
\[2-phenyl-2-hexanol\] can be prepared by Grignard synthesis. The pair of compounds giving the desired product is
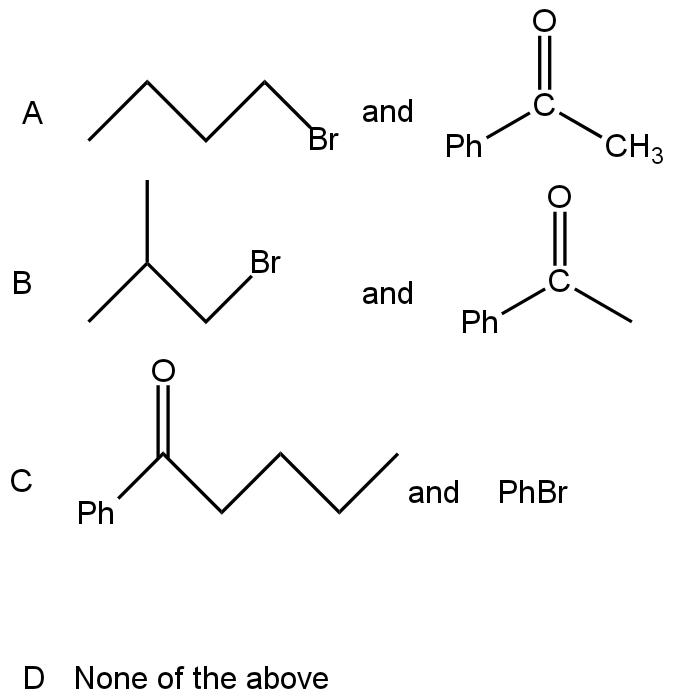
Answer
242.4k+ views
Hint: Grignard synthesis is the reaction in which organomagnesium halide (RMgX, Grignard reagent) is added to a ketone or to an aldehyde (carbonyl group-containing compound) to generate secondary or tertiary alcohol. In this question, we need to prepare \[2-phenyl-2-hexanol\], which is a chain of six carbons with one phenyl and one hydroxyl group.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
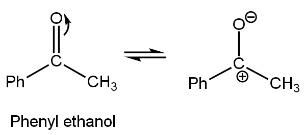
In option A, ketone compound is given (carbonyl compound), phenyl ethanon. As it is a ketonic group thus, the Grignard reagent will attack it which is\[{{C}_{4}}{{H}_{9}}MgBr\](RMgX). Oxygen group of carbonyl group in Phenyl ethanon attract one bond out of double bond due to high electronegativity of oxygen as compared to electronegativity of carbon to which it is bonded toward itself and attain negative charge such as
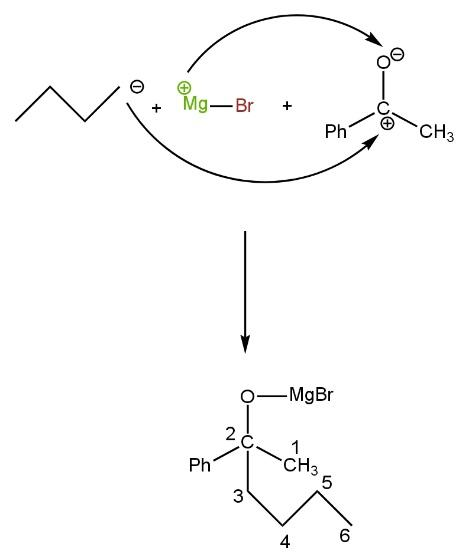
Now, the positive part of the Grignard reagent attacks the negative part of phenyl ethanone, and the negative part of the Grignard reagent attack the positive part of phenyl ethanone. Grignard reagent (\[{{C}_{4}}{{H}_{9}}MgBr\]), alkyl group,\[{{C}_{4}}{{H}_{9}}\]negatively charged while MgBr is positively charged such as
Now, this resulting compound undergoes hydrolysis (addition of water molecule). Due to this MgBr (positively charged) form bond with OH (negatively charged) and oxygen (negatively charged) form bond with H (positively charged, proton) giving three-degree alcohol, namely \[2-phenyl-2-hexanol\] such as
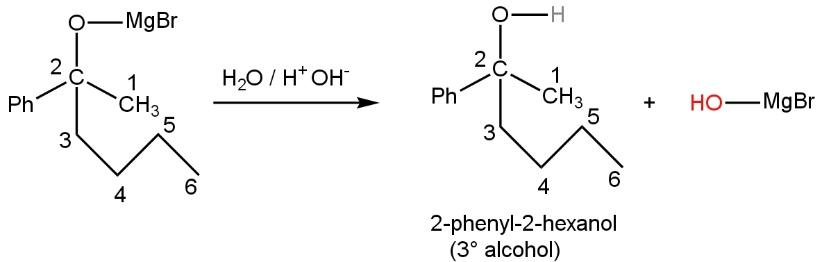
Hence we got 2-phenyl-2-hexanol from compounds of A. Thus, the correct option is A.
Note: Compounds Band D cannot form \[2-phenyl-2-hexanol\] because they do not form the resulting chain of six carbon. As discussed above, we can see that the number of ketonic group carbon (2) and Grignard reagent carbon (6) just added up. In compound B, the Grignard reagent has 3 carbon (1 is an alkyl group and not included in the main chain), and the other compound (Acetophenone) has one carbon or can be two carbon but still, it is less than 6 carbon for the main chain. While compound C has more than 6 carbon in the main chain because the Grignard reagent has 6 carbon (Ph group) and the ketonic compound has 6 carbon. Thus, the total number of carbon is more than 6.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In option A, ketone compound is given (carbonyl compound), phenyl ethanon. As it is a ketonic group thus, the Grignard reagent will attack it which is\[{{C}_{4}}{{H}_{9}}MgBr\](RMgX). Oxygen group of carbonyl group in Phenyl ethanon attract one bond out of double bond due to high electronegativity of oxygen as compared to electronegativity of carbon to which it is bonded toward itself and attain negative charge such as

Now, the positive part of the Grignard reagent attacks the negative part of phenyl ethanone, and the negative part of the Grignard reagent attack the positive part of phenyl ethanone. Grignard reagent (\[{{C}_{4}}{{H}_{9}}MgBr\]), alkyl group,\[{{C}_{4}}{{H}_{9}}\]negatively charged while MgBr is positively charged such as

Now, this resulting compound undergoes hydrolysis (addition of water molecule). Due to this MgBr (positively charged) form bond with OH (negatively charged) and oxygen (negatively charged) form bond with H (positively charged, proton) giving three-degree alcohol, namely \[2-phenyl-2-hexanol\] such as

Hence we got 2-phenyl-2-hexanol from compounds of A. Thus, the correct option is A.
Note: Compounds Band D cannot form \[2-phenyl-2-hexanol\] because they do not form the resulting chain of six carbon. As discussed above, we can see that the number of ketonic group carbon (2) and Grignard reagent carbon (6) just added up. In compound B, the Grignard reagent has 3 carbon (1 is an alkyl group and not included in the main chain), and the other compound (Acetophenone) has one carbon or can be two carbon but still, it is less than 6 carbon for the main chain. While compound C has more than 6 carbon in the main chain because the Grignard reagent has 6 carbon (Ph group) and the ketonic compound has 6 carbon. Thus, the total number of carbon is more than 6.
Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




