Essential Modals Explained for CBSE Class 9 Exams 2025-26
FAQs on Mastering Modals in Class 9 English Grammar (2025-26)
1. What are modals, and which ones are most important for the CBSE Class 9 English exam 2025-26?
Modals, or modal auxiliary verbs, are helping verbs used to express functions like ability, permission, possibility, or obligation. For the CBSE Class 9 English syllabus (2025-26), the most frequently asked modals are can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, and must. Students should focus on understanding their specific uses in different contexts to answer exam questions correctly.
2. What type of questions on modals can be expected in the Class 9 English grammar section?
In the Class 9 English exam, questions on modals are typically framed to test your contextual understanding. You can expect them in formats like:
- Gap-filling exercises: Choosing the most appropriate modal to complete a sentence.
- Dialogue completion: Filling in a conversation with suitable modals to reflect the correct tone (e.g., request, advice).
- Sentence editing/omission: Identifying and correcting errors related to the use of modals.
3. How can I differentiate between 'should', 'must', and 'ought to' in the exam?
Understanding the subtle differences is crucial for exam accuracy.
- Should: Used for giving advice or a suggestion. It is a recommendation, not a command (e.g., "You should study regularly.").
- Must: Expresses strong obligation, necessity, or compulsion, often from the speaker's perspective (e.g., "You must submit your project by tomorrow.").
- Ought to: Indicates a moral duty or a correct action. It is very similar to 'should' but often implies a stronger sense of moral obligation (e.g., "We ought to respect our elders.").
4. What is the most common mistake students make in modal verb questions and how can it be avoided?
The most common mistake is failing to understand the context and tone of the sentence. For example, using 'can' for a formal request when 'may' or 'could' would be more appropriate. To avoid this, always read the entire sentence or dialogue carefully and ask yourself: Is this a request, an order, a suggestion, or a possibility? Matching the modal to the specific function required by the context is the best way to avoid errors.
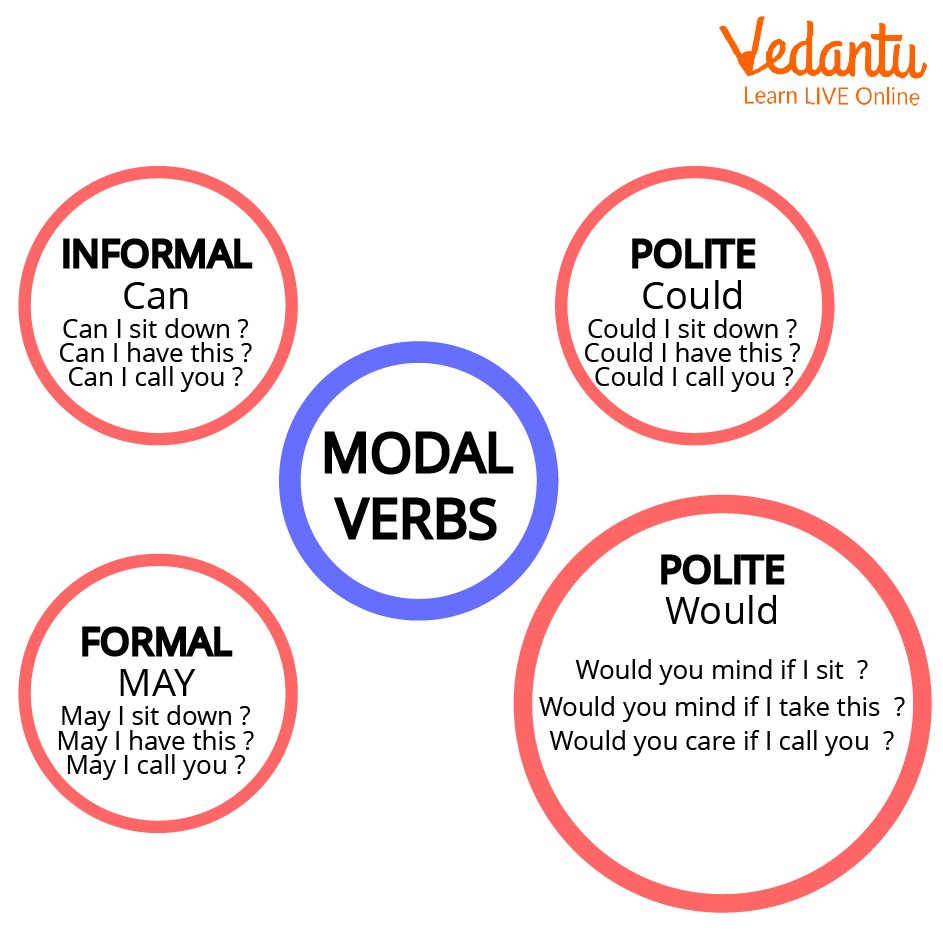
5. How do 'can' and 'could' differ when asking for permission?
'Can' and 'could' are both used to ask for permission, but they convey different levels of politeness, which is an important aspect tested in exams.
- Can: Used in informal situations, usually with friends or family (e.g., "Can I borrow your pen?").
- Could: Used in more formal or polite situations. It is a gentler and more hesitant way of asking for permission (e.g., "Could I speak to the manager, please?").
6. Why are modals considered important for scoring well in the overall English paper?
Modals are not just a grammar topic; they are essential for effective communication. A strong grasp of modals allows you to express nuances like politeness, certainty, and urgency accurately. This skill is vital not only for the grammar section but also for writing sections like letter writing, article writing, and storytelling, where conveying the correct tone can fetch you higher marks.
7. What is an effective strategy to prepare for important questions on modals for the 2025-26 exam?
An effective strategy is to create a function-based chart. List the main functions (e.g., Ability, Possibility, Advice, Obligation) and write down which modals can be used for each, along with an example sentence. For instance, for 'Possibility', you would list 'may', 'might', and 'could'. Regularly practising CBSE-style gap-filling exercises with this chart as a reference will help you master the topic for the exam.