
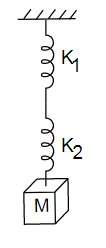
A mass M is suspended by two springs of force constants \[{K_1}\] and \[{K_2}\] respectively as shown in the diagram. The total elongation (stretch) of the two springs is
A. \[\dfrac{{Mg}}{{{K_1} + {K_2}}} \\ \]
B. \[\dfrac{{Mg\left( {{K_1} + {K_2}} \right)}}{{{K_1}{K_2}}} \\ \]
C. \[\dfrac{{Mg\left( {{K_1}{K_2}} \right)}}{{{K_1} + {K_2}}} \\ \]
D. \[\dfrac{{{K_1} + {K_2}}}{{{K_1}{K_2}Mg}}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Force on the system will be a product of effective constant for the series combination and elongation in the spring.
Formula used:
The expression of restoring force is,
\[F = Kx\]
Where, F = Force, k= Spring constant and x = Elongation (stretch) of the spring.
Complete step by step solution:
Given here is a spring mass system of two springs having constant \[{K_1}\] and \[{K_2}\] respectively. Springs are combined together in series combination and a mass M is suspended by the springs, we have to find the elongation in springs.
First we need to find the effective constant for the given combination of springs and it will be,
\[{K_{eff}} = \dfrac{{{K_1}{K_2}}}{{{K_1} + {K_2}}}\,.........(1)\]
Let the elongation in spring be x then free body diagram of suspended mass M will be,
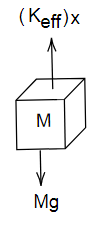
Image: Free body diagram of mass M
From free body diagram we have,
\[{K_{eff}}x = Mg \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{Mg}}{{{K_{eff}}}}\,.......(2)\]
Substituting value of \[{K_{eff}}\] form equation (1) in equation (2) we get,
\[x = \dfrac{{Mg\left( {{K_1} + {K_2}} \right)}}{{{K_1}{K_2}}}\,\]
Hence, elongation in the spring will be \[\dfrac{{Mg\left( {{K_1} + {K_2}} \right)}}{{{K_1}{K_2}}}\,\].
Therefore, option B is the correct answer.
Note: Even though in combination of springs we have multiple springs connected to each other either in series or parallel, they behave like a single spring and to solve numerical problems for combination of springs their effective constant is to be calculated first.
Formula used:
The expression of restoring force is,
\[F = Kx\]
Where, F = Force, k= Spring constant and x = Elongation (stretch) of the spring.
Complete step by step solution:
Given here is a spring mass system of two springs having constant \[{K_1}\] and \[{K_2}\] respectively. Springs are combined together in series combination and a mass M is suspended by the springs, we have to find the elongation in springs.
First we need to find the effective constant for the given combination of springs and it will be,
\[{K_{eff}} = \dfrac{{{K_1}{K_2}}}{{{K_1} + {K_2}}}\,.........(1)\]
Let the elongation in spring be x then free body diagram of suspended mass M will be,

Image: Free body diagram of mass M
From free body diagram we have,
\[{K_{eff}}x = Mg \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{Mg}}{{{K_{eff}}}}\,.......(2)\]
Substituting value of \[{K_{eff}}\] form equation (1) in equation (2) we get,
\[x = \dfrac{{Mg\left( {{K_1} + {K_2}} \right)}}{{{K_1}{K_2}}}\,\]
Hence, elongation in the spring will be \[\dfrac{{Mg\left( {{K_1} + {K_2}} \right)}}{{{K_1}{K_2}}}\,\].
Therefore, option B is the correct answer.
Note: Even though in combination of springs we have multiple springs connected to each other either in series or parallel, they behave like a single spring and to solve numerical problems for combination of springs their effective constant is to be calculated first.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




