
Which reaction is used for the preparation of \[\alpha \] -Bromoacetic acid?
A. Kolbe's Reaction
B. Reimer- Tiemann Reaction
C. Hell volhard reaction
D. Perkins Reaction
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: The chemical compound named \[\alpha \] -Bromoacetic acid is obtained from the carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula is \[{\rm{Br}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}} - {\rm{CO}} - {\rm{OH}}\] . In this compound, bromine is bonded to alpha carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
Let's discuss all the options given in the question.
First, we will understand what Kolbe's reaction is. Kolbe's reaction is the conversion of phenol into salicylic acid. In the first step, phenol is converted into phenoxide ion by reacting it with sodium hydroxide. In the second step, the reaction of phenoxide ions with carbon dioxide in an acidic medium gives salicylic acid.
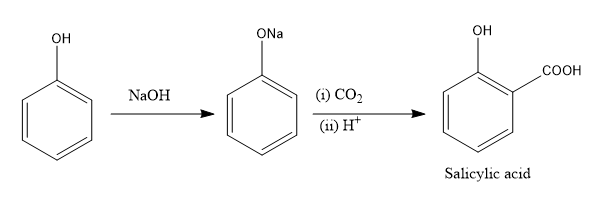
Image: Kolbe’s reaction
Therefore, option A is wrong.
In Riemer-Tiemann reaction, phenol to salicylaldehyde conversion takes place by reacting phenol with chloroform along with sodium hydroxide.
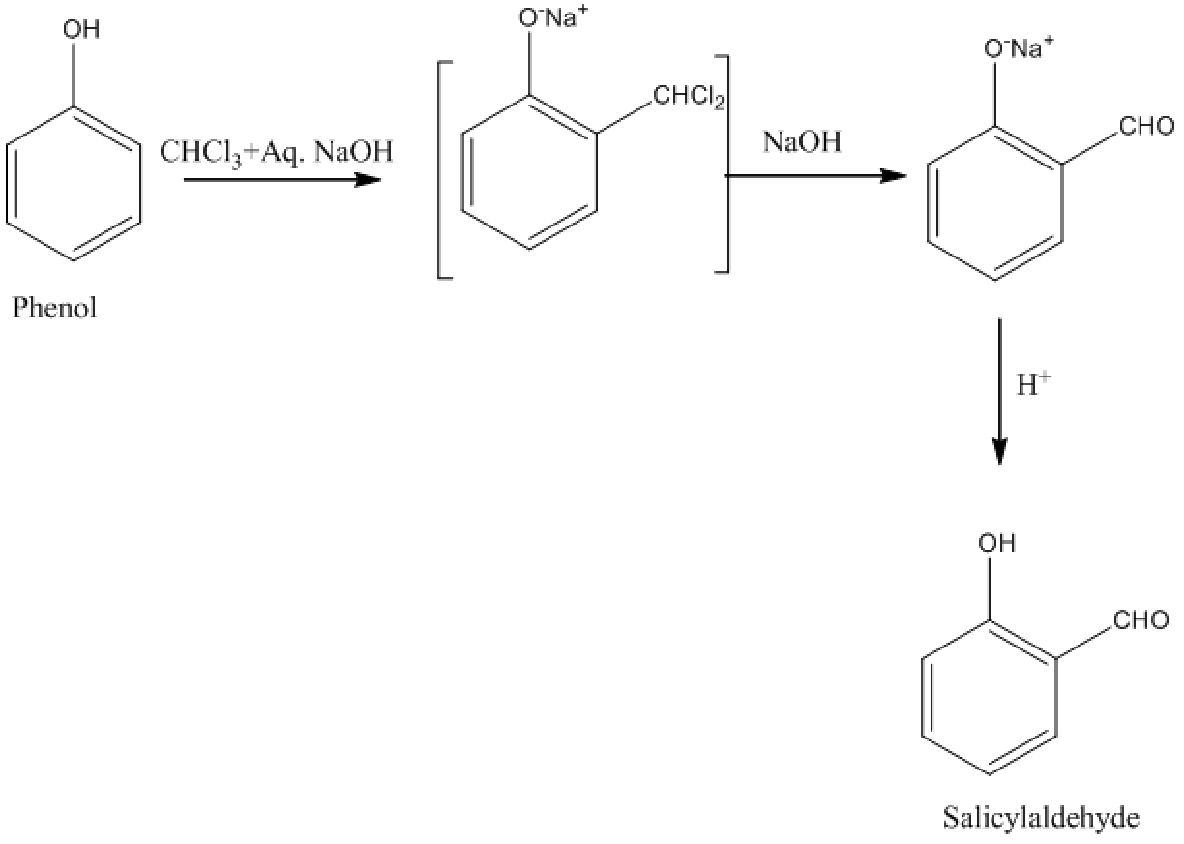
Image: Riemer-Tiemann reaction
Therefore, option B is wrong.
