
Which of the following statements are correct about Friedel-Crafts reaction?
(A) It is an aromatic electrophilic substitution
(B) The reaction intermediate is an electron deficient species
(C) The reaction involves alkylation and acylation
(D) A Lewis acid is used as a catalyst
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Friedel-Crafts reaction is used to introduce alkyl or acyl moiety in the compound in the presence of Lewis acids like\[{\text{AlC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\]through the formation of carbocation intermediate.
Complete step by step answer:
Friedel-Crafts reaction is an electrophilic aromatic substitution since an electrophile, namely carbocation, attacks the aromatic ring. It involves primarily two types of reactions that are alkylation and acylation.
The Friedel crafts alkylation can be depicted as follows:
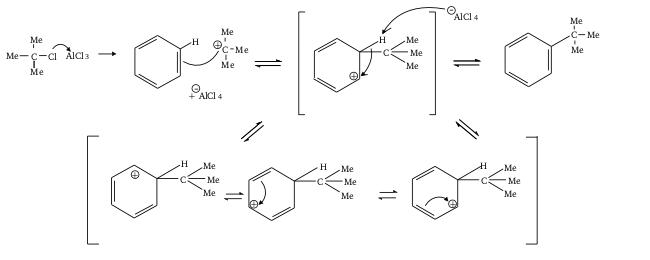
The Friedel crafts acylation can be depicted as follows:
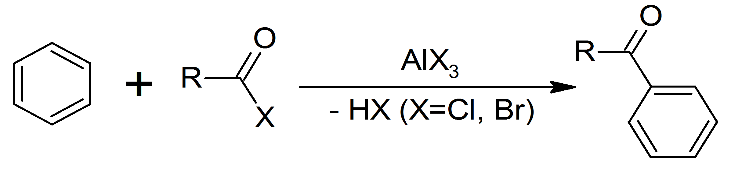
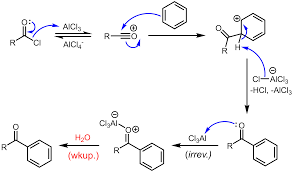
We can see in the mechanism that both of these reactions are electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Lewis acids are electron acceptors thus accepting the electron to form negatively charged species and leads to a carbocation intermediate. The intermediate carbocation is an electron deficient species. Lewis acid is obtained in its original form by giving up its electrons to halide ion thus Lewis acid acts as catalyst.
According to the question’s options, all statements are true.
So, the correct options are A, B, C, and D.
Additional Information: There are few limitations of Friedel-crafts alkylation reactions.
The carbocation formed from the alkyl halide can undergo rearrangement to form a very stable carbocation. Thus, in some cases desired products may not be formed.
The presence of deactivating groups in the aromatic system can deactivate the catalyst due to complex formation.
There are also few limitations in Friedel-crafts acylation reactions.
These reactions yield only ketones.
When formyl chloride is used, they may get decomposed to carbon dioxide and HCl when exposed to these conditions.
The aromatic ring must be more reactive than mono-halo benzenes.
Note: The carbocation formed will undergo rearrangement thus careful choice of alkyl halide is necessary to obtain desired product in Friedel-crafts alkylation reactions. The acylation reaction conditions can be followed only when we need to obtain ketones.
Complete step by step answer:
Friedel-Crafts reaction is an electrophilic aromatic substitution since an electrophile, namely carbocation, attacks the aromatic ring. It involves primarily two types of reactions that are alkylation and acylation.
The Friedel crafts alkylation can be depicted as follows:

The Friedel crafts acylation can be depicted as follows:
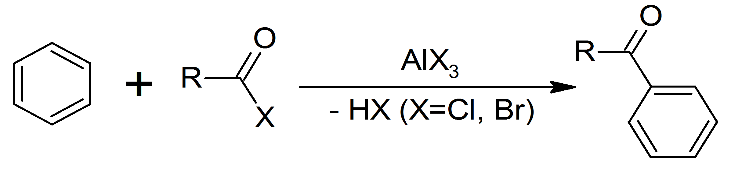

We can see in the mechanism that both of these reactions are electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Lewis acids are electron acceptors thus accepting the electron to form negatively charged species and leads to a carbocation intermediate. The intermediate carbocation is an electron deficient species. Lewis acid is obtained in its original form by giving up its electrons to halide ion thus Lewis acid acts as catalyst.
According to the question’s options, all statements are true.
So, the correct options are A, B, C, and D.
Additional Information: There are few limitations of Friedel-crafts alkylation reactions.
The carbocation formed from the alkyl halide can undergo rearrangement to form a very stable carbocation. Thus, in some cases desired products may not be formed.
The presence of deactivating groups in the aromatic system can deactivate the catalyst due to complex formation.
There are also few limitations in Friedel-crafts acylation reactions.
These reactions yield only ketones.
When formyl chloride is used, they may get decomposed to carbon dioxide and HCl when exposed to these conditions.
The aromatic ring must be more reactive than mono-halo benzenes.
Note: The carbocation formed will undergo rearrangement thus careful choice of alkyl halide is necessary to obtain desired product in Friedel-crafts alkylation reactions. The acylation reaction conditions can be followed only when we need to obtain ketones.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




