




How to Calculate the Side Length, Perimeter & Area of a Square
Have you ever wondered what a square is or how it looks? Squares are a shape with four equal sides and angles, where the space contained within them is all of the same sizes. The term "square" is a geometric shape that can be used to describe any rectangle or rhombus. Squares are easy to draw and are a common shape in our environment. The dimensions of a square are its length and width. Here you will find the dimensions of a square, you will learn about square sides and how to calculate the area of a square.

Picture of chess
Square Sides
A square is a four-sided closed two-dimensional (2D) shape. A square's four sides are all equal and parallel to one another. The basic shape of a square is depicted below. So, here the question arises, how many sides square have? From the below figure, it is clear now that there is a total of 4 sides in a square. Square sides are as follows: PQ, QS, SR, RP.
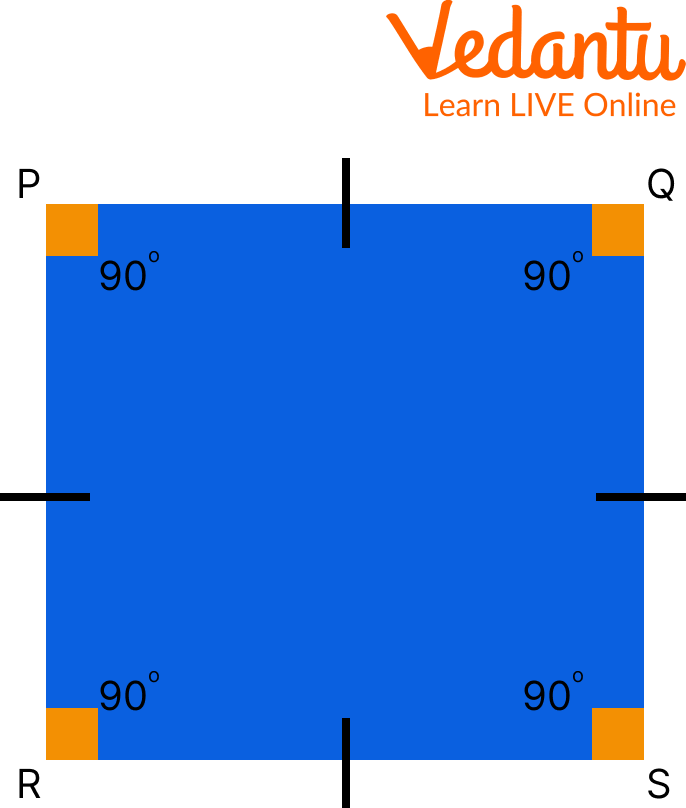
Square
What is the Area of Square?
A square's area is the amount of space it takes up. Chessboards, square wall clocks, and other square shapes are examples. The space occupied by these things can be calculated using the area of a square formula. In the below heading we will learn about how to calculate the area of a square.
How to Calculate Area of a Square?
To find the area of a square, first, calculate one side of the square (all sides of the square are equal ). then multiply by itself to get the area of the square. Hence, $\text { Area }=(\text { Side })^{2}$
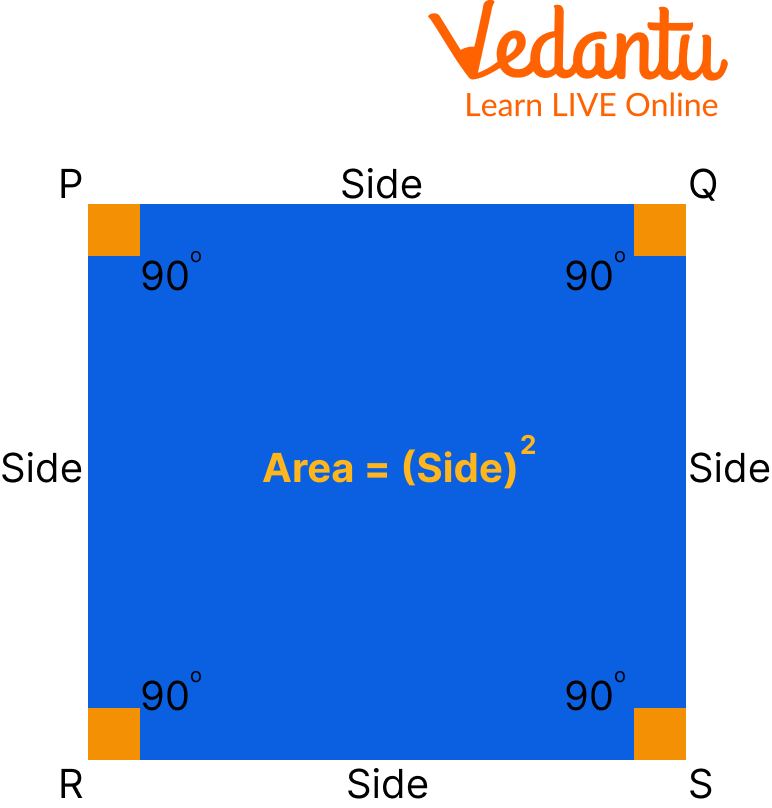
Area of Square
Similarly, we may calculate the area of any other form based on its sides, such as a rectangle, parallelogram, triangle, or polygon.
Example 1. Calculate the area of the square whose length of square sides is 20m.