Let's understand option D, that is, Perkin's reaction. In this reaction, an aliphatic acid anhydride, an aromatic aldehyde, and an alkali salt of the acid undergo a reaction to give cinnamic acid derivatives. The product obtained is \[\alpha ,\beta \]unsaturated aromatic acid. Hence, option D is wrong.
Let's understand the Hell Volhard reaction in detail. In this reaction, carboxylic acid undergoes reaction with \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{2}}}\]or \[{\rm{B}}{{\rm{r}}_{\rm{2}}}\] in the presence of red coloured phosphorus to gives \[\alpha \]-chloroacetic acid or
\[\alpha \]-bromoacetic acid. Here, one hydrogen atom of alpha carbon gets replaced by an atom of chlorine or bromine.
\[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COOH}} + {\rm{B}}{{\rm{r}}_{\rm{2}}} \overset{Red Phosphorus}{\rightarrow} \mathop {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{BrCOOH}}}\limits_{{\rm{\alpha - Bromoacetic}}\,{\rm{acid}}} \]
Hence, option C is right.
Note: It is to be noted that, in organic chemistry, the \[\alpha \] carbon indicates the first carbon atom that is bonded to the carbonyl group and the \[\beta \] carbon indicates that carbon atom which comes in the second position from the carbonyl carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
Let's discuss all the options given in the question.
First, we will understand what Kolbe's reaction is. Kolbe's reaction is the conversion of phenol into salicylic acid. In the first step, phenol is converted into phenoxide ion by reacting it with sodium hydroxide. In the second step, the reaction of phenoxide ions with carbon dioxide in an acidic medium gives salicylic acid.

Image: Kolbe’s reaction
Therefore, option A is wrong.
In Riemer-Tiemann reaction, phenol to salicylaldehyde conversion takes place by reacting phenol with chloroform along with sodium hydroxide.

Image: Riemer-Tiemann reaction
Therefore, option B is wrong.
Let's understand option D, that is, Perkin's reaction. In this reaction, an aliphatic acid anhydride, an aromatic aldehyde, and an alkali salt of the acid undergo a reaction to give cinnamic acid derivatives. The product obtained is \[\alpha ,\beta \]unsaturated aromatic acid. Hence, option D is wrong.
Let's understand the Hell Volhard reaction in detail. In this reaction, carboxylic acid undergoes reaction with \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{2}}}\]or \[{\rm{B}}{{\rm{r}}_{\rm{2}}}\] in the presence of red coloured phosphorus to gives \[\alpha \]-chloroacetic acid or
\[\alpha \]-bromoacetic acid. Here, one hydrogen atom of alpha carbon gets replaced by an atom of chlorine or bromine.
\[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COOH}} + {\rm{B}}{{\rm{r}}_{\rm{2}}} \overset{Red Phosphorus}{\rightarrow} \mathop {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{BrCOOH}}}\limits_{{\rm{\alpha - Bromoacetic}}\,{\rm{acid}}} \]
Hence, option C is right.
Note: It is to be noted that, in organic chemistry, the \[\alpha \] carbon indicates the first carbon atom that is bonded to the carbonyl group and the \[\beta \] carbon indicates that carbon atom which comes in the second position from the carbonyl carbon.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




