




How to Identify and Use Terms in Algebraic Expressions
An algebraic expression is a mathematical expression consisting of variables and constants using mathematical operations such as multiplication, division, addition, and subtraction. It is made up of terms like "coefficient," "variable," and "constant."
What is an Algebraic Expression?
An algebraic expression is an expression composed of variables, constants, and algebraic operations such as addition, subtraction, division, and multiplication.
For e.g. \[2{\rm{x}} + 3 = 0\]
Algebraic expression is composed of terms , coefficient, variable and constant.
Few more examples:
\[4x\]
\[2a + 3b\]
\[3{x^2} - 4xy + 2{y^2}^{}\]
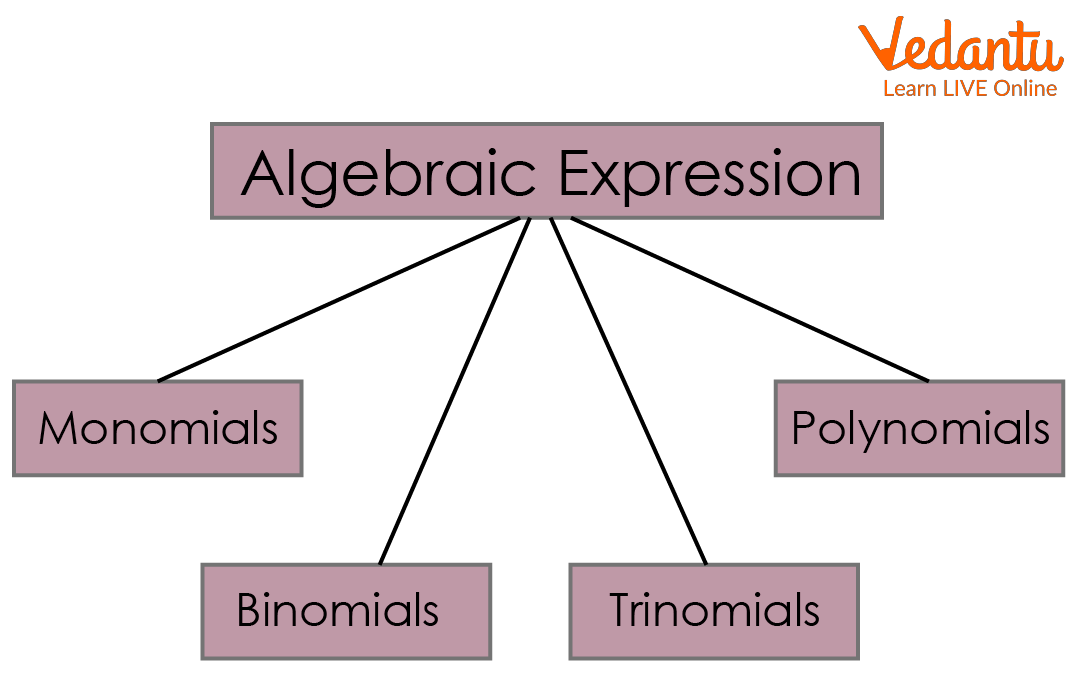
Types of Algebraic Expressions
There are three main types of algebraic expressions that contain:
Types of Algebraic Expression
Monomial : An algebraic expression with only one term is called a monomial.
Examples 3x, 9y, and so on.
Binomial : A binomial expression is an algebraic expression made up of two different terms.
Examples include \[5{\rm{x}} + 8{\rm{y}}\], \[{\rm{a}} + 4{\rm{b}}\] and so on.
Trinomial: An algebraic expression made up of three terms is known as trinomial.
Example: \[4{\rm{x}} + 3{\rm{y}} + 2{\rm{xy}}\]
Polynomial: An expression with two or more terms with nonnegative integer exponents of a variable is called a polynomial.
Examples \[a{\rm{x}} + {\rm{by}} + {\rm{c}}\], \[4{\rm{x}} + 4{\rm{y}} + 4{\rm{z}}\] , and so on.
