
A box weighing 2000 N is to be slowly slid through 20 m on a straight track having friction coefficient 0.2 with the box. Find the work done by the person pulling the box with a chain at an angle θ with the horizontal.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: For just sliding the box without any acceleration force applied on the box will be just enough to counterbalance the frictional force provided by the floor.
Apply the equilibrium conditions:
\[\sum {{F_x} = 0,\sum {{F_Y} = 0} } \]
Then, find the work done by the expression,
Work done = component of force acting in the direction of displacement $ \times $ total displacement of the box
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s start with a free body diagram.
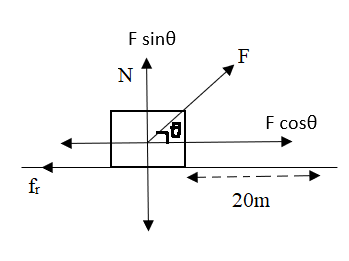
Given that,
Weight of the box = 2000 N
Friction coefficient $ = \mu = 0.2$
The box slowly slid through the floor about 20 m.
From free body diagram the forces acting on the boxes are:
Weight of the box is acting downwards,
W = mg = 2000 N
Normal reaction force will be acting upwards.
The force exerted by a person will have two components given by \[Fcos\theta \] and \[Fsin\theta \].
The frictional force acting on the box $ = {f_r} = \mu N$
To make the box to remain in its equilibrium condition, the sum of all forces acting on the box is zero.
Thus, on applying equilibrium conditions.
$\sum {{F_y} = 0} $ (forces acting in vertical direction)
$ \Rightarrow N + F\sin \theta - 2000 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow N = 2000 - F\sin \theta $
Similarly,
$\sum {{F_x} = 0} $
$ \Rightarrow F\cos \theta - {f_r} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow F\cos \theta = {f_r}$
$ \Rightarrow F\cos \theta = \mu N = 0.2N$
Substituting, the value of normal force N, we get
$ \Rightarrow F\cos \theta = 0.2(2000 - F\sin \theta )$
$ \Rightarrow F\cos \theta + 0.2F\sin \theta = 400$
$ \Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{400}}{{\cos \theta + 0.2\sin \theta }}$
Therefore, work done in pushing the block is given by
$ \Rightarrow W = F.s$
$ \Rightarrow W = F\cos \theta \times s$
$ \Rightarrow W = 20\left( {\dfrac{{400}}{{\cos \theta + 0.2\sin \theta }}} \right)\cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{8000}}{{1 + 0.2\tan \theta }}joule$
Note:
The formula for work done is given by a dot product, hence it is a scalar quantity. Mathematically it is given by $W = \vec F.\vec s$
The SI unit of work is joule(J).
Apply the equilibrium conditions:
\[\sum {{F_x} = 0,\sum {{F_Y} = 0} } \]
Then, find the work done by the expression,
Work done = component of force acting in the direction of displacement $ \times $ total displacement of the box
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s start with a free body diagram.

Given that,
Weight of the box = 2000 N
Friction coefficient $ = \mu = 0.2$
The box slowly slid through the floor about 20 m.
From free body diagram the forces acting on the boxes are:
Weight of the box is acting downwards,
W = mg = 2000 N
Normal reaction force will be acting upwards.
The force exerted by a person will have two components given by \[Fcos\theta \] and \[Fsin\theta \].
The frictional force acting on the box $ = {f_r} = \mu N$
To make the box to remain in its equilibrium condition, the sum of all forces acting on the box is zero.
Thus, on applying equilibrium conditions.
$\sum {{F_y} = 0} $ (forces acting in vertical direction)
$ \Rightarrow N + F\sin \theta - 2000 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow N = 2000 - F\sin \theta $
Similarly,
$\sum {{F_x} = 0} $
$ \Rightarrow F\cos \theta - {f_r} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow F\cos \theta = {f_r}$
$ \Rightarrow F\cos \theta = \mu N = 0.2N$
Substituting, the value of normal force N, we get
$ \Rightarrow F\cos \theta = 0.2(2000 - F\sin \theta )$
$ \Rightarrow F\cos \theta + 0.2F\sin \theta = 400$
$ \Rightarrow F = \dfrac{{400}}{{\cos \theta + 0.2\sin \theta }}$
Therefore, work done in pushing the block is given by
$ \Rightarrow W = F.s$
$ \Rightarrow W = F\cos \theta \times s$
$ \Rightarrow W = 20\left( {\dfrac{{400}}{{\cos \theta + 0.2\sin \theta }}} \right)\cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{8000}}{{1 + 0.2\tan \theta }}joule$
Note:
The formula for work done is given by a dot product, hence it is a scalar quantity. Mathematically it is given by $W = \vec F.\vec s$
The SI unit of work is joule(J).
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




