
(A) is subjected to reduction with $Zn - Hg/HCl$ and the product formed is N-methylmethanamine. (A) can be:
A. Ethane nitrile
B. Nitroethane
C. Carbylamine ethane
D. Carbylamino methane
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint : We can solve this problem with the help of Clemmensen Reduction reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
> As it is given in the problem statement that (A) is subjected to reduction with $Zn - Hg/HCl$ so it is clearly a clemmensen reduction reaction. In this reaction aldehydes and ketones (carbonyl group) with zinc amalgam $(Zn/Hg)$ in concentrated hydrochloric acid reduce the aldehydes or ketone to a hydrocarbon. The mercury alloy does not participate in the reaction it just used to provide a clean active metal surface.
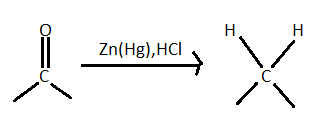
This reduction involves heating a carbonyl compound with finely divided amalgamated zinc in hydroxylic solvent which contains a mineral acid such as hydrochloric acid. In clemmensen reduction nitro group is also reduced in presence of zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid but nitro group containing compounds reduces very slowly. This reaction reduces $RCN$ to amine ($RC{H_2}N{H_2}$) and isocyanide compounds to $RNHC{H_3}$. Here in the problem it is given that the product is N-Ethylmethylamine. So it is clear that there is a isocyanide group in the A and $R$ is methyl group $C{H_3} - $ as it gives a compound which has only two carbon.
$A \to C{H_3} - NH - C{H_3}$ $ \Rightarrow $So know we know that the compound (A) is $C{H_3} - NC$ which is carboxyl amino methane.
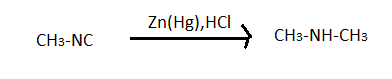
Hence the last option, that is option D is the correct answer to this problem.
Note : : We have approached this reaction with clemmensen reduction. In this reaction it reduces carbonyl group to simple hydrocarbons. Thus the compound A is here $C{H_3} - NC$ which carbylamine methane. In the problem the product is given which makes it very easy for us to determine compound (A) as we know that compound that contains iso cyanide group give such type products.
Complete step by step solution:
> As it is given in the problem statement that (A) is subjected to reduction with $Zn - Hg/HCl$ so it is clearly a clemmensen reduction reaction. In this reaction aldehydes and ketones (carbonyl group) with zinc amalgam $(Zn/Hg)$ in concentrated hydrochloric acid reduce the aldehydes or ketone to a hydrocarbon. The mercury alloy does not participate in the reaction it just used to provide a clean active metal surface.
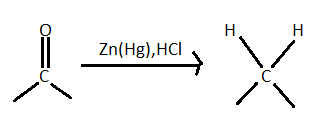
This reduction involves heating a carbonyl compound with finely divided amalgamated zinc in hydroxylic solvent which contains a mineral acid such as hydrochloric acid. In clemmensen reduction nitro group is also reduced in presence of zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid but nitro group containing compounds reduces very slowly. This reaction reduces $RCN$ to amine ($RC{H_2}N{H_2}$) and isocyanide compounds to $RNHC{H_3}$. Here in the problem it is given that the product is N-Ethylmethylamine. So it is clear that there is a isocyanide group in the A and $R$ is methyl group $C{H_3} - $ as it gives a compound which has only two carbon.
$A \to C{H_3} - NH - C{H_3}$ $ \Rightarrow $So know we know that the compound (A) is $C{H_3} - NC$ which is carboxyl amino methane.
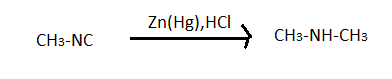
Hence the last option, that is option D is the correct answer to this problem.
Note : : We have approached this reaction with clemmensen reduction. In this reaction it reduces carbonyl group to simple hydrocarbons. Thus the compound A is here $C{H_3} - NC$ which carbylamine methane. In the problem the product is given which makes it very easy for us to determine compound (A) as we know that compound that contains iso cyanide group give such type products.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




