
1, 3-Butadiene with bromine in molar ratio generates predominantly:
(A) 1,1-dibromo-2-butene
(B) 1,4-dibromo-2-butene
(C) 1,2-dibromo-2-butene
(D) 1,3-dibromo-2-butene
Answer
240.6k+ views
Hint: First draw the structure of the molecule and then form the product by keeping in mind the conjugation due to the 2 double bonds present.
Complete step by step answer:
-Let us talk about the structure of 1,3-butadiene. It is a 4 carbon organic molecule with double bonds at 1 and 3 positions. It’s molecular formula is: ${C_4}{H_6}$.
The 2 double bonds make 1,3-butadiene structure to be conjugated (which means there is delocalisation of electrons in this structure). Its conjugated structures are as follows:
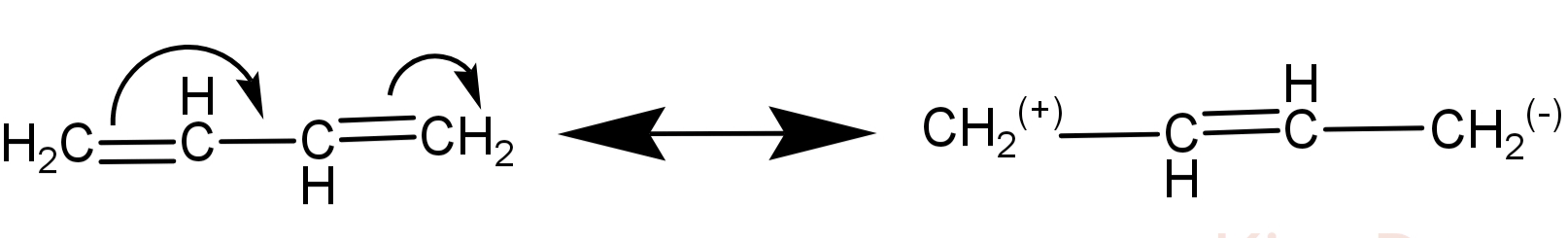
- When halogen attacks on a double bond there is scope for 2 types of products:
One which is formed by 1,2-addition and is kinetically favoured product (because it is formed fast)
And the other is formed by 1,4-addition and is a thermodynamically favoured product because it is associated with thermodynamic stability.
This thermodynamic stability gives a reason for the formation of a 1,4-addition product.
-Also when any halogen attacks on a double bond, there is addition of that halogen on that double bond and a 1,2-addition product might be formed. But this occurs only if there is no conjugation in that double bond.
Here in 1,3-butadiene there is conjugation of double bond and so addition of bromine is 1,4-addition. This means that the double bond shifts between the 2nd and the 3rd carbon (conjugated structure) and Br atoms are added at 1 and 4 position.
The above given reasons favour the formation of a 1,4-addition product. Thus the product formed is 1,4-butadiene.
This is shown in the following reaction:
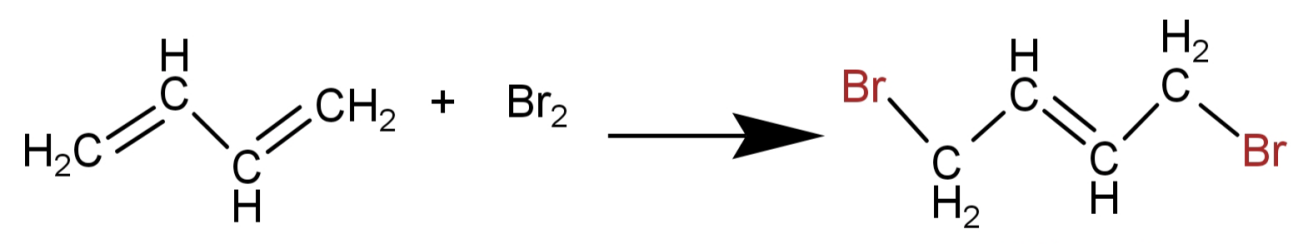
So, the correct option is: (B)1,4-dibromo-2-butene.
Note: Most common mistake we make here is of doing 1,2-addition which means adding 2 Br atoms at 1 and 2 positions of the molecule.
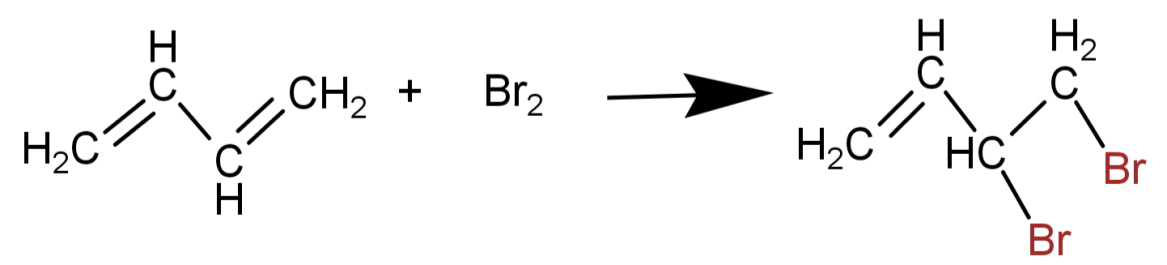
But this is wrong because conjugation is happening here. So, remember that when there is conjugation due to a double bond there will be 1,4- addition.
Complete step by step answer:
-Let us talk about the structure of 1,3-butadiene. It is a 4 carbon organic molecule with double bonds at 1 and 3 positions. It’s molecular formula is: ${C_4}{H_6}$.
The 2 double bonds make 1,3-butadiene structure to be conjugated (which means there is delocalisation of electrons in this structure). Its conjugated structures are as follows:

- When halogen attacks on a double bond there is scope for 2 types of products:
One which is formed by 1,2-addition and is kinetically favoured product (because it is formed fast)
And the other is formed by 1,4-addition and is a thermodynamically favoured product because it is associated with thermodynamic stability.
This thermodynamic stability gives a reason for the formation of a 1,4-addition product.
-Also when any halogen attacks on a double bond, there is addition of that halogen on that double bond and a 1,2-addition product might be formed. But this occurs only if there is no conjugation in that double bond.
Here in 1,3-butadiene there is conjugation of double bond and so addition of bromine is 1,4-addition. This means that the double bond shifts between the 2nd and the 3rd carbon (conjugated structure) and Br atoms are added at 1 and 4 position.
The above given reasons favour the formation of a 1,4-addition product. Thus the product formed is 1,4-butadiene.
This is shown in the following reaction:

So, the correct option is: (B)1,4-dibromo-2-butene.
Note: Most common mistake we make here is of doing 1,2-addition which means adding 2 Br atoms at 1 and 2 positions of the molecule.

But this is wrong because conjugation is happening here. So, remember that when there is conjugation due to a double bond there will be 1,4- addition.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




