
Which one doesn't liberate \[N{H_3}\] when undergoing hydrolysis?
A. Acetanilide
B. Acetonitrile
C. Acetamide
D. Phenyl isocyanide
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Hydro means water and lysis mean splitting, which means the hydrolysis reaction works with water. Here water splits into hydronium ions (protons) and hydroxyl ions, which are then attached to another molecule of the system.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
For this, a hydrolysis reaction should be done to check which one is liberating ammonia. The above options are having different functional groups, so all may have different steps of reactions.
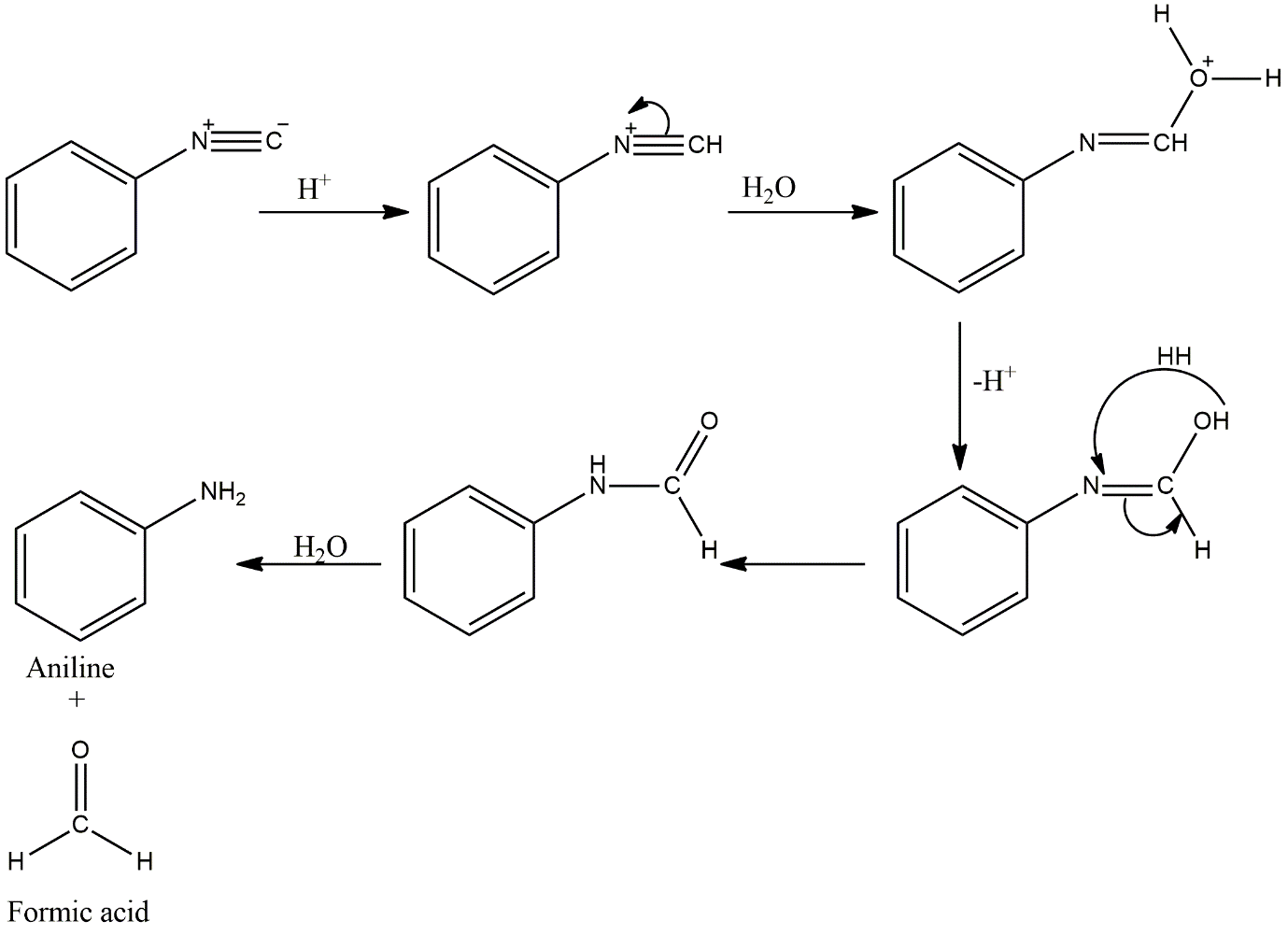
Image: Hydrolysis reactions
After hydrolysis, only phenyl isocyanide is not liberating ammonia. Instead, it has formic acid as a by-product. And also, it requires an acidic condition for hydrolysis. This is because they both are charged. So, they need an acidic condition to accelerate the reaction.
So, the option D is correct.
Additional Information: Acetanilide and acetamide, both are having amide functional groups. Their carbon is more electrophilic because of electronegative atoms adjacent to it. On hydrolysis, hydroxyl ions will attach to this carbon. And hydronium ions to the nitrogen of amide functional group as it is electronegative. This results in breaking the bond between carbon and nitrogen of the amide functional group. Similar steps apply to acetonitrile. Acetonitrile has a cyanide functional group. There is again an electronegativity difference between carbon and nitrogen which will help in hydrolysis.
Note: Complete knowledge of hydrolysis is necessary. For ease, try memorising the functional groups and the generated electronegativity difference. This will help in reactions to understand which bond is susceptible to break.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
For this, a hydrolysis reaction should be done to check which one is liberating ammonia. The above options are having different functional groups, so all may have different steps of reactions.

Image: Hydrolysis reactions
After hydrolysis, only phenyl isocyanide is not liberating ammonia. Instead, it has formic acid as a by-product. And also, it requires an acidic condition for hydrolysis. This is because they both are charged. So, they need an acidic condition to accelerate the reaction.
So, the option D is correct.
Additional Information: Acetanilide and acetamide, both are having amide functional groups. Their carbon is more electrophilic because of electronegative atoms adjacent to it. On hydrolysis, hydroxyl ions will attach to this carbon. And hydronium ions to the nitrogen of amide functional group as it is electronegative. This results in breaking the bond between carbon and nitrogen of the amide functional group. Similar steps apply to acetonitrile. Acetonitrile has a cyanide functional group. There is again an electronegativity difference between carbon and nitrogen which will help in hydrolysis.
Note: Complete knowledge of hydrolysis is necessary. For ease, try memorising the functional groups and the generated electronegativity difference. This will help in reactions to understand which bond is susceptible to break.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




