




Parts and Functions of the Midbrain Explained with Examples
The concept of midbrain function in NEET is essential in biology and helps explain real-world biological processes and exam-level questions effectively.
Understanding Midbrain Function in NEET
Midbrain function in NEET refers to the roles carried out by the midbrain (mesencephalon), the central part of the brainstem located between the thalamus and pons. This topic is important in areas like brainstem roles, motor control, and neural reflexes. For NEET, understanding midbrain function helps you answer questions related to nerve signal processing, coordination, and reflex actions.
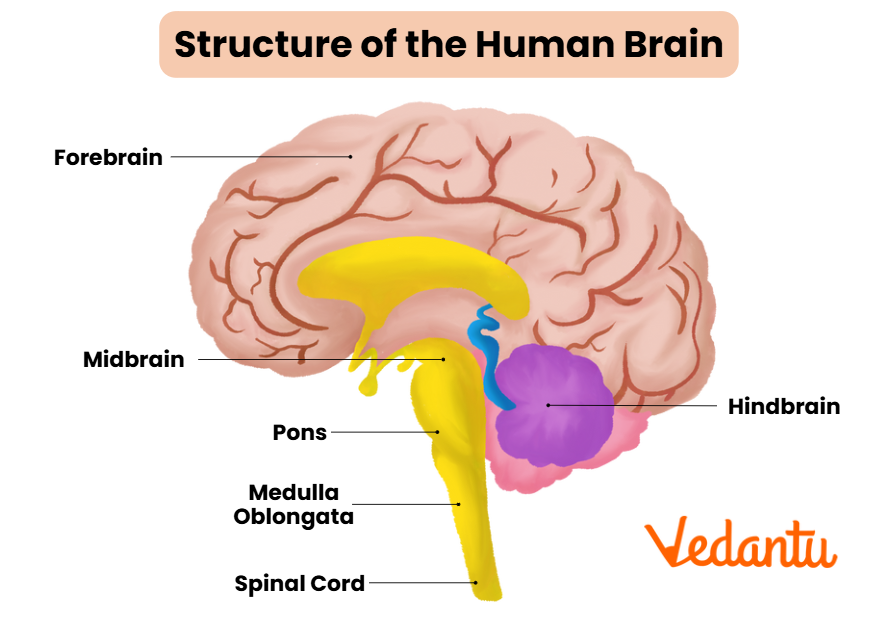
Parts and Anatomy of the Midbrain
The midbrain is a small but crucial part of the brainstem. For NEET, remembering its main parts, positions, and simple definitions is important.
- Tectum: Dorsal (upper) part. Has four colliculi (corpora quadrigemina): two superior (visual reflexes) and two inferior (auditory reflexes).
- Tegmentum: Ventral (lower) part. Contains red nucleus and periaqueductal gray (involved in motor coordination).
- Cerebral Aqueduct: Canal connecting 3rd and 4th ventricles, passing through midbrain.
- Cerebral Peduncles: Thick nerve fiber tracts, connect forebrain to hindbrain.
Here’s a helpful table to understand midbrain function better:
Midbrain Parts and Functions Table
| Part | Main Function | Example/Application |
|---|---|---|
| Tectum (Superior Colliculi) | Processes visual signals, eye movement reflexes | Tracking moving object |
| Tectum (Inferior Colliculi) | Processes auditory signals, reflex to loud noises | Turning head toward a sudden sound |
| Tegmentum (Red Nucleus) | Muscle coordination, motor control | Arm movement adjustment |
| Cerebral Peduncles | Signal relay between brain areas | Walking, standing posture |
| Cerebral Aqueduct | CSF flow between ventricles | Brain homeostasis |
Mechanism of Midbrain Function
The basic mechanism involves:
- Sensory signals (visual/auditory) arrive at colliculi in the tectum.
- Tectum processes stimuli and triggers reflex movements.
- Tegmentum coordinates muscle actions for these reflexes.
- Cerebral peduncles conduct signals to and from other brain areas.
- Cerebral aqueduct maintains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow.
Worked Example – Midbrain in Action
Let’s understand the midbrain function step by step:
1. A bright light appears suddenly in front of you.
2. Your eyes send visual information to the superior colliculi of the midbrain.
3. The midbrain processes this input and triggers an automatic reflex—your eyes turn toward the light, and pupils may constrict.
4. At the same time, auditory information from a loud sound is processed by inferior colliculi, enabling a quick response like turning your head.
Final Understanding: These reflexes help protect the eyes and improve orientation. The midbrain ensures quick, automatic responses—vital for everyday survival.
Practice Questions
- What is the role of the midbrain in the human nervous system?
- List and explain the functions of tectum and tegmentum.
- Why is the cerebral aqueduct important in midbrain anatomy?
- Draw and label a diagram of the midbrain and its main parts.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Confusing midbrain function with hindbrain or forebrain roles.
