




What Are Multiple Alleles? NEET Explanation with Blood Group Example
The concept of multiple alleles notes is essential in biology and helps explain real-world biological processes and exam-level questions effectively. Multiple alleles play a crucial role in genetics questions, especially for NEET and other medical entrance tests. Understanding this topic supports your preparation for MCQs and problem-solving in inheritance and variation chapters.
Understanding Multiple Alleles Notes
Multiple alleles notes refer to the situation where a gene has more than two alternative forms (alleles) within a population but only two are present in an individual at a time. This concept is important in areas like Principles of Inheritance and Variation, non-Mendelian inheritance, and genetic variation studies. Multiple alleles highlight genetic diversity and exceptions to Mendel’s original laws.
Key Characteristics of Multiple Alleles
- Multiple alleles occupy the same gene locus on homologous chromosomes.
- They are alternative forms of a single gene affecting the same trait.
- Only two alleles are found in one individual (may be homozygous or heterozygous).
- Multiple alleles increase the phenotypic variability in a population.
- The wild-type allele is often dominant and considered the standard.
- Mutant or variant alleles may be dominant, recessive, or show intermediate expression.
- Existence due to spontaneous mutations in the population’s gene pool.
Classic Examples of Multiple Alleles Notes
Understanding examples makes the multiple alleles notes easier to remember for NEET, especially for MCQs:
| Example | Alleles Involved | Phenotypes/Details |
|---|---|---|
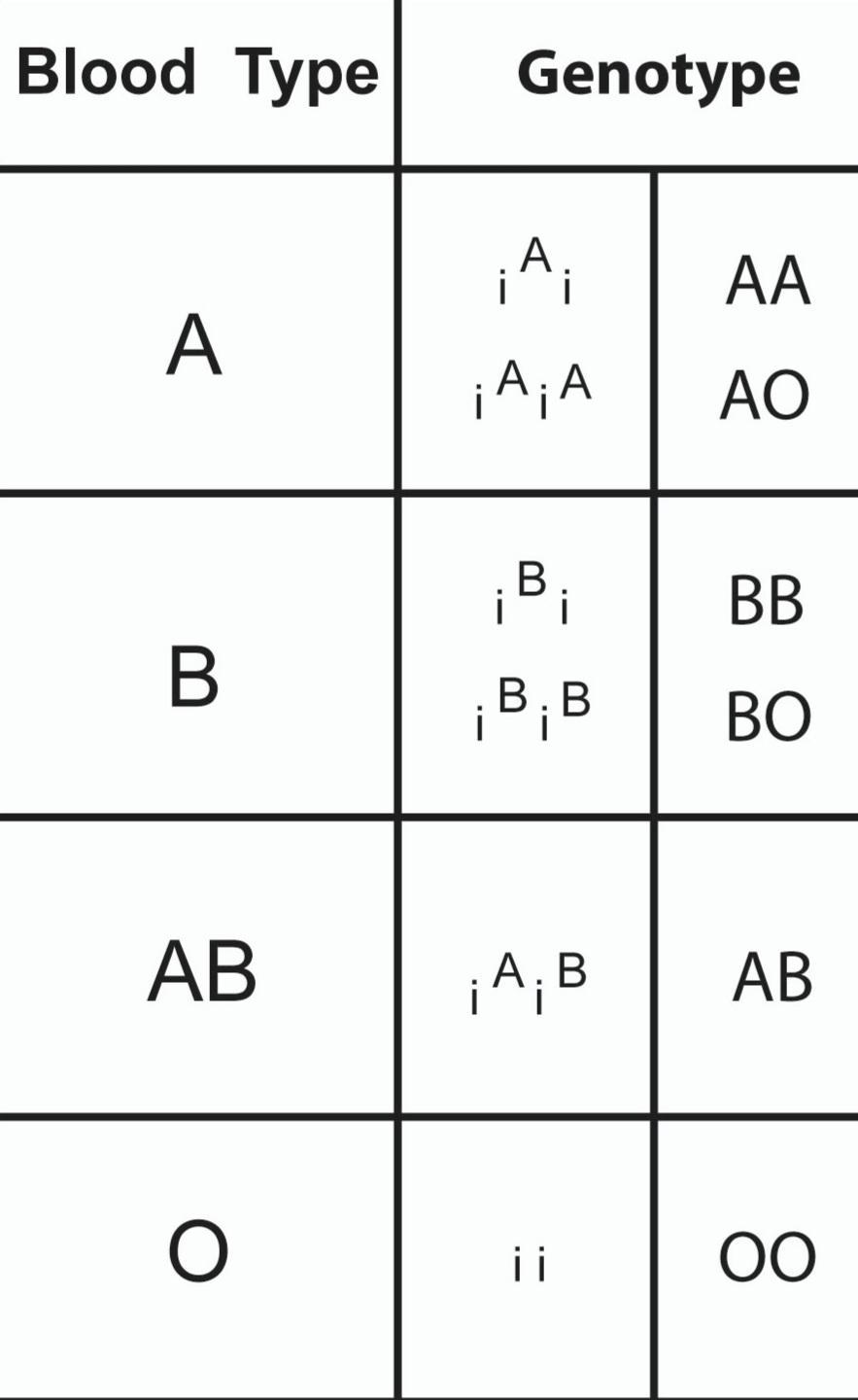
| ABO Blood Group in Humans | IA, IB, i | A, B, AB, O blood types. IA and IB are codominant; i is recessive. |
| Coat Colour in Rabbits | C, cch, ch, c | Agouti (C), Chinchilla (cch), Himalayan (ch), Albino (c) |
| Eye Colour in Drosophila | w+, w, coral, cherry, etc. | Wild red (w+) is dominant over other colours (white, coral, etc.) |
Mechanism of Multiple Alleles Notes (ABO Blood Group)