Ans: Given, length of square sides(a) = 20m
The area of the square is given by: $a \times a=a^{2}$
$\text { Area }=20 \mathrm{~m} \times 20 \mathrm{~m}=400 \mathrm{~m}^{2}$.
Example 2. Find the area of the square whose length of diagonals is 10 cm.
Ans: First we find the side length of square(a)
Length of diagonal is given by formula = d
Diagonal of square $(\mathrm{d})=\sqrt{ 2}a$
Length of diagonal $=10 \mathrm{~cm}$
Now, Area of the square $=\mathrm{a}=\dfrac{(\mathrm{d})^{2}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{(\mathrm{d})^{2}}{2}=\dfrac{100}{2} =50\mathrm{~cm}^{2}$
Example 3. Calculate the area of a square whose side is $11 \mathrm{~cm}$.
Ans: Given that, side $=11 \mathrm{~cm}$
Area of square is given by $=11 \times 11=121 \mathrm{~cm}^{2}$
Dimensions of a Square
To determine the dimensions of a square, its area or perimeter must be specified.
Let us assume a square has a surface area of 36 square feet. First, write down the square area Formula: A = x2, where "A" represents the area and "x" represents one of the side lengths. Because the square has four equal sides, you only need to find one dimension. Work out the area equation. It will appear as 36 = x2. To find the dimension of the square, you must first isolate "x", Take the square root of 36 to cancel out the square sign on the right side of the equation. The answer to the square root problem is 6 . The final answer is x = 6, which means that each dimension of the square is 6 m.
Using the perimeter, calculate the dimensions of the square. The perimeter of the square in this case will be 20 m. Write the perimeter equation for a square down: P = 4t, where "P" represents the perimeter and "x" represents the side dimension. Work out the perimeter equation. It will seem as follows: 20 = 5x. Divide each side of the equation by 4 , and write down the result: x = 4. The final result is x = 5, indicating that the square dimensions are 4 m each.
Practice Questions
Q 1. Find the area of the square whose side is $14 \mathrm{~m}$.
Ans: $196 \mathrm{~m}^{2}$.
Q 2. Find the side of the square whose area is $225 \mathrm{~m}^{2}$.
Ans: $15 \mathrm{~m}$.
Summary
A square is a plane figure with four equal straight sides and four right angles. It is also a regular polygon, meaning that all of its sides and angles are equal. The area of a square is the space inside the perimeter or boundary of the square. The dimensions of a square are its length and width, which are always the same. We have also learned about the area of square, i.e. Area = (Side)2. In the end we have learned to find the dimensions of the square, using the perimeter and area of the square.
FAQs on Dimensions of a Square: A Complete Guide
1. What are the fundamental dimensions of a square?
A square's most fundamental dimension is its side length. Because all four sides of a square are equal by definition, knowing the length of just one side is enough to calculate all its other properties, including its perimeter, area, and diagonal length. It is a two-dimensional shape with equal length and width.
2. How do you explain the difference between a square's perimeter and its area?
The key difference lies in what they measure. The perimeter is the total length of the boundary around the square, which is a one-dimensional measurement (e.g., in cm). Think of it as the length of a fence needed to enclose a square field. The area is the total space covered inside the boundary, which is a two-dimensional measurement (e.g., in cm²). This would be the amount of grass inside the fence.
3. Why is a square classified as a two-dimensional (2D) shape?
A square is a 2D shape because it has two dimensions: length and width. Even though these dimensions are equal in a square, they represent two distinct directions on a flat plane. A shape with only one dimension, like a line, has only length. A shape with three dimensions, like a cube, has length, width, and height.
4. What are the essential formulas related to the dimensions of a square?
The main formulas that use the side length (let's call it 's') of a square are:
- Area: Area = s × s or s²
- Perimeter: Perimeter = 4 × s
- Diagonal (d): d = s√2
5. How can you find the side length of a square if you only know its area?
You can determine the side length by calculating the square root of the area. Since the area is found by multiplying the side by itself (Area = side²), you can reverse this operation. For instance, if a square has an area of 64 square metres, its side length is the square root of 64, which is 8 metres.
6. What is the mathematical relationship between a square's side and its diagonal?
The relationship is derived from the Pythagorean theorem. The diagonal of a square divides it into two right-angled triangles, with the diagonal being the hypotenuse. The formula that connects them is Diagonal = side × √2. This means the diagonal of any square is always approximately 1.414 times longer than its side.
7. Is it possible for a square to have a different width and height?
No, by definition, a square cannot have a different width and height. The defining characteristic of a square is that all four of its sides are of equal length. If a four-sided figure has different width and height, it is a rectangle, not a square.
8. If you double the side length of a square, what happens to its area?
This is a common point of confusion. If you double the side length of a square, its area does not just double; it becomes four times larger. For example, a square with a 2 cm side has an area of 4 cm² (2x2). If you double the side to 4 cm, the new area becomes 16 cm² (4x4), which is four times the original area.
9. Where are calculations involving a square's dimensions used in everyday life?
Understanding the dimensions of a square is practical in many real-world scenarios. For example:
- Home Improvement: Calculating the number of square tiles needed for a floor or the area of a square room for carpeting.
- Gardening: Planning the layout of a square garden bed to determine how many plants can fit.
- Art and Craft: Cutting a piece of paper or fabric into a perfect square for an origami or a quilt project.
- Construction: Ensuring that the foundation of a structure or a window frame is perfectly square for stability and proper fit.























