
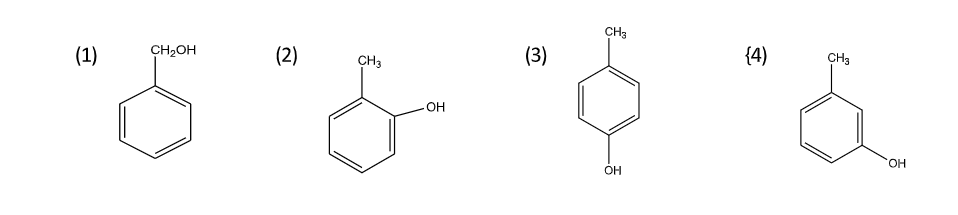
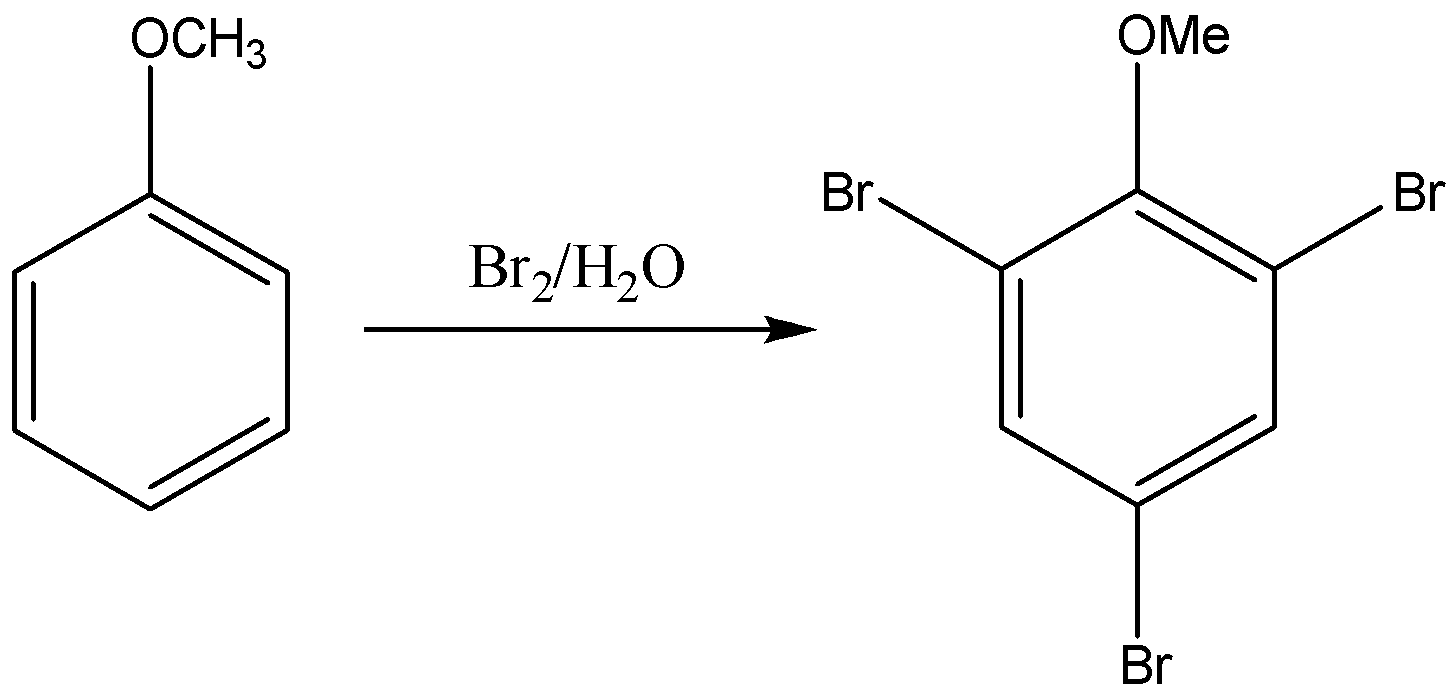
A compound (A) of molecular formula \[{C_7}{H_{8}}O\;\]is insoluble in water and dilute sodium bicarbonate but dissolves in dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide and gives a characteristic colour with aqueous\[FeC{l_3}\]. On treatment with bromine water, it readily gives a precipitate of\[{C_{7}}{H_{5}}OB{r_{3\;}}\] . Write down the structure of the compound (A).
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: We all are familiar with the fact that Benzyl alcohol is a colourless liquid with a mild pleasant aromatic odour. It is a useful solvent due to its polarity, low toxicity, and low vapor pressure.
Benzyl alcohol has moderate solubility in water \[\left( {4{\text{ }}g/100{\text{ }}mL} \right)\]and is miscible in alcohols and diethyl ether.
Again, Benzyl alcohol has a methylene \[\left( { - - CH2 - - } \right)\] group separating the phenyl ring and the anionic oxygen in the conjugate base and hence prevents resonance stabilization of the conjugate base. Hence phenol is stronger acid than benzyl alcohol and hence the latter doesn't dissolve in \[NaOH\] .
So we can conclude that since, the compound is insoluble in water and $NaHCO_3$ but dissolve in \[NaOH\] and gives characteristic colour with \[FeC{l_3}\], hence it must be phenol i.e,\[o - ,{\text{ }}p - {\text{ }}or{\text{ }}m - cresol\].
Complete step by step answer:
We can discuss this problem as following ;-
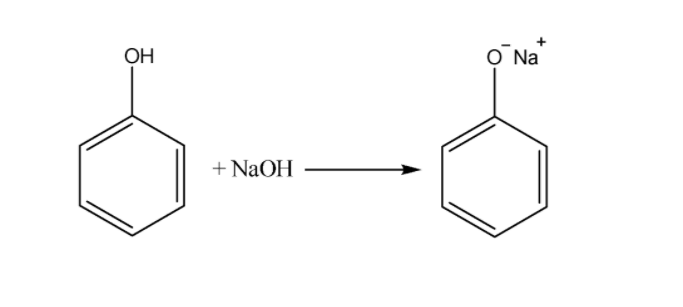
