
A farmer travelled a distance of 61 km in 9 hours. He partly travelled on foot @ 4 km/hr and partly on bicycle @ 9km/hr. The distance travelled on foot is
A. 14 km
B. 15 km
C. 16 km
D. 17 km
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Speed is defined as the distance covered by any object divided by the time taken to cover that distance.
Where Distance is the total length of the path covered by that object.
\[Speed = \dfrac{{Distance}}{{Time}}\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given, Farmer goes from point A to B
Then,
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{Distance{\text{ }}AB{\text{ }}\left( S \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}61{\text{ }}km} \\
{Total{\text{ }}Time{\text{ }}taken{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}travel{\text{ }}61{\text{ }}km{\text{ }}\left( T \right){\text{ }} = 9{\text{ }}hours} \\
{Speed{\text{ }}at{\text{ }}which{\text{ }}farmer{\text{ }}travels{\text{ }}on{\text{ }}foot{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}4{\text{ }}km/hr} \\
{Speed{\text{ }}at{\text{ }}which{\text{ }}farmer{\text{ }}travels{\text{ }}on{\text{ }}bicycle{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}9{\text{ }}km/hr}
\end{array}\]
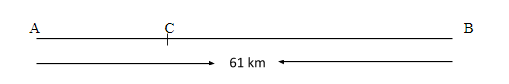
Let the distance travelled on foot and bicycle be AC and BC respectively.
\[\begin{gathered}
Let{\text{ }}the{\text{ }}time{\text{ }}for{\text{ }}which{\text{ }}farmer{\text{ }}travels{\text{ }}on{\text{ }}foot{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}x{\text{ }}hrs, \\
Then{\text{ }}time{\text{ }}for{\text{ }}which{\text{ }}farmer{\text{ }}travels{\text{ }}on{\text{ }}bicycle{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\left( {9 - x} \right){\text{ }}hrs \\
\end{gathered} \]
We know that,
\[Distance = Speed \times Time\]
Then, \[AC = 4km/hr \times xhr = 4x\] eqn (i)
\[BC = 9km/hr \times (9 - x)hr = 81 - 9x\] eqn (ii)
Also, \[AB = AC + BC\]
Using value of AB, AC and BC
We get,
\[\begin{gathered}
61 = 4x + 81 - 9x \\
5x = 20 \\
x = 4km \\
\end{gathered} \]
By putting value of x in eqn (i) and eqn (ii) we get,
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{AC{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}16{\text{ }}km} \\
{BC = {\text{ }}45{\text{ }}km} \\
{\therefore Distance{\text{ }}travelled{\text{ }}on{\text{ }}foot{\text{ }}by{\text{ }}farmer{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}16{\text{ }}km}
\end{array}\]
Hence option (C) is correct
Note: Always check the unit of all the given data. For example, if the distance is given in km and speed is given in m/s then convert both the quantity into the same unit.
\[1{\text{ }}km{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1000{\text{ }}m\]
\[1km/hr = \dfrac{5}{{18}}m/s\]
Where Distance is the total length of the path covered by that object.
\[Speed = \dfrac{{Distance}}{{Time}}\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given, Farmer goes from point A to B
Then,
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{Distance{\text{ }}AB{\text{ }}\left( S \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}61{\text{ }}km} \\
{Total{\text{ }}Time{\text{ }}taken{\text{ }}to{\text{ }}travel{\text{ }}61{\text{ }}km{\text{ }}\left( T \right){\text{ }} = 9{\text{ }}hours} \\
{Speed{\text{ }}at{\text{ }}which{\text{ }}farmer{\text{ }}travels{\text{ }}on{\text{ }}foot{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}4{\text{ }}km/hr} \\
{Speed{\text{ }}at{\text{ }}which{\text{ }}farmer{\text{ }}travels{\text{ }}on{\text{ }}bicycle{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}9{\text{ }}km/hr}
\end{array}\]

Let the distance travelled on foot and bicycle be AC and BC respectively.
\[\begin{gathered}
Let{\text{ }}the{\text{ }}time{\text{ }}for{\text{ }}which{\text{ }}farmer{\text{ }}travels{\text{ }}on{\text{ }}foot{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}x{\text{ }}hrs, \\
Then{\text{ }}time{\text{ }}for{\text{ }}which{\text{ }}farmer{\text{ }}travels{\text{ }}on{\text{ }}bicycle{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\left( {9 - x} \right){\text{ }}hrs \\
\end{gathered} \]
We know that,
\[Distance = Speed \times Time\]
Then, \[AC = 4km/hr \times xhr = 4x\] eqn (i)
\[BC = 9km/hr \times (9 - x)hr = 81 - 9x\] eqn (ii)
Also, \[AB = AC + BC\]
Using value of AB, AC and BC
We get,
\[\begin{gathered}
61 = 4x + 81 - 9x \\
5x = 20 \\
x = 4km \\
\end{gathered} \]
By putting value of x in eqn (i) and eqn (ii) we get,
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}}
{AC{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}16{\text{ }}km} \\
{BC = {\text{ }}45{\text{ }}km} \\
{\therefore Distance{\text{ }}travelled{\text{ }}on{\text{ }}foot{\text{ }}by{\text{ }}farmer{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}16{\text{ }}km}
\end{array}\]
Hence option (C) is correct
Note: Always check the unit of all the given data. For example, if the distance is given in km and speed is given in m/s then convert both the quantity into the same unit.
\[1{\text{ }}km{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1000{\text{ }}m\]
\[1km/hr = \dfrac{5}{{18}}m/s\]
Recently Updated Pages
Mutually Exclusive vs Independent Events: Key Differences Explained

Area vs Volume: Key Differences Explained for Students

Area of an Octagon Formula Explained Simply

Absolute Pressure Formula Explained: Key Equation & Examples

Central Angle of a Circle Formula Explained Quickly

Difference Between Vapor and Gas: JEE Main 2026

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Jan 21 Shift 1 Question Papers with Solutions & Answer Keys – Detailed Day 1 Analysis

JEE Main Response Sheet 2026 Released – Key Dates and Official Updates by NTA

JEE Main 2026 Answer Key OUT – Download Session 1 PDF, Response Sheet & Challenge Link

JEE Main Marks vs Percentile 2026: Calculate Percentile and Rank Using Marks

JEE Main 2026 Jan 22 Shift 1 Today Paper Live Analysis With Detailed Solutions

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 9 Circles (2025-26)

Fuel Cost Calculator – Estimate Your Journey Expenses Easily

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 Surface Areas and Volumes (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 Surface Areas And Volumes Exercise 11.3 (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Statistics (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Heron's Formula (2025-26)




