
Which of the following metals is present in the green-colored pigment chlorophyll of plants?
A. Fe
B. Mg
C. Na
D. Al
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Chlorophyll is a green pigment present in the chloroplasts of algae and plants.It is one of the significant elements used in the process of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process through which green plants and other organisms utilise sunlight to prepare nutrients from carbon dioxide and water.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The colour of green plants is due to the chlorophyll pigment. Pyrrole is a five-membered heterocyclic aromatic organic compound containing a nitrogen atom.
The structure of pyrrole is as follows:
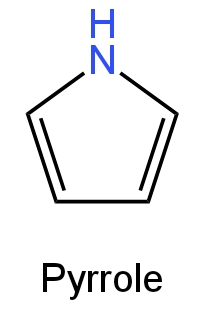
Image: Pyrrole
When four pyrrole subunits are connected through methine bridges, they form a union of heterocyclic organic compounds called porphyrins.
Methine is derived from methane and is a trivalent functional group.
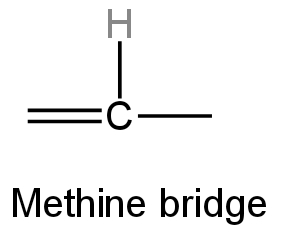
Image: Methine bridge
Metal complexes originating from porphyrins are formed naturally.
Heme, a pigment in red blood cells and also a cofactor of the protein haemoglobin, is one type of the porphyrin complex.
Chlorophyll also originates from porphyrin.
In chlorophyll, the four pyrrole units are attached by a central metal atom which is Magnesium.
Here the central magnesium atom is enclosed by a porphyrin ring which is attached to a long carbon-hydrogen side chain called a phytol chain.
So, option B is correct.
Additional Information: The word chlorophyll originates from the Greek word khloros which means green and phyllon which means leaves.
Chlorophyll is a green pigment that works as a photoreceptor in plants.
Note: Chlorophyll has a crucial part in photosynthesis as it enables the plants to absorb energy from the light given by the sun. This energy is later used to carry on the photosynthesis process. Magnesium is an important unit of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is categorised into five types i.e., chlorophyll a, b, c, d, and d and e.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The colour of green plants is due to the chlorophyll pigment. Pyrrole is a five-membered heterocyclic aromatic organic compound containing a nitrogen atom.
The structure of pyrrole is as follows:

Image: Pyrrole
When four pyrrole subunits are connected through methine bridges, they form a union of heterocyclic organic compounds called porphyrins.
Methine is derived from methane and is a trivalent functional group.

Image: Methine bridge
Metal complexes originating from porphyrins are formed naturally.
Heme, a pigment in red blood cells and also a cofactor of the protein haemoglobin, is one type of the porphyrin complex.
Chlorophyll also originates from porphyrin.
In chlorophyll, the four pyrrole units are attached by a central metal atom which is Magnesium.
Here the central magnesium atom is enclosed by a porphyrin ring which is attached to a long carbon-hydrogen side chain called a phytol chain.
So, option B is correct.
Additional Information: The word chlorophyll originates from the Greek word khloros which means green and phyllon which means leaves.
Chlorophyll is a green pigment that works as a photoreceptor in plants.
Note: Chlorophyll has a crucial part in photosynthesis as it enables the plants to absorb energy from the light given by the sun. This energy is later used to carry on the photosynthesis process. Magnesium is an important unit of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is categorised into five types i.e., chlorophyll a, b, c, d, and d and e.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




