
Which one of the following shows maximum paramagnetic character?
A) ${{\left[ Cr{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{6}} \right]}^{3+}}$
B) ${{\left[ Fe{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]}^{4-}}$
C) ${{\left[ Fe{{\left( CN \right)}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}$
D) ${{\left[ Cu{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{6}} \right]}^{2+}}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In the coordination complexes, when the central metal ion consists of unpaired electrons in its orbital, then the complex is said to have a paramagnetic character. The greater the number of unpaired electrons, the greater will be the paramagnetic character of the complex.
Complete answer:Paramagnetism is the magnetic moment that occurs due to the orientation of the atoms in alignment with the direction of the applied magnetic field. It is weakly attracted by the external magnetic field.
Cause of paramagnetism: In the orbitals of an atom, electrons are present which are the negatively charged species and have the tendency to spin on their own axis. Due to this motion, a magnetic moment is generated which is responsible for the magnetic nature of the atom. In the case of coordination complexes, the transition metal is responsible for determining the magnetic character of the complex. The greater the number of unpaired electrons, the greater will be the magnetic moment and thus, the complex will have a greater paramagnetic character.
Among the given complexes, the data of the unpaired electrons can be collated as follows:
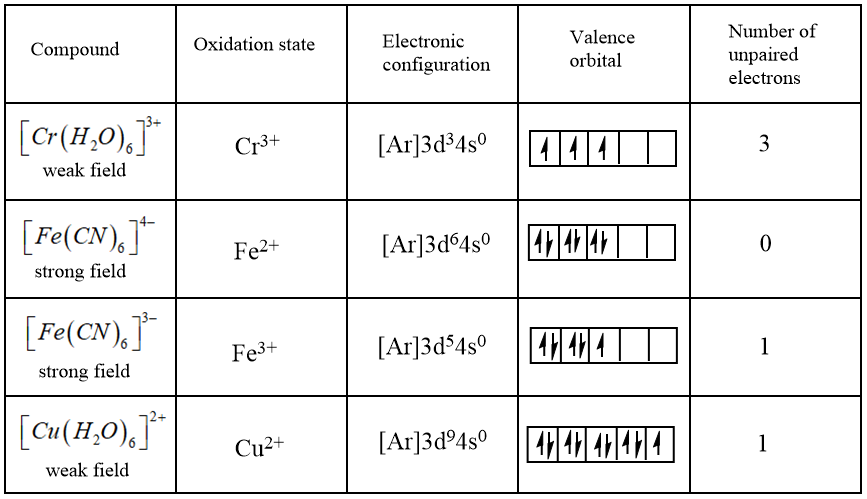
Here, the weak field and strong field are determined by the strength of the ligand bonded with the central metal ion. Strong field ligands like $C{{N}^{-}}$have the tendency to pair up the electrons within the valence orbitals while the weak field ligands like ${{H}_{2}}O$ do not have such tendency.
Thus, as per the data, the maximum number of unpaired electrons are present in ${{\left[ Cr{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{6}} \right]}^{3+}}$ and therefore has the maximum paramagnetic nature.
option (A) is the correct answer.
Note: It is important to note that the compound in which the central metal ion consists of paired electrons only does not show the paramagnetic nature because the electrons in the orbitals have an opposite spin and thus, the magnetic field generated by the electrons cancel each other because of equal and opposite nature of the magnetic moment. These complexes have a diamagnetic nature and tend to repel the external magnetic field.
Complete answer:Paramagnetism is the magnetic moment that occurs due to the orientation of the atoms in alignment with the direction of the applied magnetic field. It is weakly attracted by the external magnetic field.
Cause of paramagnetism: In the orbitals of an atom, electrons are present which are the negatively charged species and have the tendency to spin on their own axis. Due to this motion, a magnetic moment is generated which is responsible for the magnetic nature of the atom. In the case of coordination complexes, the transition metal is responsible for determining the magnetic character of the complex. The greater the number of unpaired electrons, the greater will be the magnetic moment and thus, the complex will have a greater paramagnetic character.
Among the given complexes, the data of the unpaired electrons can be collated as follows:

Here, the weak field and strong field are determined by the strength of the ligand bonded with the central metal ion. Strong field ligands like $C{{N}^{-}}$have the tendency to pair up the electrons within the valence orbitals while the weak field ligands like ${{H}_{2}}O$ do not have such tendency.
Thus, as per the data, the maximum number of unpaired electrons are present in ${{\left[ Cr{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{6}} \right]}^{3+}}$ and therefore has the maximum paramagnetic nature.
option (A) is the correct answer.
Note: It is important to note that the compound in which the central metal ion consists of paired electrons only does not show the paramagnetic nature because the electrons in the orbitals have an opposite spin and thus, the magnetic field generated by the electrons cancel each other because of equal and opposite nature of the magnetic moment. These complexes have a diamagnetic nature and tend to repel the external magnetic field.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




