
Which of the subsequent polymers doesn't have vinylic monomer units?
(A) Acrilan
(B) Nylon
(C) Polystyrene
(D) Neoprene
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Polymers are materials product of long, repeating chains of molecules. The materials have unique properties, betting on the kind of molecules that are bonded and the way bonded they're. It is done due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles.
Complete step by step answer:
Vinyl polymers are polymers made of vinyl monomers; that's, small molecules containing carbon-carbon double bonds. They create the largest family of polymers. Let's examine how we get from a vinyl monomer to a polyvinyl resin using for example the best vinyl resin, polyethylene. Polyethylene is formed from the monomer ethylene, which is additionally called ethene. When polymerized, the ethylene molecules are joined along the axes of their double bonds to create a protracted chain of many thousands of carbon atoms containing only single bonds between atoms.
Now let us see Vinylic monomer, they’re basically a monomer containing a carbon-carbon covalent bond in them.
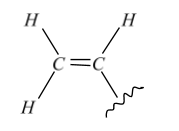
Acrilan
${{\left( -C{{H}_{2}}=CHCN- \right)}_{n}}$
Polystyrene
${{\left( -{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-C{{H}_{2}}=C{{H}_{2}}- \right)}_{n}}$
Neoprene
${{\left( -C{{H}_{2}}=CHCl- \right)}_{n}}$
Nylon
$\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
~{{\left( Hexamethylene\,diamine+adipicacid \right)}_{n}} \\
\end{array}$
Only nylon does not have vinylic monomer units.
So, the correct option is (B).
Note:
Vinyl polymers are made up of monomers within which one or more of the hydrogen atoms of ethylene has been replaced by another atom or groups of atoms. Not many monomers during which hydrogen atoms have been replaced on both carbon atoms will polymerize.
Complete step by step answer:
Vinyl polymers are polymers made of vinyl monomers; that's, small molecules containing carbon-carbon double bonds. They create the largest family of polymers. Let's examine how we get from a vinyl monomer to a polyvinyl resin using for example the best vinyl resin, polyethylene. Polyethylene is formed from the monomer ethylene, which is additionally called ethene. When polymerized, the ethylene molecules are joined along the axes of their double bonds to create a protracted chain of many thousands of carbon atoms containing only single bonds between atoms.
Now let us see Vinylic monomer, they’re basically a monomer containing a carbon-carbon covalent bond in them.

Acrilan
${{\left( -C{{H}_{2}}=CHCN- \right)}_{n}}$
Polystyrene
${{\left( -{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-C{{H}_{2}}=C{{H}_{2}}- \right)}_{n}}$
Neoprene
${{\left( -C{{H}_{2}}=CHCl- \right)}_{n}}$
Nylon
$\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
~{{\left( Hexamethylene\,diamine+adipicacid \right)}_{n}} \\
\end{array}$
Only nylon does not have vinylic monomer units.
So, the correct option is (B).
Note:
Vinyl polymers are made up of monomers within which one or more of the hydrogen atoms of ethylene has been replaced by another atom or groups of atoms. Not many monomers during which hydrogen atoms have been replaced on both carbon atoms will polymerize.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