- Forgeting specific reflex actions controlled by the midbrain (like visual and auditory reflexes).
- Mislabelling the colliculi or cerebral aqueduct in a diagram.
Real-World Applications
The concept of midbrain function in NEET is used in fields like medicine (diagnosing brain injuries), neuroscience (studying reflexes), and physiology. Understanding this also relates to real-life examples like how you react quickly to sudden sights and sounds. Vedantu helps students relate such topics to practical examples in daily life and reinforces these key points for NEET exam success.
In this article, we explored midbrain function in NEET, its key processes, real-life significance, and how to solve questions based on it. To learn more and build confidence, keep practicing with Vedantu.
- Human Brain – Full overview and relation to the midbrain.
- Hindbrain – Compare with midbrain for NEET MCQs.
- Control and Coordination – Neural circuits and reflex integration.
- Central Nervous System – Context of midbrain within the nervous system.
- Neurons and Nerves – Signal flow through the midbrain.
- Cerebrum – Comparison with brain regions.
- Brain Facts – Memory tips and trivia for revision.
- Spinal Cord – Midbrain-spinal cord connectivity in reflexes.
- Nerves – Functional links to the rest of the nervous system.
FAQs on Midbrain Function Notes for NEET Exam 2025
1. What is the main function of the midbrain in NEET?
The midbrain, also called the mesencephalon, primarily regulates visual and auditory reflexes, controls eye movement and pupil dilation, and is involved in motor coordination. It acts as a crucial relay station for nerve signals between the forebrain and hindbrain, making it essential for NEET students to understand its diverse functions related to the brainstem and nervous system.
2. How to easily remember the parts of the midbrain for exam?
To recall the parts of the midbrain efficiently, focus on four main components: tectum (with superior and inferior colliculi), tegmentum, cerebral peduncles, and the cerebral aqueduct. Using visualization aids like diagrams and mnemonics—e.g., "Tiny Tectum, Tegmental Movement, Peduncles link"—helps with quick recall during exams.
3. What are some common midbrain function examples?
Examples of midbrain functions include processing visual reflexes via the superior colliculi, managing auditory reflexes through the inferior colliculi, regulating muscle movement through the red nucleus, and coordinating eye tracking and pupil response. Understanding these roles helps in answering application-based NEET MCQs.
4. What is the simple definition of midbrain function?
The midbrain function is to serve as the brain’s relay center that controls reflex actions related to vision and hearing, coordinates motor movements, and connects higher brain centers with the rest of the nervous system, making it vital for bodily coordination.
5. What is another name for the midbrain?
The midbrain is also known as the mesencephalon. This term is widely used in NEET syllabus and refers specifically to the middle region of the brainstem, situated between the forebrain and hindbrain.
6. What are the four lobes of the midbrain?
The so-called "four lobes" refer to the corpora quadrigemina located in the tectum of the midbrain. These are the two superior colliculi (visual reflex centers) and the two inferior colliculi (auditory reflex centers), essential for sensory processing and reflexes.
7. Why is the midbrain often confused with the hindbrain in MCQs?
The midbrain is frequently confused with the hindbrain due to their close anatomical location within the brainstem. However, the midbrain is the uppermost part connecting to the forebrain, while the hindbrain includes the pons, medulla oblongata, and cerebellum. Understanding these distinctions is key to avoiding errors in NEET.
8. How can I avoid mislabelling midbrain parts in diagrams?
To avoid mislabelling:
1. Memorize the key parts: tectum, tegmentum, cerebral peduncles, and cerebral aqueduct.
2. Use labelled diagrams repeatedly.
3. Associate functions with each part (e.g., superior colliculi for vision).
4. Practice drawing the midbrain, focusing on spatial relations to other brain regions.
9. Does spelling error (mid-brain vs midbrain) affect NEET answers?
In NEET, writing "midbrain" as one word is preferred as it matches the official terminology (mesencephalon). Minor spelling variations like "mid-brain" are usually understood and do not affect marking unless causing confusion. However, it’s best to use the standard form "midbrain" to demonstrate clarity.
10. How do I remember functional examples for quick revision?
For quick revision of midbrain functions:
• Create flashcards with function-part pairs (e.g., superior colliculi = visual reflex).
• Use mnemonics like "Visual & Auditory Reflexes, Motor Movement Control, and Signal Relay."
• Practice with NEET-style MCQs.
• Review diagrams highlighting each function.
These methods reinforce memory and improve exam recall.
11. Can questions repeat from previous midbrain function PYQs?
Yes, many midbrain function questions in NEET recur with similar patterns, such as identifying functions of tectum or the role of red nucleus. Reviewing past year questions helps predict frequently tested concepts and prepares students for common MCQ formats.