The ABO blood group system in humans is a key NEET example. It involves three alleles: IA, IB, and i. Each person inherits two alleles. Their combinations determine blood group:
- IAIA or IAi = Blood group A
- IBIB or IBi = Blood group B
- IAIB = Blood group AB (codominance)
- ii = Blood group O
This mechanism explains codominance and illustrates how more than two alleles contribute to genetic diversity, but only two are present per person.
Practice Questions
- What are multiple alleles? Give a common example found in humans.
- How many alleles are present in a population for rabbit coat colour? Name two phenotypes.
- Explain why only two alleles are inherited by one individual even if there are many in a population.
- Draw and label the ABO blood group allele table.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Mixing up codominance and multiple allelism – not every codominant trait is from multiple alleles.
- Assuming an individual can possess more than two alleles for a single gene – this is not correct.
- Confusing gene (section of DNA) with allele (variant form).
- Not distinguishing between multiple alleles (same gene, many forms) and polygenic inheritance (many genes, one trait).
Real-World Applications
The concept of multiple alleles notes is used in fields like medicine (transfusion compatibility), breeding programs (animal coats), and genetic research. For example, matching donor and recipient blood types during transfusion is based on understanding multiple alleles. Vedantu helps students relate such topics to practical examples in daily life and solve application-based NEET and CBSE questions on genetics.
Here’s a helpful table to summarise common multiple alleles examples:
Summary Table – Multiple Alleles Notes
| Gene / Trait | Wild & Mutant Alleles | Phenotypic Variation |
|---|---|---|
| ABO blood group | IA (A), IB (B), i (O) | A, B, AB, O blood types |
| Rabbit coat colour | C, cch, ch, c | Black, chinchilla, Himalayan, albino |
| Drosophila eye colour | w+ (red), w, others | Red, white, coral, cherry, etc. |
In this article, we explored multiple alleles notes, key textbook examples, MCQ applications, and common NEET mistakes. To learn more and build confidence, keep practicing with Vedantu and revise genetics topics regularly.
