
\[4{s^2}4{p^1}\] identify the element that is diagonally a part of the next period in p-block.
A. Ge
B. Sn
C. In
D. Pb
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The distribution of an atom's electrons is crucial for deciding how that atom will behave chemically. Electrons are those atoms' components that exist outside of the nucleus. There are several commonalities between the diagonal neighbours. Moving from left to right and down the group reveals this relationship.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Travelling diagonally over the periodic table reveals the similarities between the elements, but these are far less striking than the similarities within a group. The diagonal link is particularly clear in the elements of the second and third periods of the periodic table. Between Li and Mg, Be and Al, B and Si, and so forth are a few examples.
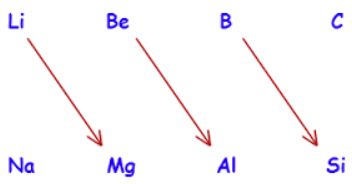
Image: Diagonal relationship of elements
Gallium is the element having the outer electron configuration \[4{s^2}4{p^1}\] (Ga). As a result, the outer electron configuration of the subsequent period in the p-block diagonally will be \[5{s^2}5{p^2}\] .
Tin (Sn) is the element that corresponds to this arrangement.
Therefore, option (b) is the right answer.
Note: The electrical configuration of an atom refers to how the electrons are arranged within its orbitals. The fixed number of electrons that make up each neutral atom is the atomic number, equal to the number of protons in each neutral atom. Along with electrons and protons, an atom also contains neutrons, which may or may not have the same number as protons. A relatively minor role in controlling any chemical reaction is played by the protons and neutrons that make up an atom's nucleus. The diagonal relationship is due to the polarising power, that is ionic radius being similar for the diagonally placed elements. Fundamentally, the element's similar ionic sizes account for the diagonal relationship.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Travelling diagonally over the periodic table reveals the similarities between the elements, but these are far less striking than the similarities within a group. The diagonal link is particularly clear in the elements of the second and third periods of the periodic table. Between Li and Mg, Be and Al, B and Si, and so forth are a few examples.

Image: Diagonal relationship of elements
Gallium is the element having the outer electron configuration \[4{s^2}4{p^1}\] (Ga). As a result, the outer electron configuration of the subsequent period in the p-block diagonally will be \[5{s^2}5{p^2}\] .
Tin (Sn) is the element that corresponds to this arrangement.
Therefore, option (b) is the right answer.
Note: The electrical configuration of an atom refers to how the electrons are arranged within its orbitals. The fixed number of electrons that make up each neutral atom is the atomic number, equal to the number of protons in each neutral atom. Along with electrons and protons, an atom also contains neutrons, which may or may not have the same number as protons. A relatively minor role in controlling any chemical reaction is played by the protons and neutrons that make up an atom's nucleus. The diagonal relationship is due to the polarising power, that is ionic radius being similar for the diagonally placed elements. Fundamentally, the element's similar ionic sizes account for the diagonal relationship.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