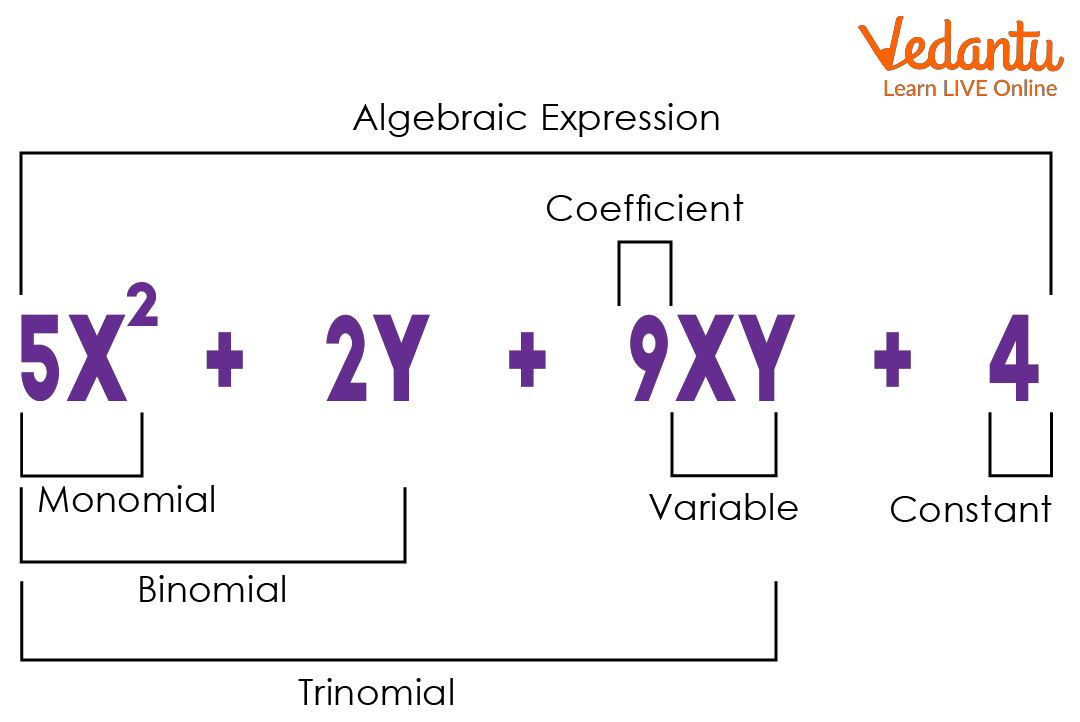
Algebraic Expression
Terms Related to Expression
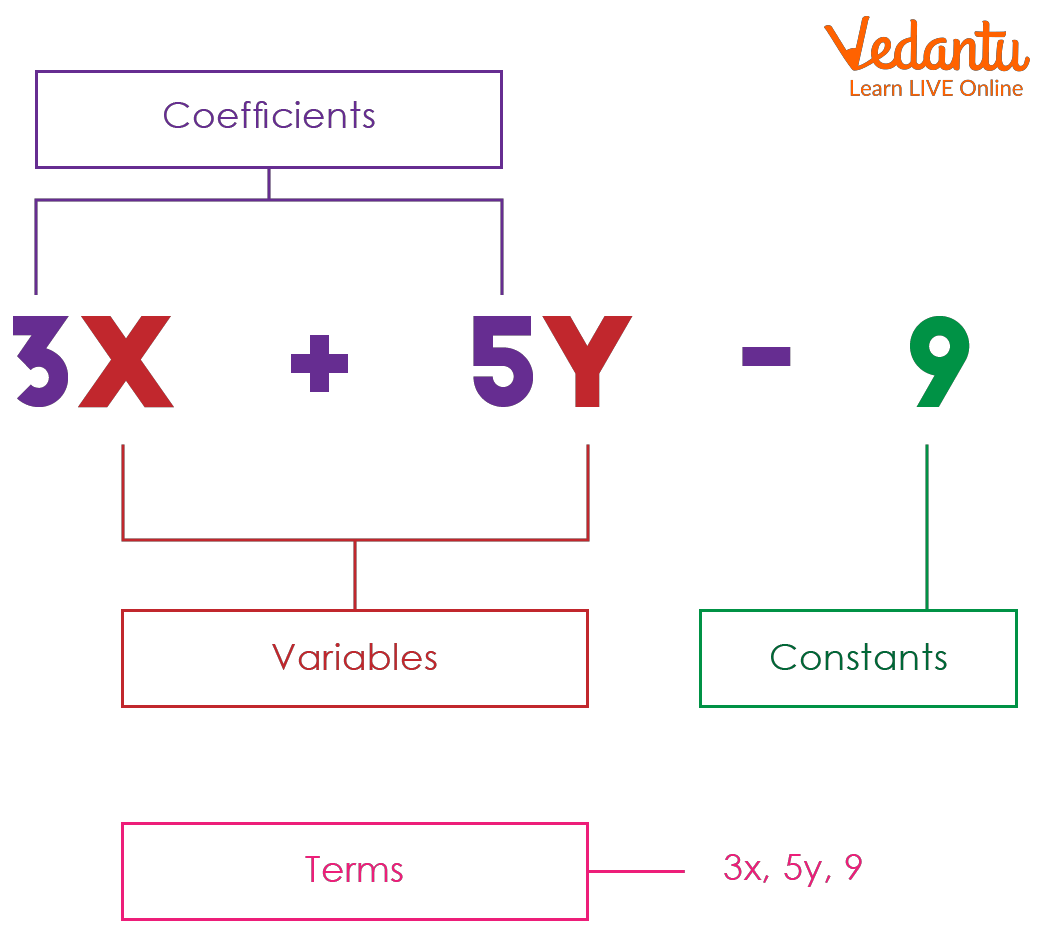
Terms: Each expression consists of terms. A term can be a signed number, variable, or constant multiplied by a variable.
