
Which one of the following statement is true for ammonium ion
A) All bonds are ionic
B) All bonds are coordinate covalent
C) H atoms are situated at the corners of a square
D) H atoms are situated at the corners of a tetrahedron
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: When an ammonia molecule acquires a proton, then an ammonium ion forms. The molecular formula of ammonium ion is \[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}^ + \] . Here, first we will discuss all types of bond so that we will identify the type of bond in the ammonium ion.
Complete step by step solution:Let’s understand what an ionic bond is. This type of bond is formed due to the electrostatic attraction of oppositely charged ions. For example, sodium chloride is an ionic bond.
Now we will discuss what a coordinate bond is. A bond whose formation takes place due to the donation of both the electrons by an atom is called a coordinate bond.
A covalent bond is the one in which the bond formation takes place due to the sharing of electrons between the atoms.
Let’s understand the ammonium ion.
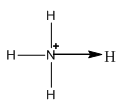
Image: Ammonium ion
In the ammonium three N-H bonds are covalent in nature because they formed due to the sharing of electrons. And the bond denoted by the arrow bond is a coordinate bond.
So, in the ammonia ion three covalent bonds and one coordinate bond are present.
Let’s find the shape of \[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}^ + \]. It is \[s{p^3}\] hybridized and therefore its molecular geometry is tetrahedral. Therefore, each hydrogen atom occupies the corners of a tetrahedron.
So, option D is right.
Note: The shape of a molecule is decided by applying the VSEPR theory. According to this theory, if we know the count of bond pairs and the lone pairs of a central atom, we can easily identify its shape.
Complete step by step solution:Let’s understand what an ionic bond is. This type of bond is formed due to the electrostatic attraction of oppositely charged ions. For example, sodium chloride is an ionic bond.
Now we will discuss what a coordinate bond is. A bond whose formation takes place due to the donation of both the electrons by an atom is called a coordinate bond.
A covalent bond is the one in which the bond formation takes place due to the sharing of electrons between the atoms.
Let’s understand the ammonium ion.

Image: Ammonium ion
In the ammonium three N-H bonds are covalent in nature because they formed due to the sharing of electrons. And the bond denoted by the arrow bond is a coordinate bond.
So, in the ammonia ion three covalent bonds and one coordinate bond are present.
Let’s find the shape of \[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}^ + \]. It is \[s{p^3}\] hybridized and therefore its molecular geometry is tetrahedral. Therefore, each hydrogen atom occupies the corners of a tetrahedron.
So, option D is right.
Note: The shape of a molecule is decided by applying the VSEPR theory. According to this theory, if we know the count of bond pairs and the lone pairs of a central atom, we can easily identify its shape.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