phenols are weak acids, they will react with bases. If phenol is reacted with\[NaOH{\text{ }}\left( {a{\text{ }}strong{\text{ }}base} \right)\] , it is completely converted to the phenoxide ion, which is soluble in water because it is charged. Phenol itself is not very soluble in water.
Sodium Bicarbonate is a weak base\[\left( {N{a^ + }{\text{ }}HC{O_3}^ - } \right)\]. So, it easily accepts protons when reacting with a stronger acid like a carbonic acid, but its not strong enough to pull the proton off phenol. Using a stronger base, like NaOH, it can pull the proton off the phenol.That's why phenol is not soluble in sodium bicarbonate.
Phenols show acidic nature and hence are soluble in alkalies like \[NaOH,{\text{ }}N{a_2}C{O_3}\;\]etc. The acidic nature is due to formation of resonance stabilized phenoxide ion formed by losing a proton from \[ - OH\] group.Thus more and more phenol is converted to phenoxide ion that is soluble in water.
Now it’s also known to all of you that Phenols form a complex with ferric ions. This complex has an intense colour, which may vary from blue, green or even red depending upon the nature of the phenol. Here in case of cresols we can see As an example using the chemical phenol itself:
\[6{\text{ }}PhOH{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}F{e^{3 + }}\; \to {\text{ }}{[Fe{\left( {OPh} \right)_6}]^{3-}}\]
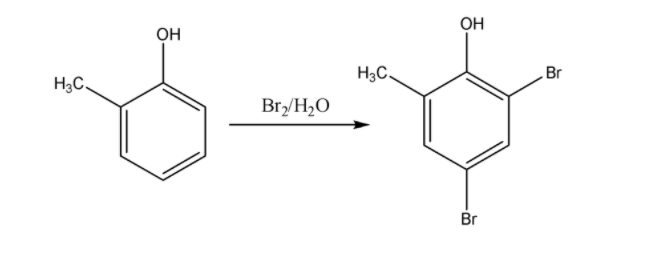
As we know electron donating \[ - OH\]group is ortho and para directing group ; so now among all three cresols, \[o - \] cresol forms Ortho and para bromo derivatives with respect to \[ - OH\]group. So in this complex there will be two Br atoms.
Also \[p - \] cresol forms Ortho bromo derivatives with respect to the \[ - OH\]group. So in this complex there will be two Br atoms;

