${107.3^\circ }$ , which results in bond pair-lone pair repulsions that push the N-H bonds inward.
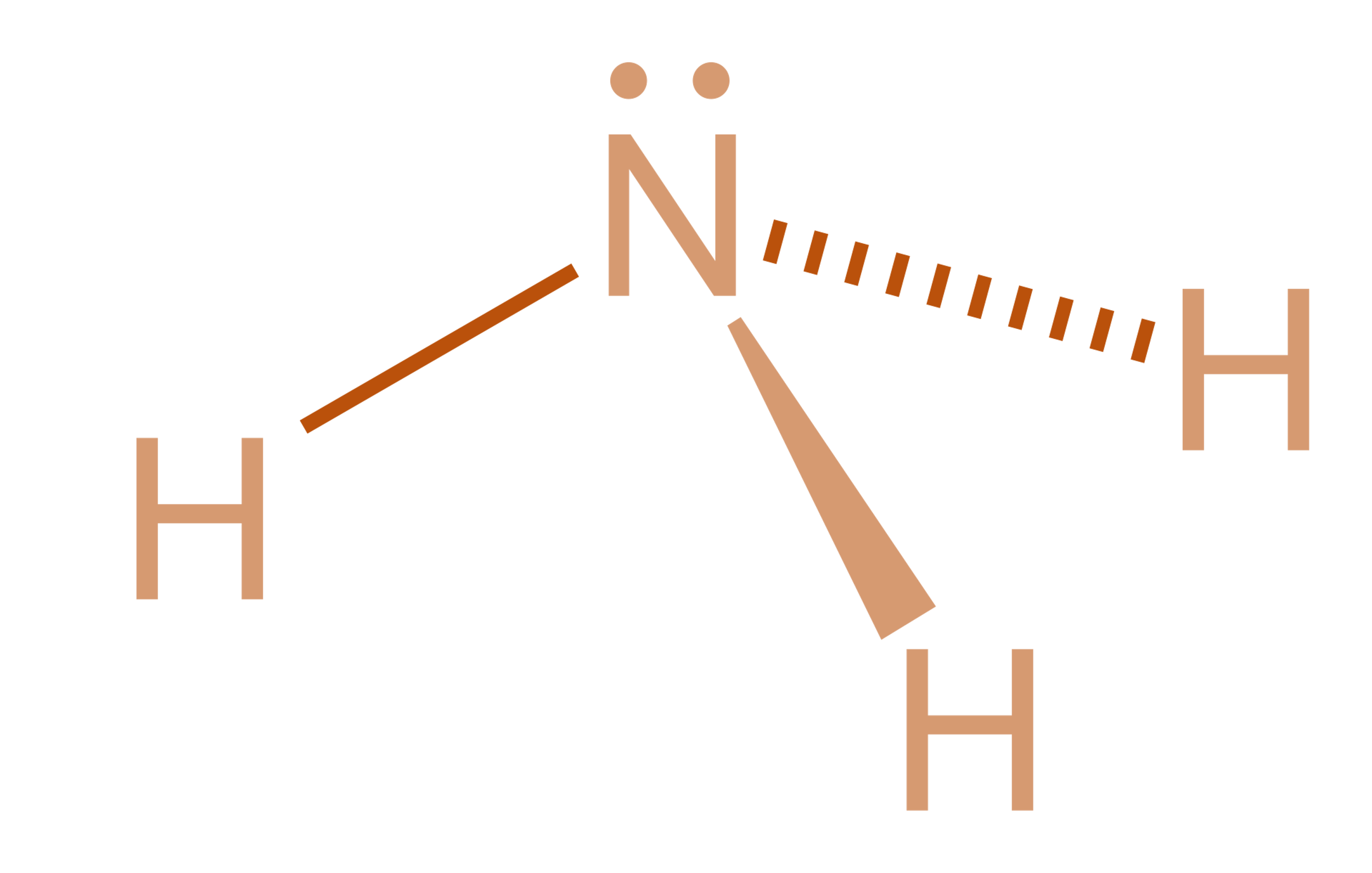
Such a molecule tends to have a trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry because the lone pair although invisible when looking at structure yet exert its influence. Therefore, it has three single bonds and a lone pair.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: The nitrogen has five valence electrons and gets three more electrons from three hydrogen atoms to complete its octet. It leaves a lone electron pair on nitrogen that is not bonded to any other atom and freely available for binding. This might also resemble tetrahedral geometry, having a somewhat similar bond angle of ${109^\circ }$.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Ammonia is a colourless gas, consisting of hydrogen and nitrogen. It has a pungent smell and it is dangerous in its concentrated form. It behaves as a weak base as it forms salts with many acids. Ammonia is also called azane or nitrogen trihydride. It is a polar molecule due to the presence of lone pairs and readily forms hydrogen bonds.
Ammonia is a covalent atom because of the overlap of orbitals of three hydrogen atoms and three \[s{p^3}\] hybrid orbitals of nitrogen in the structure. The fourth \[s{p^3}\] hybrid orbital is denoted by a lone pair. The lone pair exerts an extra repulsion on the three-bonding hydrogen atoms and creates a slight compression to a ${107.3^\circ }$ bond angle. The H-N-H bond angle is ${107.3^\circ }$ , which results in bond pair-lone pair repulsions that push the N-H bonds inward.

Such a molecule tends to have a trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry because the lone pair although invisible when looking at structure yet exert its influence. Therefore, it has three single bonds and a lone pair.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: The nitrogen has five valence electrons and gets three more electrons from three hydrogen atoms to complete its octet. It leaves a lone electron pair on nitrogen that is not bonded to any other atom and freely available for binding. This might also resemble tetrahedral geometry, having a somewhat similar bond angle of ${109^\circ }$.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques - 2025-26




