
A body projected from the surface of the earth attains a height equal to the radius of the earth. The velocity with which the body was projected is
$\left( a \right)$ $\sqrt {\dfrac{{2GM}}{R}} $
$\left( b \right)$ $\sqrt {\dfrac{{GM}}{R}} $
$\left( c \right)$ $\sqrt {\dfrac{{3GM}}{R}} $
$\left( d \right)$ $\sqrt {\dfrac{{5GM}}{{4R}}} $
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint Here in this question we have to find the velocity with which the body was projected and for this, we will use the conservation of energy and we know that the conservation of energy will be equal to energy at the earth's surface will be equal to the energy at the point at which the body will be after some velocity.
Formula used
Kinetic energy,
$K = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
And potential energy,
$V = \dfrac{{ - GMm}}{R}$
Here,
$K$, will be the kinetic energy
$m$, will be the mass of the body
$v$, will be the velocity
$V$, will be the potential energy
$G$, will be the gravitational constant
$M$, will be the mass of the earth
$R$, will be the radius of the earth
Complete Step By Step Solution first of all we make the diagram to solve the question. So at the earth's surface, there is the body that is being projected from the earth’s surface. The body will cover the height which will be equal to the earth's radius.
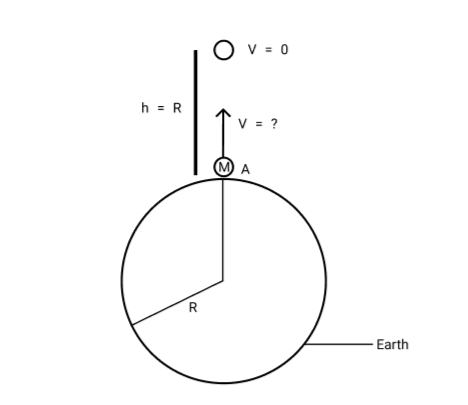
So from this, we can say that
$h = R$
Now by using the conservation of energy,
The energy at the point $A$will be equal to the energy at the point $B$
Therefore,
$K{E_A} + P{E_A} = K{E_B} + P{E_B}$
Now putting the value we know already from the formula, we get
Since at point $A$ the $PE$will be zero. And at height, $B$the kinetic energy will be zero.
Therefore,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} + \dfrac{{ - GMm}}{R} = 0 - \dfrac{{GMm}}{{R + R}}$
Now, we will solve the above equation and we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} = \dfrac{{ - GMm}}{{2R}} + \dfrac{{GMm}}{R}$
On solving the RHS, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} = \dfrac{{GMm}}{{2R}}$
Since $m$is common so it will cancel out, we have left
$ \Rightarrow {v^2} = \dfrac{{GM}}{R}$
Now, we will remove the root and we get
$ \Rightarrow v = \sqrt {\dfrac{{GM}}{R}} $
Therefore, the option $B$ will be correct.
Note So to understand the energy conservation we should have to be clear abo it. Energy conversion means to change its form, for example when supplied current to an electric motor then electric energy is converted into mechanical energy, and pumping of water takes place. Energy conservation means to conserve energy, for example, we switch off the bulb when it is not in use, so here electrical energy is conserved.
Formula used
Kinetic energy,
$K = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
And potential energy,
$V = \dfrac{{ - GMm}}{R}$
Here,
$K$, will be the kinetic energy
$m$, will be the mass of the body
$v$, will be the velocity
$V$, will be the potential energy
$G$, will be the gravitational constant
$M$, will be the mass of the earth
$R$, will be the radius of the earth
Complete Step By Step Solution first of all we make the diagram to solve the question. So at the earth's surface, there is the body that is being projected from the earth’s surface. The body will cover the height which will be equal to the earth's radius.

So from this, we can say that
$h = R$
Now by using the conservation of energy,
The energy at the point $A$will be equal to the energy at the point $B$
Therefore,
$K{E_A} + P{E_A} = K{E_B} + P{E_B}$
Now putting the value we know already from the formula, we get
Since at point $A$ the $PE$will be zero. And at height, $B$the kinetic energy will be zero.
Therefore,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} + \dfrac{{ - GMm}}{R} = 0 - \dfrac{{GMm}}{{R + R}}$
Now, we will solve the above equation and we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} = \dfrac{{ - GMm}}{{2R}} + \dfrac{{GMm}}{R}$
On solving the RHS, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} = \dfrac{{GMm}}{{2R}}$
Since $m$is common so it will cancel out, we have left
$ \Rightarrow {v^2} = \dfrac{{GM}}{R}$
Now, we will remove the root and we get
$ \Rightarrow v = \sqrt {\dfrac{{GM}}{R}} $
Therefore, the option $B$ will be correct.
Note So to understand the energy conservation we should have to be clear abo it. Energy conversion means to change its form, for example when supplied current to an electric motor then electric energy is converted into mechanical energy, and pumping of water takes place. Energy conservation means to conserve energy, for example, we switch off the bulb when it is not in use, so here electrical energy is conserved.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




