




How to Calculate Volume and Surface Area of a Cuboid
What is Cuboid?
A cuboid is around us in day-to-day life. We see it in the form of bricks, shoeboxes, cuboid objects, etc. A cuboid is a three-dimensional figure which has six rectangular faces, twelve edges, and eight vertices. The cuboid shape is formed with a closed rectangular face.
Cuboid Examples
The boxes we use, the lunch boxes we take to school, the bricks we use to build a house, the pencil box, etc. are the known examples existing around us. These are some common examples that we have seen in our surroundings. The following pictures have some of the common examples.

Cuboid Examples
What is Surface Area?
The surface area is the area of a solid object that measures the surface that occupies the object. The surface area of a cuboid is the area of 6 rectangular faces. There is a formula to calculate the surface area of a cuboid.
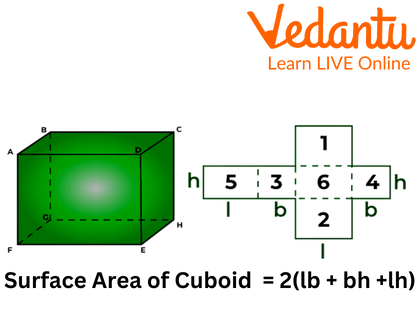
Surface Area
Formula for the Surface Area of Cuboid:
Curved surface area : \[2h\left( {l + b} \right)\]
Total Surface area : \[2\left( {lb + bh + hl} \right)\]
Where l is length, b is the breadth and h stands for height.
Cuboid Examples: Surface Area
Example 1: The cuboid has its dimension given as length is 8 cm, width is 6 cm and height is 5 cm. Find the Total surface area of the given cuboid.
Given
Height(h) \[ = {\rm{ }}5{\rm{ }}cm\]
Width(w) \[ = {\rm{ }}6{\rm{ }}cm\]
Length(l) \[ = {\rm{ }}8{\rm{ }}cm\]
Total surface area \[ = {\rm{ }}2\left( {lb + bh + hl} \right)\]
\[ = {\rm{ }}2\left[ {{\rm{ }}\left( {8 \times 6} \right){\rm{ }} + {\rm{ }}\left( {6 \times 5} \right){\rm{ }} + {\rm{ }}\left( {5 \times 8} \right)} \right]\]
\[ = {\rm{ }}2{\rm{ }}\left[ {{\rm{ }}48{\rm{ }} + {\rm{ }}30{\rm{ }} + {\rm{ }}40{\rm{ }}} \right]\]
\[ = {\rm{ }}2 \times 118\]
\[ = 236\]
Hence, the total surface area is \[236c{m^2}.\]
Volume Of Cuboid
The volume of a cuboid is the product of length, breadth, and height in cubic units.
The formula of the volume of cuboid: length \[ \times \] breadth \[ \times \] height
Let’s understand it by doing some examples.
Cuboid Example: Volume Of The Cuboid
Example 2: Calculate the volume of a cuboid with a length of 8 cm, breadth of 25 cm, and height of 50 cm.
Given
Length \[ = \;8{\rm{ }}cm\]
Breadth \[ = {\rm{ }}25{\rm{ }}cm\]
Height \[ = {\rm{ }}50{\rm{ }}cm\]
The volume of cuboid: length \[ \times \] breadth \[ \times \] height
\[ = \,8\, \times \,25\, \times \,50\]
\[ = \,10000\,\,c{m^3}\]
Solved Questions:
1. Find the surface area of a cuboid whose length is 5 cm, breadth is 6 cm and height is 9 cm.
Given
Length \[ = {\rm{ }}5{\rm{ }}cm\]
Breadth \[ = \,6{\rm{ }}cm\]
Height \[{\rm{ = }}9{\rm{ }}cm\]
Surface are of cuboid \[ = {\rm{ }}2\left( {lb + bh + hl} \right)\]
\[ = {\rm{ }}2{\rm{ }}\left[ {\left( {5 \times 6} \right){\rm{ }} + {\rm{ }}\left( {6 \times 9} \right){\rm{ }} + {\rm{ }}\left( {9 \times 5} \right)} \right]\]
\[ = {\rm{ }}2{\rm{ }}\left[ {{\rm{ }}30 + 54 + 45{\rm{ }}} \right]\]
\[ = {\rm{ }}2 \times 129\]
\[\; = {\rm{ }}258{\rm{ }}c{m^2}.\]
2. Find the volume of the cuboid whose length is 8 cm, breadth is 7 cm and height is 4cm.
Given
Length \[{\rm{ = }}8{\rm{ }}cm\]
Breadth \[{\rm{ = }}7{\rm{ }}cm\]
Height \[{\rm{ = }}4{\rm{ }}cm\]
The volume of the cuboid is length × breadth × height
\[ = {\rm{ }}8 \times 7 \times 4\]
\[ = {\rm{ }}224{\rm{ }}c{m^3}.\]
3. Find the sum of the surface area and the volume of the cuboid whose length is 4 cm, breadth is 2 cm and height is 1 cm.
