
Which functional group is present in a molecule of \[C{H_3}OH\]
(A) Ketone
(B) Aldehyde
(C) Ester
(D) Alcohol
(E) Halide
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Functional groups are a type of molecules that carry certain characteristic properties. They get linked to other molecules, but do not move away from their true nature. They get linked to other molecules by either ionic or covalent bonds.
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
In order to understand which functional group is present in a molecule of \[C{H_3}OH\], let us first discuss all the options:
1. Ketone: A ketone is a functional group in which a secondary carbon of any compound is attached with an oxygen atom. Since the oxygen atom has only one carbon to satisfy its oxidation state, it forms a double bond with this carbon. The general representation of a ketone is (R-O-R’):
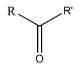
Where R and R’ are alkyl or aryl groups. The double bonded oxygen is also known as the carbonyl group.
2. Aldehyde: An Aldehyde is a functional group in which a primary carbon of any compound is attached with an oxygen atom. To put it in simpler terms, the carbonyl group is attached to the terminal carbon. The general representation of an aldehyde is (R-CHO):
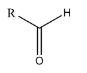
3. Ester: An ester is a functional group, in which the hydrogen atom from the carboxylic acid is substituted by another alkyl group. The general representation of an ester is (R-COOR’):
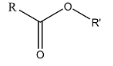
4. Alcohol: alcohol functional group consists of an oxygen and a hydrogen atom bonded together. They link to any compound through the oxygen atom and are commonly known as the hydroxyl group. The general representation of an alcohol is (R-OH):
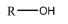
5. Halide: halide means the functional group is just the element which is a halogen. The general representation of a halide is (R-X), where X is the halide:
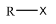
Hence from this data, we can conclude that a functional group is present in a molecule of alcohol.
Hence, Option D is the correct option.
Note: Each type of organic molecule has its own specific type of functional group. Functional groups in biological molecules play an important role in the formation of molecules like DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Functional groups include hydroxyl, methyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, phosphate, and sulfhydryl.
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
In order to understand which functional group is present in a molecule of \[C{H_3}OH\], let us first discuss all the options:
1. Ketone: A ketone is a functional group in which a secondary carbon of any compound is attached with an oxygen atom. Since the oxygen atom has only one carbon to satisfy its oxidation state, it forms a double bond with this carbon. The general representation of a ketone is (R-O-R’):

Where R and R’ are alkyl or aryl groups. The double bonded oxygen is also known as the carbonyl group.
2. Aldehyde: An Aldehyde is a functional group in which a primary carbon of any compound is attached with an oxygen atom. To put it in simpler terms, the carbonyl group is attached to the terminal carbon. The general representation of an aldehyde is (R-CHO):

3. Ester: An ester is a functional group, in which the hydrogen atom from the carboxylic acid is substituted by another alkyl group. The general representation of an ester is (R-COOR’):

4. Alcohol: alcohol functional group consists of an oxygen and a hydrogen atom bonded together. They link to any compound through the oxygen atom and are commonly known as the hydroxyl group. The general representation of an alcohol is (R-OH):
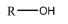
5. Halide: halide means the functional group is just the element which is a halogen. The general representation of a halide is (R-X), where X is the halide:
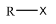
Hence from this data, we can conclude that a functional group is present in a molecule of alcohol.
Hence, Option D is the correct option.
Note: Each type of organic molecule has its own specific type of functional group. Functional groups in biological molecules play an important role in the formation of molecules like DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Functional groups include hydroxyl, methyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, phosphate, and sulfhydryl.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