For more on genetics and inheritance patterns, check out these valuable NEET learning resources:
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Mendelian Genetics
- Codominance and Multiple Alleles
- Non-Mendelian Inheritance
- Human Blood Groups
- Basics of Genetics
- MCQs on Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
- Genetics and Evolution
- Heredity and Evolution
FAQs on Multiple Alleles Notes for NEET 2025: Definition, Features & Examples
1. What are multiple alleles in NEET genetics?
In NEET genetics, multiple alleles refer to the presence of more than two alternative forms of a gene at the same locus in a population. However, an individual organism carries only two alleles (one from each parent) for a given gene. This concept is important for understanding inheritance patterns, especially for traits like the ABO blood group system in humans.
2. Give a NEET-relevant example of multiple alleles in humans.
A key example of multiple alleles in humans is the ABO blood group system. The blood type gene (I gene) has three alleles: IA, IB, and i. The alleles IA and IB are codominant, meaning both express equally in the phenotype, while i is recessive. These alleles combine in various ways to give blood groups A, B, AB, and O.
3. How to quickly revise multiple alleles for NEET 2025?
For a fast revision of multiple alleles before NEET 2025:
• Focus on definition and key features with examples like ABO blood groups and rabbit coat colour.
• Memorize the codominance concept and relations among alleles.
• Practice MCQs based on inheritance patterns.
• Download concise PDF notes for quick reference.
• Use labeled diagrams showing genotype-phenotype correlations.
4. Why do NEET MCQs focus on ABO blood groups?
NEET MCQs emphasise the ABO blood group because it exemplifies the principle of multiple alleles and codominance. It is a straightforward, well-defined inheritance pattern with clinical relevance, which tests concepts such as allele interaction, genotype-phenotype relationship, and non-Mendelian genetics, making it ideal for evaluating students’ understanding.
5. What is the difference between multiple alleles and polygenic inheritance?
The key difference is that multiple alleles involve several alternative forms of a single gene at one locus, whereas polygenic inheritance involves multiple genes, each contributing to a trait. Multiple alleles affect one character with multiple allele variants, while polygenic traits are controlled by many genes resulting in continuous variation in phenotype.
6. Where can I find multiple alleles notes pdf download?
You can download comprehensive and concise multiple alleles notes PDF from trusted NEET preparation platforms like Vedantu. These notes cover definitions, important characteristics, examples such as ABO blood groups, and exam-focused MCQs to aid last-minute revision effectively.
7. Why do students confuse codominance with multiple alleles in NEET MCQs?
Students often confuse codominance with multiple alleles because they frequently occur together, especially in the ABO blood group system. Codominance describes the expression of two alleles equally in the phenotype, whereas multiple alleles refer to several allelic forms of a gene present in the population. Understanding that codominance is a type of allele interaction helps clarify this confusion.
8. Can a person have more than two multiple alleles in their genome?
No, an individual can carry only two alleles for a gene—one inherited from each parent—even if multiple alleles exist in the population. The term multiple alleles means several alternative alleles exist in the wider population, but not all are present simultaneously in a single organism.
9. How to avoid errors linking genotypes to phenotypes for ABO blood groups?
To avoid errors when linking genotypes to phenotypes in ABO blood groups:
• Clearly memorize the genotype combinations and their resulting blood groups.
• Remember IA and IB alleles are codominant and both expressed in AB blood type.
• The i allele is recessive and produces blood group O only in homozygous condition.
• Use visual genotype-phenotype tables for quick recall.
10. Is coat colour inheritance in cats included as a NEET multiple allele question?
While coat colour inheritance in rabbits is a classic NEET example of multiple alleles, coat colour in cats is less commonly featured in NEET syllabus but may appear in advanced genetics discussions. It is advisable to focus on standard NEET examples such as ABO blood groups and rabbit coat colour for exam preparation.
11. Does multiple alleles always mean non-Mendelian inheritance?
Not always. While multiple alleles can represent a deviation from simple Mendelian inheritance patterns, especially when combined with phenomena like codominance or incomplete dominance, multiple alleles alone do not necessarily mean non-Mendelian inheritance. They extend Mendel’s principles by introducing allele diversity, but classical dominance and recessiveness can still apply.























