
Which of the following compounds doesn't have a linear structure
A. Carbon dioxide
B. Sulfur dioxide
C. Beryllium chloride
D. Ethylene
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Linear compounds undergo sp hybridization and remain at an angle of \[180^o\] with each other. When multiple bonds are involved in a molecule, only one electron group is considered for multiple bonds for hybridization in these types of compounds.
Complete step by step solution:A. Carbon dioxide
Carbon is the central atom. It has four valence electrons. Each oxygen atom is doubly bonded to the carbon atom.
There are two sigma bonds and two pi-bonds on C.
So, there will be sp hybridization.
So, it has a linear structure.
So, A is incorrect.
B. Sulfur dioxide
Sulfur is the central atom. It has six electrons in its valence shell.
Each oxygen atom is doubly bonded to the carbon atom.
There are two bond pairs and one lone pair on S.
So, there will be \[sp^2\] hybridization.
So, it has a bent structure.
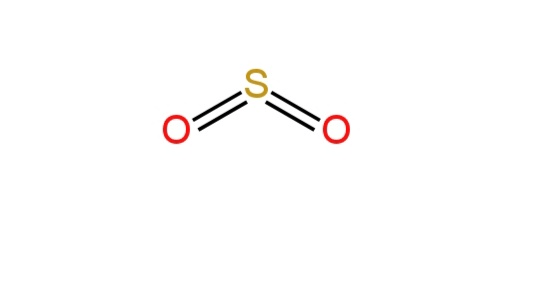
Structure: Structure of sulfur dioxide
So, B is correct.
C. Beryllium chloride
Be is the central atom. It has two valence electrons.
Each chlorine atom is bonded to the Be atom through a sigma bond.
There are two bond pairs.
So, there will be sp hybridization.
So, it has a linear structure.
So, C is incorrect.
D. Ethylene
In this, each carbon atom is bound with one hydrogen atom and the two carbon atoms are joined together. The bond between the carbon and carbon atom is a triple bond.
Considering the triple bond as one electron group, we see that there are two electron groups on carbon.
Here the hybridization will be sp.
The structure of ethylene is provided below:
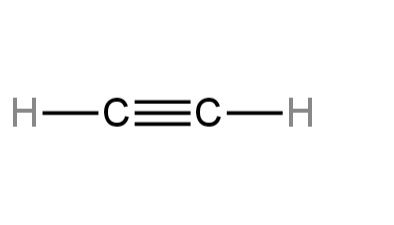
So, D is incorrect.
Sulfur dioxide has a bent structure.
So, option B is correct.
Note: Sulfur dioxide is utilized in numerous industries. It's utilized to manufacture sulfuric acid, paper, and food preservatives. It works as a bleaching agent to pull out the excess chlorine and as a disinfectant. In a cold storage plant, it behaves as a refrigerant.
Complete step by step solution:A. Carbon dioxide
Carbon is the central atom. It has four valence electrons. Each oxygen atom is doubly bonded to the carbon atom.
There are two sigma bonds and two pi-bonds on C.
So, there will be sp hybridization.
So, it has a linear structure.
So, A is incorrect.
B. Sulfur dioxide
Sulfur is the central atom. It has six electrons in its valence shell.
Each oxygen atom is doubly bonded to the carbon atom.
There are two bond pairs and one lone pair on S.
So, there will be \[sp^2\] hybridization.
So, it has a bent structure.

Structure: Structure of sulfur dioxide
So, B is correct.
C. Beryllium chloride
Be is the central atom. It has two valence electrons.
Each chlorine atom is bonded to the Be atom through a sigma bond.
There are two bond pairs.
So, there will be sp hybridization.
So, it has a linear structure.
So, C is incorrect.
D. Ethylene
In this, each carbon atom is bound with one hydrogen atom and the two carbon atoms are joined together. The bond between the carbon and carbon atom is a triple bond.
Considering the triple bond as one electron group, we see that there are two electron groups on carbon.
Here the hybridization will be sp.
The structure of ethylene is provided below:

So, D is incorrect.
Sulfur dioxide has a bent structure.
So, option B is correct.
Note: Sulfur dioxide is utilized in numerous industries. It's utilized to manufacture sulfuric acid, paper, and food preservatives. It works as a bleaching agent to pull out the excess chlorine and as a disinfectant. In a cold storage plant, it behaves as a refrigerant.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




