
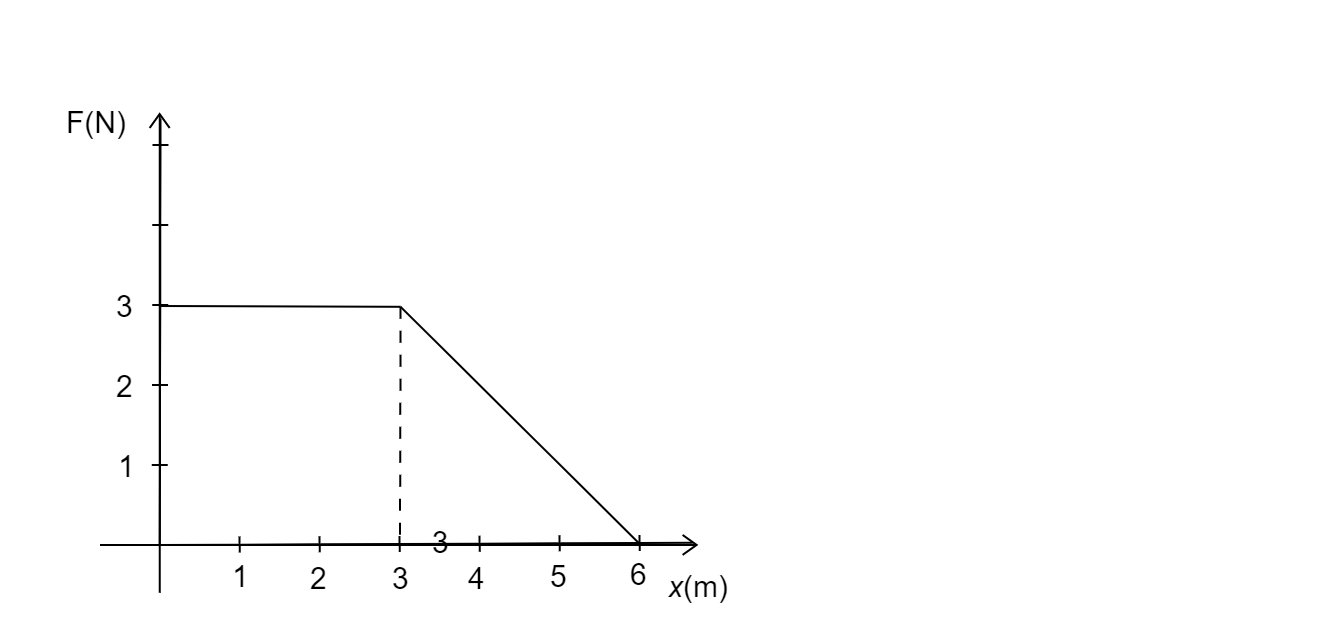
A force F acting on an object varies with distance x as shown in figure. The force is in N and x in m. The work done by the force in moving the object from $x = 0{\text{ to }}x = 6m$is:
(A) $13.5{\text{ J}}$
(B) $10{\text{ J}}$
(C) $15{\text{ J}}$
(D) $20{\text{ J}}$
Answer
242.1k+ views
Hint: Work is said to be done when a force produces motion in an object. The work done can be defined as the product of the force F and the displacement produced in the object, x. In a graphical form, F and x can be multiplied, and the area gives us the total value of the work done.
Complete step by step answer:
In a graphical representation of F vs x, we can integrate the curve and/or find the area enclosed between the two quantities.
This is the equivalent of multiplying in both quantities.
So, In the given graph we can divide the complex shape formed, into 2 simple shapes namely: A rectangle and a triangle.
Finding out areas of both these figures and adding them gives the value of total work done.
Area of triangle, ${A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}bh$
From the graph, $b = 6 - 3 = 3$
$h = 3$
$\therefore {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 3$
${A_1} = 4.5Nm$
Now, Area of rectangle (square here)
${A_2} = {a^2}$
Where the side length, $a = 3$
${A_2} = {3^2}$
${A_2} = 9Nm$
The total work done, W is defined as:
$W = {A_1} + {A_2}$
$W = 4.5 + 9$
$W = 13.5Nm{\text{ or }}13.5J$
The correct option is (A).
Additional Information
Work done is highly dependent on the displacement of the body, no matter how much force is applied, if displacement or deformation of the body is zero, work done remains zero. It is a scalar quantity, but it is also a dot product of two vector quantities.
Note: If the shapes are given in forms of functions, then the work done can be calculated by integrating the function and applying limits, and adding up all the integrals. Even this question can be solved as an integral, but applying the formula for area simple shapes makes it easier to solve.
Complete step by step answer:
In a graphical representation of F vs x, we can integrate the curve and/or find the area enclosed between the two quantities.
This is the equivalent of multiplying in both quantities.
So, In the given graph we can divide the complex shape formed, into 2 simple shapes namely: A rectangle and a triangle.
Finding out areas of both these figures and adding them gives the value of total work done.
Area of triangle, ${A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2}bh$
From the graph, $b = 6 - 3 = 3$
$h = 3$
$\therefore {A_1} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 3$
${A_1} = 4.5Nm$
Now, Area of rectangle (square here)
${A_2} = {a^2}$
Where the side length, $a = 3$
${A_2} = {3^2}$
${A_2} = 9Nm$
The total work done, W is defined as:
$W = {A_1} + {A_2}$
$W = 4.5 + 9$
$W = 13.5Nm{\text{ or }}13.5J$
The correct option is (A).
Additional Information
Work done is highly dependent on the displacement of the body, no matter how much force is applied, if displacement or deformation of the body is zero, work done remains zero. It is a scalar quantity, but it is also a dot product of two vector quantities.
Note: If the shapes are given in forms of functions, then the work done can be calculated by integrating the function and applying limits, and adding up all the integrals. Even this question can be solved as an integral, but applying the formula for area simple shapes makes it easier to solve.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