Given
Length \[ = {\rm{ }}4{\rm{ }}cm\]
Breath \[ = {\rm{ }}2{\rm{ }}cm\]
Height \[ = {\rm{ }}1{\rm{ }}cm\]
Surface area of cuboid \[ = {\rm{ }}2\left( {lb + bh + hl} \right)\]
\[ = {\rm{ }}2{\rm{ }}\left[ {{\rm{ }}\left( {4 \times 2} \right){\rm{ }} + {\rm{ }}\left( {2 \times 1} \right){\rm{ }} + {\rm{ }}\left( {1 \times 4} \right)} \right]\]
\[ = {\rm{ }}2{\rm{ }}\left[ {{\rm{ }}8{\rm{ }} + {\rm{ }}2{\rm{ }} + {\rm{ }}4{\rm{ }}} \right]\]
\[ = {\rm{ }}2 \times 14\]
\[ = {\rm{ }}28{\rm{ }}c{m^2}\].
The volume of the cuboid is length × breadth × height
\[ = {\rm{ }}4 \times 2 \times 1\]
\[ = {\rm{ }}8{\rm{ }}c{m^3}.\]
Sum of the surface area and the volume \[ = \,\,28\,\, + \,\,8\,\, = \,\,36\,cm\]
Summary
In this chapter, we have studied the cuboid. A cuboid is a three-dimensional solid object and the measure that the object occupies is the surface of the cuboid and the product of length, breadth, and height is the volume of the object.We also solved the various examples and solved questions to understand the surface area and volume of a cuboid.
FAQs on Volume and Surface Area of a Cuboid Explained
1. What is a cuboid in mathematics?
A cuboid is a three-dimensional geometric figure with six rectangular faces, twelve edges, and eight vertices. Each of its angles is a right angle. The cuboid's opposite faces are equal, making it a common topic in geometry and measurement.
2. How do you calculate the volume of a cuboid?
The volume of a cuboid is found by multiplying its
- length ($l$)
- width ($w$)
- height ($h$)
3. What is the surface area of a cuboid?
The surface area of a cuboid is the total area of all its six rectangular faces. The formula is $2(lw + lh + wh)$, where $l$ is length, $w$ is width, and $h$ is height. Surface area is measured in square units.
4. Can a cube be considered a special case of a cuboid?
Yes, a cube is a special type of cuboid where all sides are equal in length. While a cuboid has different lengths, widths, or heights, a cube's length, width, and height are the same, making every face a square.
5. Why are volume and surface area important for a cuboid?
Knowing the volume and surface area of a cuboid helps in real-life applications such as calculating how much a box can hold or how much material is needed to cover it. These measurements are commonly used in packaging, shipping, and construction.
6. What are the units used for volume and surface area of a cuboid?
For a cuboid, volume is typically measured in cubic units such as cubic centimeters (cm3) or cubic meters (m3), while surface area is measured in square units like square centimeters (cm2) or square meters (m2).
7. How is the lateral surface area of a cuboid different from total surface area?
The lateral surface area of a cuboid is the sum of the areas of only its four side faces, excluding the top and bottom. It is calculated as $2h(l + w)$. The total surface area includes all six faces.
8. Can you find the height of a cuboid if volume and base area are given?
Yes, the height of a cuboid can be found using $\text{height} = \text{volume} \div \text{base area}$. If the volume and the area of the base (length × width) are known, divide them to get the height.
9. What is the difference between face diagonal and space diagonal in a cuboid?
In a cuboid:
- The face diagonal crosses one rectangular face from corner to opposite corner.
- The space diagonal crosses the cuboid from one vertex to its farthest opposite vertex.
10. How do you find the length of a space diagonal in a cuboid?
The space diagonal of a cuboid can be found using $d = \sqrt{l^2 + w^2 + h^2}$, where $l$ is length, $w$ is width, and $h$ is height. This gives the longest straight line that fits inside the cuboid.
11. Why does the order of dimensions not matter when calculating cuboid volume?
The cuboid volume formula uses multiplication, so the order of
- length
- width
- height

















