
A compound whose molecule is superimposable on its mirror image despite containing chiral carbon atoms is:
(A) Threo isomer
(B) Meso compound
(C) Enantiomer
(D) None of the above
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: A compound whose molecules are superimposable on its mirror image despite containing chiral carbon atom is called meso compound.
Complete step by step answer:
Chiral carbon is also known as asymmetric carbon. When four valencies of carbon atom are satisfied by different groups, then C atom is known as asymmetric carbon.
Example: 2-chlorobutane
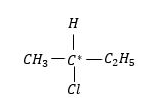
Here, four valencies satisfied by $ - H, - C{H_3}, - {C_2}{H_5}$and $ - Cl$group.
Threo: Compounds having two different chiral or asymmetric carbon atoms are named by using prefix threo.
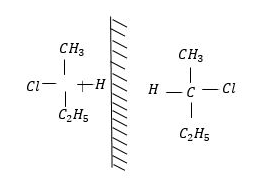
Enantiomers: Enantiomers are chiral molecules that are mirror images of one another.
The molecules are non-superimposable on one another. This means that molecules cannot be placed on top of one another and give the same molecules. Enantiomers have same chemical and physical properties, but differ in the effect on plane polarized light. They rotate plane polarized light in equal but opposite direction.
Example: 2-chlorobutane.
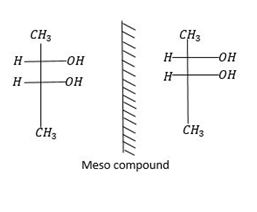
Meso: Meso compounds are superimposable on its mirror image. So they are non-optically active members of a set of stereoisomers at least two of which are optically active
Thus, Option C is correct.
Note:
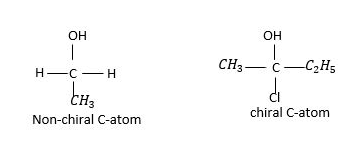
Four different groups should be bonded to chiral carbon. If two of them are the same then C-atom is not chiral.
Complete step by step answer:
Chiral carbon is also known as asymmetric carbon. When four valencies of carbon atom are satisfied by different groups, then C atom is known as asymmetric carbon.
Example: 2-chlorobutane

Here, four valencies satisfied by $ - H, - C{H_3}, - {C_2}{H_5}$and $ - Cl$group.
Threo: Compounds having two different chiral or asymmetric carbon atoms are named by using prefix threo.
Enantiomers: Enantiomers are chiral molecules that are mirror images of one another.
The molecules are non-superimposable on one another. This means that molecules cannot be placed on top of one another and give the same molecules. Enantiomers have same chemical and physical properties, but differ in the effect on plane polarized light. They rotate plane polarized light in equal but opposite direction.
Example: 2-chlorobutane.

Meso: Meso compounds are superimposable on its mirror image. So they are non-optically active members of a set of stereoisomers at least two of which are optically active

Thus, Option C is correct.
Note:
Four different groups should be bonded to chiral carbon. If two of them are the same then C-atom is not chiral.

Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




