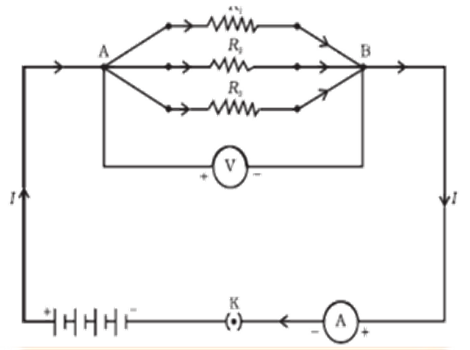
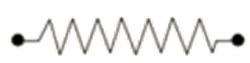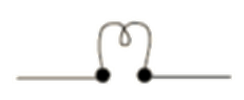An Overview of Cbse Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 11 Electricity
CBSE Notes Class 10 Science Chapter 11 - Electricity - 2025-26
FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 10 Science Chapter 11 - Electricity - 2025-26
1. What are the most important concepts to remember while revising Electricity Class 10 Notes for the CBSE 2025–26 exam?
When revising Electricity Class 10 Notes, focus on electric current, potential difference, Ohm’s Law, resistance and resistivity, the difference between series and parallel circuits, Joule’s law of heating, and key formulas. Make sure to understand basic definitions, how to solve numericals, and the application of formulas in real situations.
2. How should a student efficiently revise the key formulas in CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Electricity?
To efficiently revise key formulas for Electricity, create summary sheets or a formula chart. Practice examples for each formula, such as V = IR (Ohm's Law), P = VI (Electrical Power), and the rules for combining resistances in series and parallel. Regular practice helps memorise and understand their use in solving problems.
3. What is the best revision sequence for mastering all topics in Class 10 Electricity Notes?
A recommended revision sequence is:
- Start with Electric Current and Circuits
- Revise Potential Difference and Electric Potential
- Understand Ohm’s Law
- Study Resistance, Factors Affecting Resistance, and Resistivity
- Practice Series and Parallel Combinations
- Review Joule’s Law and Applications
- Cover Applications and Circuit Symbols
4. How can concept maps or quick revision summaries help in last-minute exam preparation for Electricity?
Concept maps visually connect all key terms and formulas, making it easier to recall interlinked topics during revision. Quick revision summaries distil chapters into essential points, allowing last-minute revision without missing crucial facts for the exam.
5. Which common misconceptions should students avoid while revising the topic of resistance and resistivity?
Students should avoid confusing resistance (a property of the wire itself) with resistivity (a material-specific property independent of length or area). Also, remember that in series circuits current stays constant, while in parallel circuits voltage stays constant across each branch.
6. What are some effective methods for quick revision before the Class 10 Science Electricity exam?
Effective methods include:
- Solving short concept-based questions
- Practicing important numerical problems
- Testing yourself using flashcards for definitions
- Teaching key points to a peer or family member to reinforce understanding
- Rewriting all important formulas and SI units just before the exam.
7. How can linking real-life applications to concepts in Electricity improve revision and retention?
Relating concepts like heating effect of current to appliances such as irons and heaters, or connecting resistivity to wire materials used at home, makes learning memorable and easier to retain for exams. Application-based understanding also builds confidence in tackling HOTS and case-based questions.
8. What key terms or definitions are essential for a quick recap of the Electricity chapter during revision?
Key terms include: Current, Potential Difference, Resistance, Ohm’s Law, Resistivity, Series Circuit, Parallel Circuit, Electric Power, Joule’s Law of Heating, and Fuse. Ensure you can define each term concisely as per CBSE guidelines.
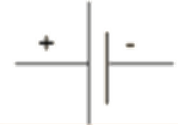
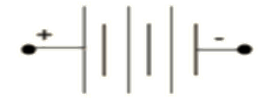
9. Why is it important to regularly revise circuit diagrams and symbols for the CBSE Class 10 Science exam?
Circuit diagrams and symbols are frequently used in exam questions for drawing or interpreting circuits. Regular revision ensures you quickly recognise and construct diagrams, which is essential for scoring in practical and theory questions.
10. How can practice of value-based or application-oriented questions in Electricity boost exam preparation?
Practicing value-based and application-oriented questions strengthens the ability to apply theoretical concepts to real situations, a common requirement in CBSE Board exams. It also prepares you for case-study and HOTS (Higher-Order Thinking Skills) questions, which carry significant weightage.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video