
A cube of aluminium of sides $0.1m$ is subjected to a shearing force of $100N$. The top face of the cube is displaced through $0.02cm$ with respect to the bottom face. The shearing strain would be:
(A) $0.02$
(B) $0.1$
(C) $0.005$
(D) $0.002$
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: Let's start with what is strain and then shearing strain. After that try to find out the formula for the shearing strain and what are the values needed in order to find the shearing strain then put all the information provided in the question in that formula and hence get the required answer.
Formula used:
$Shear~strain=\theta\sim~tan\theta$
Complete answer:
Shearing strains are caused by shearing stresses in a material. Consider a rectangular block of material subjected to shearing stresses in one plane. The shearing stresses transform the block's rectangular face into a parallelogram. Since the angle is measured in radians, it is non-dimensional.
The given problem can be expressed by the below diagram:
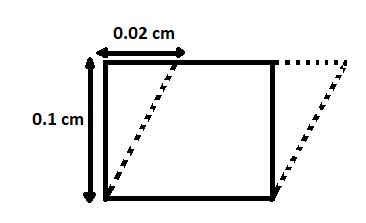
Now, mathematically, shearing strain is $Shear~strain=\theta\sim~tan\theta$
We know, $\tan\theta$ is the ratio of perpendicular to the base. From, the diagram, the value of the perpendicular is $0.02~cm$ and the base is $0.1m$.
Here, we need to change the unit of the perpendicular from cm to m, which is equal to $0.02\times10^{-2}m$. Here, the displaced distance is $0.02\times10^{-2}m$ and the original distance is $0.1m$.
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
$\theta=\frac{0.02\times10^{-2}}{0.1}$
Therefore, $\theta=0.002$
The correct option is D.
Note: It needs to be observed that shearing stresses alone do not cause volume changes. If the angular strain is small, the volume of the strained block is approximately equivalent to the volume of the original rectangular prism in the figure.
Formula used:
$Shear~strain=\theta\sim~tan\theta$
Complete answer:
Shearing strains are caused by shearing stresses in a material. Consider a rectangular block of material subjected to shearing stresses in one plane. The shearing stresses transform the block's rectangular face into a parallelogram. Since the angle is measured in radians, it is non-dimensional.
The given problem can be expressed by the below diagram:

Now, mathematically, shearing strain is $Shear~strain=\theta\sim~tan\theta$
We know, $\tan\theta$ is the ratio of perpendicular to the base. From, the diagram, the value of the perpendicular is $0.02~cm$ and the base is $0.1m$.
Here, we need to change the unit of the perpendicular from cm to m, which is equal to $0.02\times10^{-2}m$. Here, the displaced distance is $0.02\times10^{-2}m$ and the original distance is $0.1m$.
Substituting the values in the formula we get,
$\theta=\frac{0.02\times10^{-2}}{0.1}$
Therefore, $\theta=0.002$
The correct option is D.
Note: It needs to be observed that shearing stresses alone do not cause volume changes. If the angular strain is small, the volume of the strained block is approximately equivalent to the volume of the original rectangular prism in the figure.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