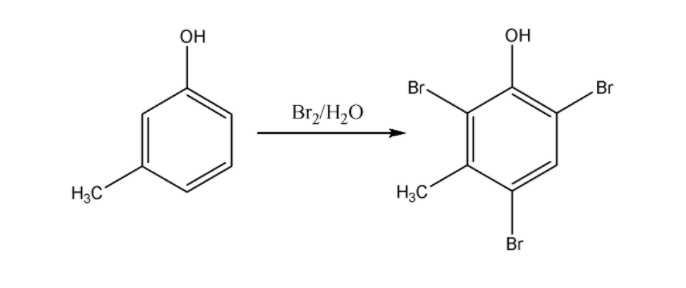
But in case of m-cresol we can see it forms Ortho and para bromo derivatives with respect to \[ - OH\] group. So in this complex there will be total three Br atoms;
Hence, Option 4 is correct.
Note: You should take care of choosing the correct structure because \[C7H8O\] can also give another structure like–
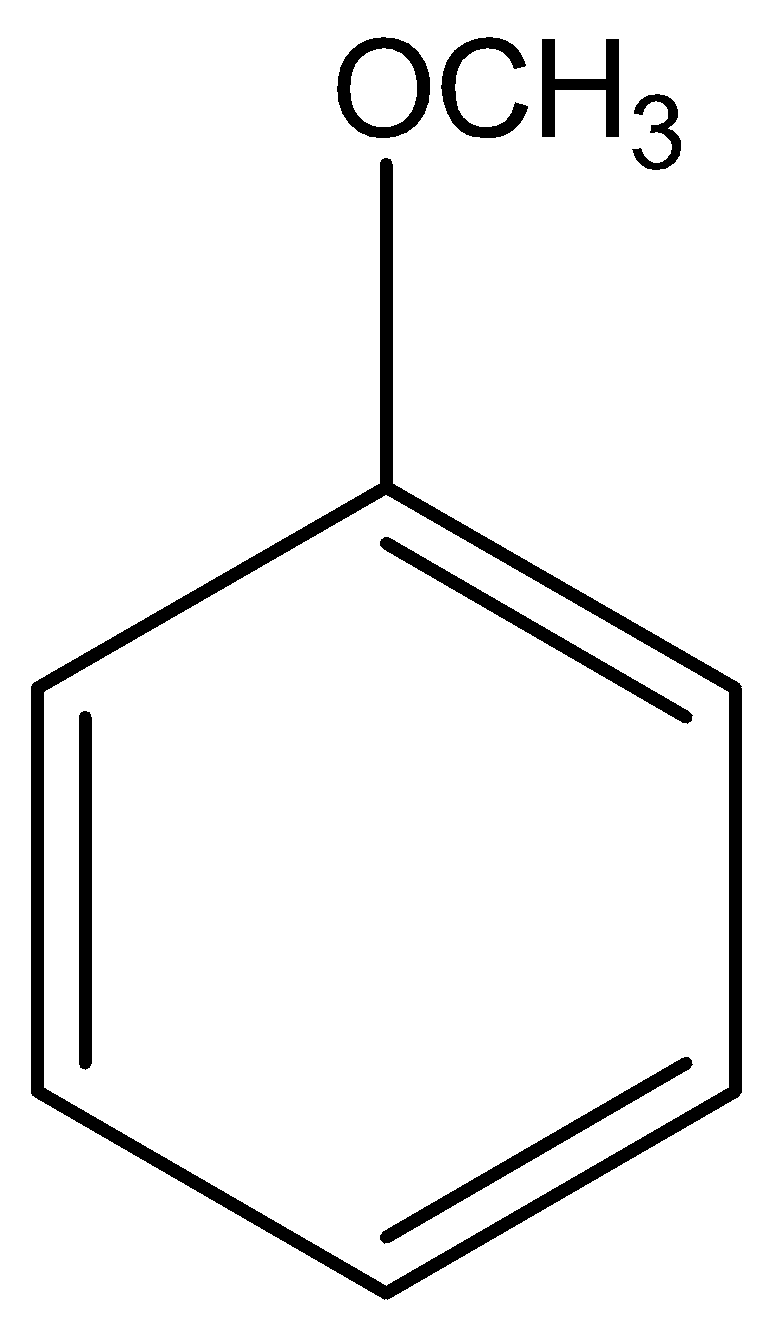
This structure also readily gives a precipitate of\[{C_{7}}{H_{5}}OB{r_{3\;}}\]
Benzyl alcohol has moderate solubility in water \[\left( {4{\text{ }}g/100{\text{ }}mL} \right)\]and is miscible in alcohols and diethyl ether.
Again, Benzyl alcohol has a methylene \[\left( { - - CH2 - - } \right)\] group separating the phenyl ring and the anionic oxygen in the conjugate base and hence prevents resonance stabilization of the conjugate base. Hence phenol is stronger acid than benzyl alcohol and hence the latter doesn't dissolve in \[NaOH\] .
So we can conclude that since, the compound is insoluble in water and $NaHCO_3$ but dissolve in \[NaOH\] and gives characteristic colour with \[FeC{l_3}\], hence it must be phenol i.e,\[o - ,{\text{ }}p - {\text{ }}or{\text{ }}m - cresol\].
Complete step by step answer:
We can discuss this problem as following ;-
phenols are weak acids, they will react with bases. If phenol is reacted with\[NaOH{\text{ }}\left( {a{\text{ }}strong{\text{ }}base} \right)\] , it is completely converted to the phenoxide ion, which is soluble in water because it is charged. Phenol itself is not very soluble in water.
Sodium Bicarbonate is a weak base\[\left( {N{a^ + }{\text{ }}HC{O_3}^ - } \right)\]. So, it easily accepts protons when reacting with a stronger acid like a carbonic acid, but its not strong enough to pull the proton off phenol. Using a stronger base, like NaOH, it can pull the proton off the phenol.That's why phenol is not soluble in sodium bicarbonate.
