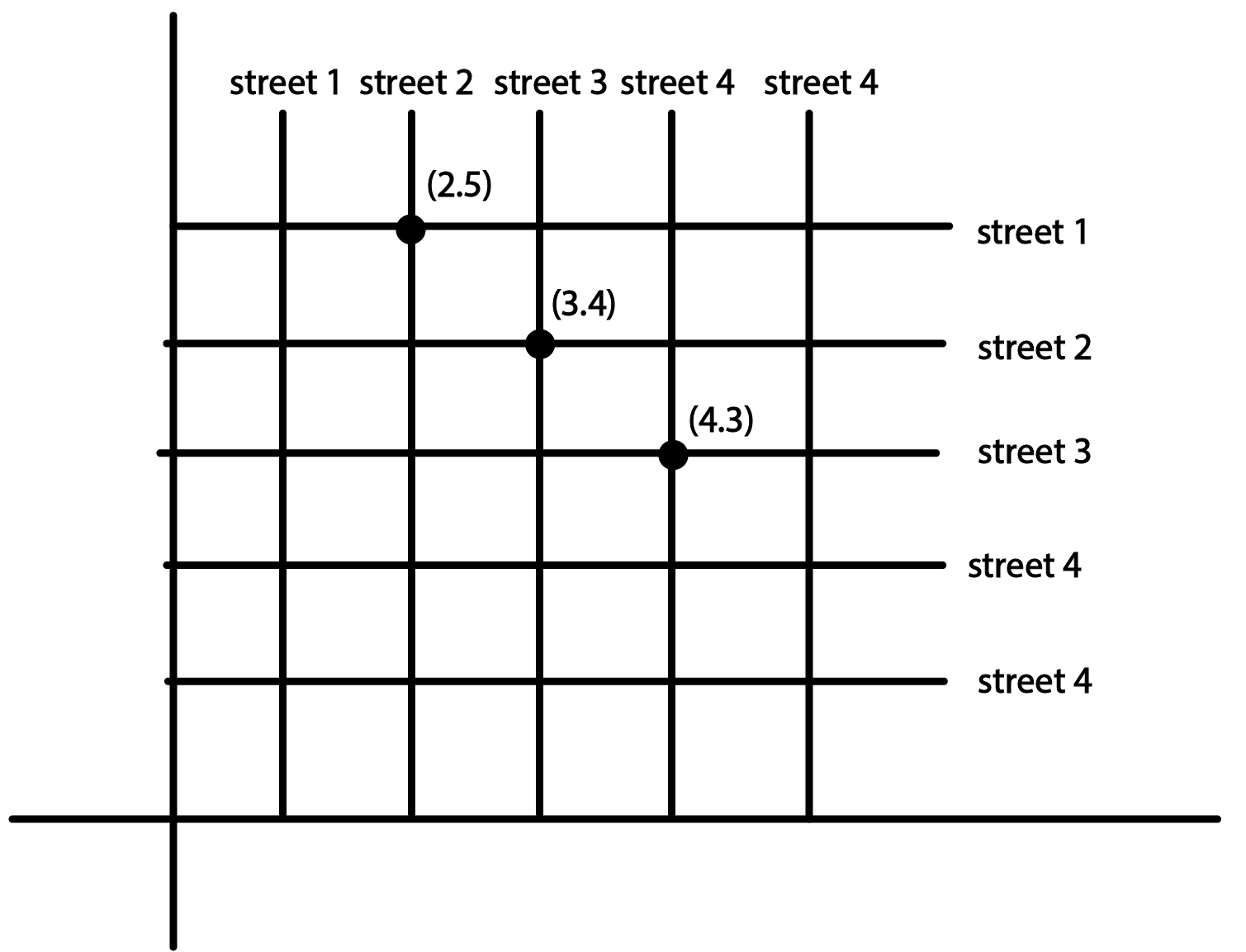
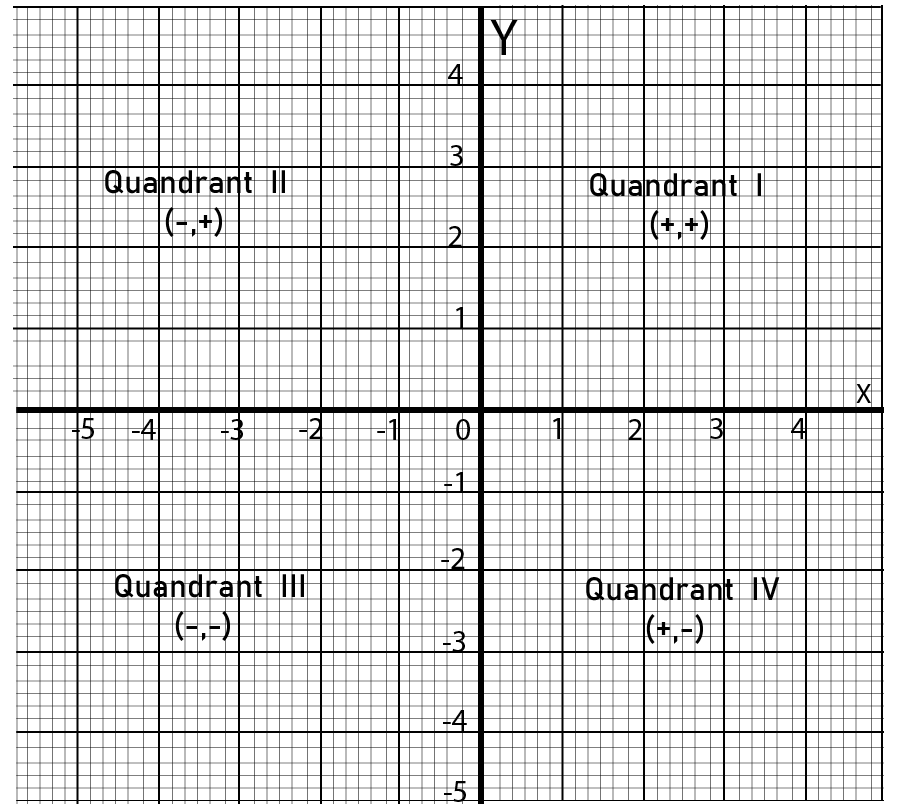
Find Complete Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry Questions and Answers With Easy Solutions | FREE PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry - 2025-26
1. Are NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry suitable for school homework?
Yes, NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry on Vedantu provide clear answers that students can use to complete homework and written practice.
2. Do Coordinate Geometry Class 9 solutions follow the NCERT textbook order?
Yes, Coordinate Geometry Class 9 solutions available on Vedantu follow the same question order and structure as the NCERT textbook.
3. Can students use Coordinate Geometry Class 9 solutions for test preparation?
Yes, Coordinate Geometry Class 9 solutions from Vedantu are written to support revision and preparation for school tests.
4. Are all exercise questions included in the Class 9 Maths Coordinate Geometry solutions?
Yes, all exercise questions from Class 9 Maths Coordinate Geometry are covered in the NCERT Solutions provided on Vedantu.
5. Is there a PDF of Coordinate Geometry Class 9 solutions?
Yes, you can access a PDF of Coordinate Geometry Class 9 solutions through the NCERT Solutions section on Vedantu for easy offline practice.
6. Are the Class 9th Maths Coordinate Geometry solutions written in simple language?
Yes, the Class 9th Maths Coordinate Geometry solutions on Vedantu are written in clear, student-friendly language.
7. Can private students use Coordinate Geometry Class 9 solutions?
Yes, private students following the NCERT curriculum can use Coordinate Geometry Class 9 solutions available on Vedantu.
8. Are the Class 9 Coordinate Geometry solutions aligned with the latest syllabus?
Yes, the Class 9 Coordinate Geometry solutions on Vedantu are aligned with the latest NCERT and CBSE syllabus.
9. Do the Coordinate Geometry Class 9 solutions show step-by-step methods?
Yes, the Coordinate Geometry Class 9 solutions on Vedantu include step-by-step answers to help students understand how to solve the problems.