
A detergent is:
A. Cleaning agent
B. Drugs
C. Soap
D. Catalyst
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: A detergent or synthetic detergent or a syndet is a soapless soap which means it has all the properties of soap, but does not contain any soap.
They are a class of surfactants which are chemical substances that concentrate at the surface of the solution, form surface films, reduce surface tension of the solution and emulsify grease.
Complete step by step answer:
Detergents are actually ammonium, sulfate or sulphate salts of long chain hydrocarbons which contain 12 to 18 carbon atoms. But the more common detergents are the sodium salts of long chain sulphonic acids.
Detergents are surface active agents and they can remove dirt and dust by emulsifying grease. So, they act as cleansing agents. The molecule of a detergent consists of two characteristic groups, one of which is water soluble or hydrophilic and the other is oil soluble or lipophilic.
For example, sodium lauryl sulphate is a detergent. It consists of sodium ion and lauryl sulphate anion.
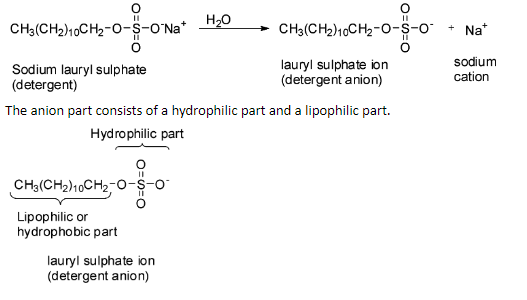
When a detergent is applied on a cloth with a greasy stain, the detergent reduces the surface tension of the water due to which the surface of the cloth is wetted thoroughly. The lipophilic parts of the detergent anion will be soluble in grease and the hydrophilic parts will be soluble in water.
When the cloth is scrubbed, the grease is pulled away from the cloth and broken into smaller droplets. Repulsion between the droplets will cause them to be suspended in water, thus forming an emulsion. Thus, the droplets will not coagulate or redeposit on the cloth. As a result, rinsing will wash away the droplets making the cloth clean.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
An advantage of detergent over soap is that detergents can be used even in hard water without any wastage but some of the soap gets wasted in hard water.
However, a disadvantage of detergents is that detergents having highly branched hydrocarbon chains cause pollution in rivers. This is because the side chains stop bacteria from attacking and breaking the chains which results in slow degradation of the detergent molecule leading to their accumulation in rivers. This causes water pollution.
They are a class of surfactants which are chemical substances that concentrate at the surface of the solution, form surface films, reduce surface tension of the solution and emulsify grease.
Complete step by step answer:
Detergents are actually ammonium, sulfate or sulphate salts of long chain hydrocarbons which contain 12 to 18 carbon atoms. But the more common detergents are the sodium salts of long chain sulphonic acids.
Detergents are surface active agents and they can remove dirt and dust by emulsifying grease. So, they act as cleansing agents. The molecule of a detergent consists of two characteristic groups, one of which is water soluble or hydrophilic and the other is oil soluble or lipophilic.
For example, sodium lauryl sulphate is a detergent. It consists of sodium ion and lauryl sulphate anion.

When a detergent is applied on a cloth with a greasy stain, the detergent reduces the surface tension of the water due to which the surface of the cloth is wetted thoroughly. The lipophilic parts of the detergent anion will be soluble in grease and the hydrophilic parts will be soluble in water.
When the cloth is scrubbed, the grease is pulled away from the cloth and broken into smaller droplets. Repulsion between the droplets will cause them to be suspended in water, thus forming an emulsion. Thus, the droplets will not coagulate or redeposit on the cloth. As a result, rinsing will wash away the droplets making the cloth clean.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
An advantage of detergent over soap is that detergents can be used even in hard water without any wastage but some of the soap gets wasted in hard water.
However, a disadvantage of detergents is that detergents having highly branched hydrocarbon chains cause pollution in rivers. This is because the side chains stop bacteria from attacking and breaking the chains which results in slow degradation of the detergent molecule leading to their accumulation in rivers. This causes water pollution.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

For pure water A pH increases while pOH decreases with class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Which of the following is most stable A Sn2+ B Ge2+ class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 8 Redox Reactions (2025-26)

An ideal gas is at pressure P and temperature T in class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

In Carius method of estimation of halogens 015g of class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (2025-26)

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages




