
Which of the following is not used to distinguish ethene from ethane
A. Iodine in \[CC{{l}_{4}}\]
B. Bromine in \[CC{{l}_{4}}\]
C. Alkaline \[KMn{{O}_{4}}\]
D. Ammoniacal \[C{{u}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Ethane is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula \[{C_2}{H_6}\]. It is a saturated compound as it contains single bonds only. Ethene on the other hand has the molecular formula \[{C_2}{H_4}\]. It is an unsaturated compound. Ethane can be distinguished from ethene based on the different types of bonds present in them.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Here in this question, we have to find out which one of the given options is not used to distinguish ethene from ethane.
A. Iodine in\[CC{l_4}\]
This reagent is helpful in the iodination of ethene.
Ethene when reacted with iodine in carbon tetrachloride forms 1,2-diiodoethane.
Iodine loses its violet colour and gives a colourless liquid due to the formation of 1,2-diiodoethane.
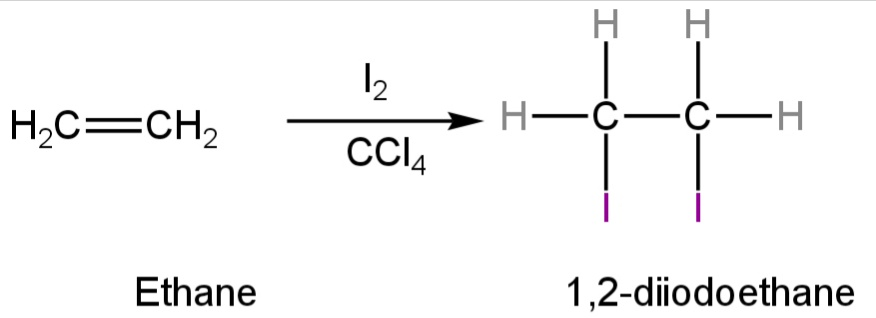
Image: Reaction of ethene with Iodine in\[CC{l_4}\]
This is an addition reaction.
Ethane doesn't react with iodine in the presence of carbon tetrachloride.
So, this reaction can be used to distinguish between ethene and ethane.
So, A is incorrect.
B. Bromine in \[CC{l_4}\]
This is also an addition reaction.
Ethene when reacted with bromine in carbon tetrachloride forms 1,2-dibromoethane.
The double bond breaks and a bromine atom is connected to each carbon.
The bromine loses its original red-brown colour and gives a colourless liquid.
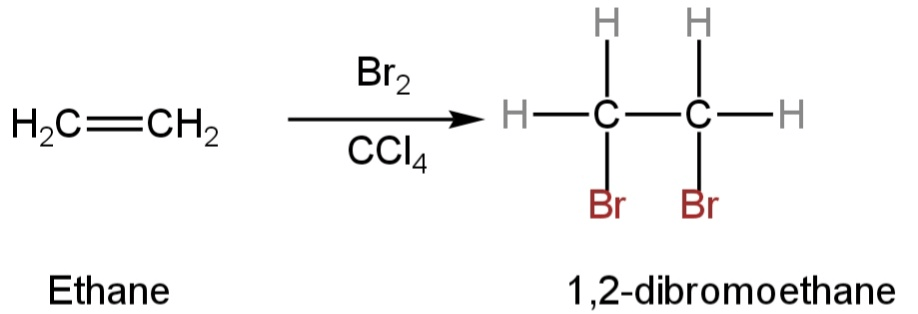
Image: Reaction of ethene with Bromine in \[CC{l_4}\].
Ethane doesn't react with bromine in the presence of carbon tetrachloride.
So, this reaction can be used to distinguish between ethene and ethane.
So, B is incorrect.
C. Alkaline\[KMn{O_4}\]
Potassium permanganate is an oxidising agent.
Due to the presence of unsaturation in ethene, it gets oxidised into ethane-1,2-diol or ethylene glycol.
The reaction is given as follows:
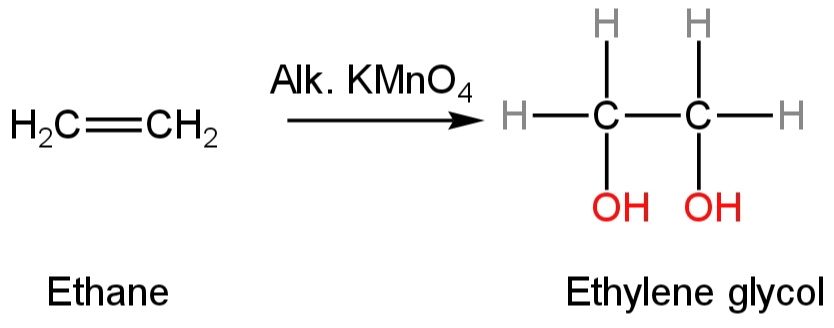
Image: Reaction of Alkaline\[KMn{O_4}\] with ethene.
The pink colour of the potassium permanganate is discharged and a brown-colored precipitate of manganese dioxide is observed.
Ethane doesn't react with potassium permanganate.
So, this reaction can be used as a test for unsaturation called Baeyer’s test.
So, C is incorrect.
D. Ammoniacal \[C{u_2}C{l_2}\]
It is used to distinguish terminal alkynes.
In this reaction, a terminal alkyne when reacted with basic cupric chloride and on successive oxidation in the air produces diyne. For instance, two molecules of ethyne react to produce but-1,3-yne which is a red-brown precipitate. This reaction is not used as a test for ethene or ethane.
So, D is correct.
So, option D is correct.
Note: In terminal alkynes the triple bonds are present on the ends of the compound.
Ammoniacal cuprous chloride is made by dissolving cuprous chloride in water and ammonia forming a blue-colored solution.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Here in this question, we have to find out which one of the given options is not used to distinguish ethene from ethane.
A. Iodine in\[CC{l_4}\]
This reagent is helpful in the iodination of ethene.
Ethene when reacted with iodine in carbon tetrachloride forms 1,2-diiodoethane.
Iodine loses its violet colour and gives a colourless liquid due to the formation of 1,2-diiodoethane.

Image: Reaction of ethene with Iodine in\[CC{l_4}\]
This is an addition reaction.
Ethane doesn't react with iodine in the presence of carbon tetrachloride.
So, this reaction can be used to distinguish between ethene and ethane.
So, A is incorrect.
B. Bromine in \[CC{l_4}\]
This is also an addition reaction.
Ethene when reacted with bromine in carbon tetrachloride forms 1,2-dibromoethane.
The double bond breaks and a bromine atom is connected to each carbon.
The bromine loses its original red-brown colour and gives a colourless liquid.

Image: Reaction of ethene with Bromine in \[CC{l_4}\].
Ethane doesn't react with bromine in the presence of carbon tetrachloride.
So, this reaction can be used to distinguish between ethene and ethane.
So, B is incorrect.
C. Alkaline\[KMn{O_4}\]
Potassium permanganate is an oxidising agent.
Due to the presence of unsaturation in ethene, it gets oxidised into ethane-1,2-diol or ethylene glycol.
The reaction is given as follows:

Image: Reaction of Alkaline\[KMn{O_4}\] with ethene.
The pink colour of the potassium permanganate is discharged and a brown-colored precipitate of manganese dioxide is observed.
Ethane doesn't react with potassium permanganate.
So, this reaction can be used as a test for unsaturation called Baeyer’s test.
So, C is incorrect.
D. Ammoniacal \[C{u_2}C{l_2}\]
It is used to distinguish terminal alkynes.
In this reaction, a terminal alkyne when reacted with basic cupric chloride and on successive oxidation in the air produces diyne. For instance, two molecules of ethyne react to produce but-1,3-yne which is a red-brown precipitate. This reaction is not used as a test for ethene or ethane.
So, D is correct.
So, option D is correct.
Note: In terminal alkynes the triple bonds are present on the ends of the compound.
Ammoniacal cuprous chloride is made by dissolving cuprous chloride in water and ammonia forming a blue-colored solution.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