Phenols show acidic nature and hence are soluble in alkalies like \[NaOH,{\text{ }}N{a_2}C{O_3}\;\]etc. The acidic nature is due to formation of resonance stabilized phenoxide ion formed by losing a proton from \[ - OH\] group.Thus more and more phenol is converted to phenoxide ion that is soluble in water.

Now it’s also known to all of you that Phenols form a complex with ferric ions. This complex has an intense colour, which may vary from blue, green or even red depending upon the nature of the phenol. Here in case of cresols we can see As an example using the chemical phenol itself:
\[6{\text{ }}PhOH{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}F{e^{3 + }}\; \to {\text{ }}{[Fe{\left( {OPh} \right)_6}]^{3-}}\]
As we know electron donating \[ - OH\]group is ortho and para directing group ; so now among all three cresols, \[o - \] cresol forms Ortho and para bromo derivatives with respect to \[ - OH\]group. So in this complex there will be two Br atoms.

Also \[p - \] cresol forms Ortho bromo derivatives with respect to the \[ - OH\]group. So in this complex there will be two Br atoms;

But in case of m-cresol we can see it forms Ortho and para bromo derivatives with respect to \[ - OH\] group. So in this complex there will be total three Br atoms;

Hence, Option 4 is correct.
Note: You should take care of choosing the correct structure because \[C7H8O\] can also give another structure like–

This structure also readily gives a precipitate of\[{C_{7}}{H_{5}}OB{r_{3\;}}\]

Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




