
Write the structural formula of all the isomers of an alkane with six C-atoms \[({C_6}{H_{14}})\].
Answer
239.1k+ views
Hint: The molecular formula is a way to write a substance using the chemical symbol and number subscripts to mention the number of the atoms into that chemical compound. On the other hand, a condensed formula is basically like the structural formula but here it is showing that all groups are attached with one single atom.
Complete step by step answer:
There are some compounds which have the same molecular formula but a different arrangement of atoms with different properties are known as isomers to each other.
There are different kinds of isomers. They are,
Constitutional isomers: which compounds are the same in the molecular formula but bonds are different in between the atoms is called constitutional isomers.
Stereoisomers: which compounds are the same in the molecular formula; bonds are the same in between the atoms but the relative positions of the groups are different; those compounds are called Stereoisomers.
In case \[{C_6}{H_{14}}\] there are a total of five constitutional isomers present but no stereoisomers are present.
Now the molecular formula of those isomers of hexane is \[{C_6}{H_{14}}\] . But the condensed isomers are different in each isomer, this is because the bonds between the atoms of the molecule are different in the isomers of hexane.
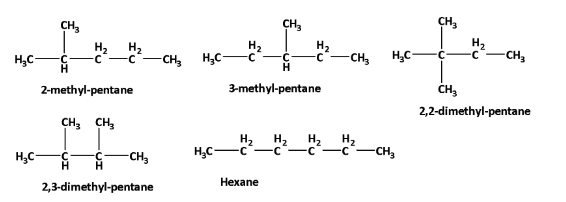
The structural formula of all five isomers of hexane with six C-atoms \[({C_6}{H_{14}})\] is,
2-methyl-pentane \[(C{H_3}CH(C{H_3})C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3})\] , 3-methyl-pentane \[(C{H_3}C{H_2}CH(C{H_3})C{H_2}C{H_3})\] , 2,2-dimethyl-butane \[(C{H_3}C{(C{H_3})_2}C{H_2}C{H_3})\] , 2,3-dimethyl-butane \[(C{H_3}CH(C{H_3})CH(C{H_3})C{H_3})\] , hexane\[(C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3})\] .
Structures are,
Note:
The empirical formula of any compound gives the lowest value of the ratio of the elements present in a molecule. But from this formula the actual number of the elements present in the molecule cannot be defined. . The molecular formula of a compound is with the actual number of the elements present in a compound. The relation between them is given by,\[{\text{ }}molecular{\text{ }}formula = {\left( {{\text{ }}emperical{\text{ }}formula} \right)_n}\].
Complete step by step answer:
There are some compounds which have the same molecular formula but a different arrangement of atoms with different properties are known as isomers to each other.
There are different kinds of isomers. They are,
Constitutional isomers: which compounds are the same in the molecular formula but bonds are different in between the atoms is called constitutional isomers.
Stereoisomers: which compounds are the same in the molecular formula; bonds are the same in between the atoms but the relative positions of the groups are different; those compounds are called Stereoisomers.
In case \[{C_6}{H_{14}}\] there are a total of five constitutional isomers present but no stereoisomers are present.
Now the molecular formula of those isomers of hexane is \[{C_6}{H_{14}}\] . But the condensed isomers are different in each isomer, this is because the bonds between the atoms of the molecule are different in the isomers of hexane.
The structural formula of all five isomers of hexane with six C-atoms \[({C_6}{H_{14}})\] is,
2-methyl-pentane \[(C{H_3}CH(C{H_3})C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3})\] , 3-methyl-pentane \[(C{H_3}C{H_2}CH(C{H_3})C{H_2}C{H_3})\] , 2,2-dimethyl-butane \[(C{H_3}C{(C{H_3})_2}C{H_2}C{H_3})\] , 2,3-dimethyl-butane \[(C{H_3}CH(C{H_3})CH(C{H_3})C{H_3})\] , hexane\[(C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3})\] .
Structures are,

Note:
The empirical formula of any compound gives the lowest value of the ratio of the elements present in a molecule. But from this formula the actual number of the elements present in the molecule cannot be defined. . The molecular formula of a compound is with the actual number of the elements present in a compound. The relation between them is given by,\[{\text{ }}molecular{\text{ }}formula = {\left( {{\text{ }}emperical{\text{ }}formula} \right)_n}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Common Ion Effect: Concept, Applications, and Problem-Solving

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques - 2025-26