Coefficients in Algebraic Expression: A coefficient is an integer that is either multiplied by the variable it is associated with or written alongside the variable.
Variable: A variable is defined as a numeric value or literal symbol representing a number whose value keeps on changing.
Constant in Algebraic Expression: A number whose value cannot be changed.
Terms, Coefficient, Variable and Constant
What is a Term in Algebraic Expression?
Each part of an algebraic expression separated by a plus sign $(+)$ or minus sign $(-)$ is known as a term of the algebraic expression. Division sign $(\div)$ or multiplication sign [ (\times) ] does not separate terms in algebraic expressions. Algebraic expressions can be simple, complex, or constant:
A simple algebraic expression consists of a single term.
A complex algebraic expression consists of two or more terms.
A term in an algebraic expression that has a fixed numerical value and no variables is called a constant term in an algebraic expression.
Conclusion
In mathematics, an algebraic expression is one that comprises variables, constants, coefficients, and arithmetic operations. The algebraic expression's multiple parts are broken down into the following list. Expressions with a monomial have only one term. The terms in binomial expressions are two. An expression having three terms is referred to as a trinomial, and so on.
Solved Examples:
Define the terms of the following expression.
a]\[12{\rm{x}} + 4\]
b] \[3{\rm{ab}} + 4{\rm{a}} + 2{\rm{abc}}\]
Solution:
a] \[12x + 4\]
Terms: \[12x, 4\]
b] \[3{\rm{ab}} + 4{\rm{a}} + 2{\rm{abc}}\]
Terms: \[3ab, 4a, 2abc\]
Classify the types of following algebraic expressions.
\[12x + 5y\]
\[5{\rm{a}} + 4{\rm{c}} + 5{\rm{ab}}\]
Solution:
a]\[12x + 5y\]
Binomial as it has two terms.
b]\[5{\rm{a}} + 4{\rm{c}} + 5{\rm{ab}}\]
Trinomial as well as polynomial as it has three term ( more than two terms)
Find the value of the expression \[5x + 4\] if the value of \[{\rm{x}} = - 5\]
Solution: \[5x + 4\]
Substitute \[{\rm{x}} = - 5\] in the expression \[ = 5[ - 5] + 4\]
\[ = - 25 + 4\]
\[ = - 21\]
Thus the value of expression is \[-21\]
Is 9 an algebraic expression?
Solution: Yes, 9 is algebraic because it can be viewed as a monomial.
FAQs on Terms in Algebraic Expressions Explained
1. What are terms in an algebraic expression, and how are they identified?
In an algebraic expression, terms are the individual parts that are separated by addition (+) or subtraction (-) signs. For example, in the expression 4x - 5y + 7, the terms are 4x, -5y, and 7. Each term is formed by the product of factors, which can be numerical (constants) or algebraic (variables).
2. What are the key components of a term, such as coefficients, variables, and constants?
The key components of a term are:
- Variable: A symbol, usually a letter (like x or y), that represents an unknown value.
- Constant: A term with a fixed numerical value that does not change, such as 7 or -10.
- Coefficient: The numerical factor that is multiplied by the variable(s) in a term. For example, in the term 8ab, the coefficient is 8. In the term x², the coefficient is understood to be 1.
3. How are algebraic expressions classified based on the number of terms they contain?
Algebraic expressions are classified based on the number of unlike terms they have:
- A monomial is an expression with only one term (e.g.,
5x²y). - A binomial is an expression with two unlike terms (e.g.,
a + 2b). - A trinomial is an expression with three unlike terms (e.g.,
x² + 3x - 4).
4. What is the important difference between 'like terms' and 'unlike terms'?
The key difference lies in their variable factors. Like terms are terms that have the exact same variables raised to the exact same powers, although their numerical coefficients can be different. For example, 7xy and -2xy are like terms. Unlike terms have different variables or the same variables raised to different powers, such as 7xy and 7x²y. This distinction is crucial because only like terms can be added or subtracted together to simplify an expression.
5. Why is it necessary to identify individual terms before simplifying an algebraic expression?
Identifying individual terms is the essential first step for simplification because it allows you to correctly group like terms. Simplification of an expression involves combining these like terms through addition or subtraction to make the expression more compact and easier to work with. For example, in 3x + 5y - 2x, you must first identify the terms 3x and -2x as 'like' to combine them into x, resulting in the simplified expression x + 5y.
6. How does a 'term' in a general algebraic expression differ from a 'term' in a polynomial?
While all terms in a polynomial are also terms in an algebraic expression, the reverse is not always true. The main difference is the exponent of the variable. For an expression to be a polynomial, all its terms must have variables with non-negative integer exponents (e.g., 0, 1, 2, 3...). A general algebraic expression can include terms where variable exponents are negative or fractional (e.g., x⁻² or √y, which is y¹/²). These are valid algebraic terms but are not considered polynomial terms.























