
Which one of the following octahedral complexes will not show geometric isomerism (A and B are monodentate ligands)
A) $\left[ M{{A}_{5}}B \right]$
B) $\left[ M{{A}_{2}}{{B}_{4}} \right]$
C) $\left[ M{{A}_{3}}{{B}_{3}} \right]$
D) $\left[ M{{A}_{4}}{{B}_{2}} \right]$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The geometrical isomerism is only exhibited by the square planar complexes and the octahedral complexes due to the presence of planar geometry. The only condition required by a coordination complex to show geometrical isomerism is the positioning of the ligands should not be equivalent i.e., the structures should not superimpose to each other.
Complete answer:In the octahedral complexes which are heteroleptic in nature i.e., the complexes in which the metal ion is surrounded by more than one type of ligands, show geometrical isomerism due to the possibility of the ligands to get arranged in different positions.
Geometrical isomerism is broadly categorized into two types i.e., cis-geometrical isomerism and trans-geometrical isomerism. If the identical ligands are placed in the adjacent position with respect to the central metal ion then it is said to be cis-geometrical isomerism. If the identical ligands are placed in the opposite direction, then it is called trans-geometrical isomerism.
In the case of octahedral complexes having monodentate ligands, the geometrical isomerism can be summarised as follows:
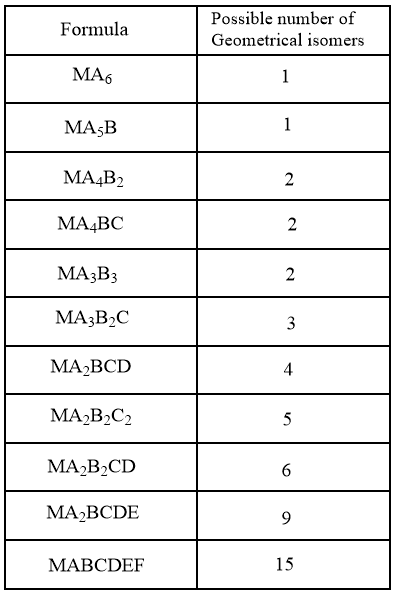
Where, M is the central metal ion and A, B, C, D, E and F are the monodentate ligands.
As summarised in the data, it is observed that the complexes of type ${{\left[ M{{A}_{6}} \right]}^{n\pm }}$ and ${{\left[ M{{A}_{5}}B \right]}^{n\pm }}$ does not show geometrical isomerism because all the corners of the regular octahedron are equivalent and no arrangement is observed. An example of such complexes is given below:
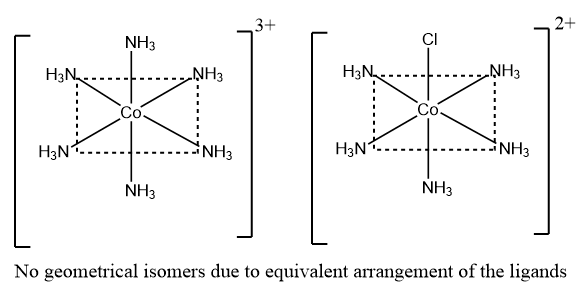
Thus, among the given options, the complex which does not show geometrical isomerism is $\left[ M{{A}_{5}}B \right]$, and therefore option A is the correct answer.
Note: It is important to note that cis geometrical isomerism is also known as facial or fac-isomer as the similar groups are occupied in the adjacent positions of the octahedral faces while the trans geometrical isomerism is known as meridional or mer-isomer because the position of the donor atom is around the meridian of the octahedron.
Complete answer:In the octahedral complexes which are heteroleptic in nature i.e., the complexes in which the metal ion is surrounded by more than one type of ligands, show geometrical isomerism due to the possibility of the ligands to get arranged in different positions.
Geometrical isomerism is broadly categorized into two types i.e., cis-geometrical isomerism and trans-geometrical isomerism. If the identical ligands are placed in the adjacent position with respect to the central metal ion then it is said to be cis-geometrical isomerism. If the identical ligands are placed in the opposite direction, then it is called trans-geometrical isomerism.
In the case of octahedral complexes having monodentate ligands, the geometrical isomerism can be summarised as follows:

Where, M is the central metal ion and A, B, C, D, E and F are the monodentate ligands.
As summarised in the data, it is observed that the complexes of type ${{\left[ M{{A}_{6}} \right]}^{n\pm }}$ and ${{\left[ M{{A}_{5}}B \right]}^{n\pm }}$ does not show geometrical isomerism because all the corners of the regular octahedron are equivalent and no arrangement is observed. An example of such complexes is given below:

Thus, among the given options, the complex which does not show geometrical isomerism is $\left[ M{{A}_{5}}B \right]$, and therefore option A is the correct answer.
Note: It is important to note that cis geometrical isomerism is also known as facial or fac-isomer as the similar groups are occupied in the adjacent positions of the octahedral faces while the trans geometrical isomerism is known as meridional or mer-isomer because the position of the donor atom is around the meridian of the octahedron.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Area of an Octagon Formula Explained Simply

Absolute Pressure Formula Explained: Key Equation & Examples

Central Angle of a Circle Formula Explained Quickly

Difference Between Vapor and Gas: JEE Main 2026

Difference Between Atom and Molecule: JEE Main 2026

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Jan 21 Shift 1 Question Papers with Solutions & Answer Keys – Detailed Day 1 Analysis

JEE Main Response Sheet 2026 Released – Key Dates and Official Updates by NTA

JEE Main 2026 Answer Key OUT – Download Session 1 PDF, Response Sheet & Challenge Link

JEE Main Marks vs Percentile 2026: Calculate Percentile and Rank Using Marks

JEE Main 2026 Jan 22 Shift 1 Today Paper Live Analysis With Detailed Solutions

Other Pages
Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages

One Day International Cricket

Valentine Week 2026: Complete List of Valentine Week Days & Meaning of Each Day

List of Highest T20 Scores in International Cricket

Makar Sankranti Wishes: Happy Makar Sankranti Wishes in Marathi, Hindi, Kannada, and English

What is the Full Form of UGC? Detailed Guide for Students





