
Which compound in each of the following pairs is most reactive to the conditions indicated?
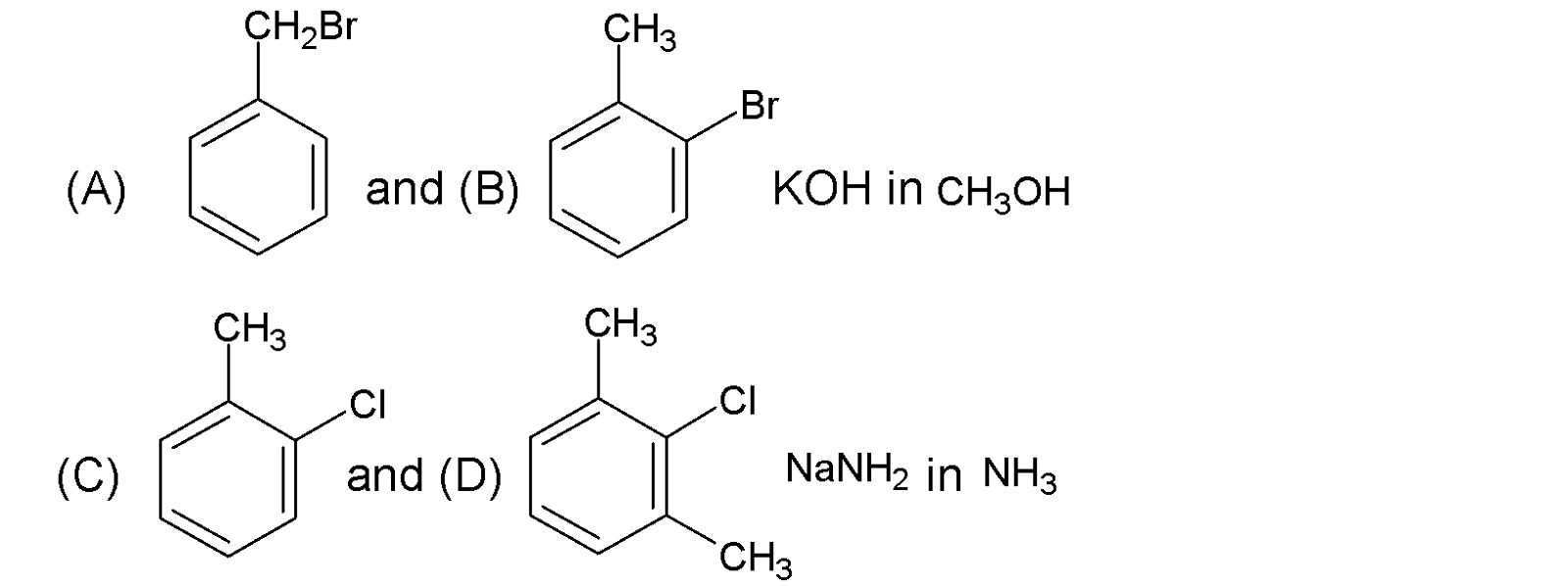
A. A and C
B. B and C
C. A and D
D. B and D
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Alcoholic KOH dissociates $R{{O}^{-}}$ into the water which acts as a strong base than $H{{O}^{-}}$ an ion, then it favours an elimination reaction. But sometimes the substitution reaction is favoured over elimination reaction due to unstable intermediate. In the presence of $NaN{{H}_{2}}$in $N{{H}_{3}}$, aromatic halide undergoes elimination –addition reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
In the case of a given aromatic halide, the elimination reaction is not favoured because an unstable carbanion is formed. A side chain substitution reaction (${{S}_{{{N}^{2}}}}$) is preferred over elimination which $H{{O}^{-}}$acts as a nucleophile. Primary carbon is more reactive than secondary carbon centres in ${{S}_{{{N}^{2}}}}$reaction. Compound (A) has a ${{1}^{{\mathrm O}}}$carbon centre, whereas in (B) has a ${{2}^{{\mathrm O}}}$ carbon centre. Hence (A) is more reactive than (B) under the given conditions.
Mechanism:

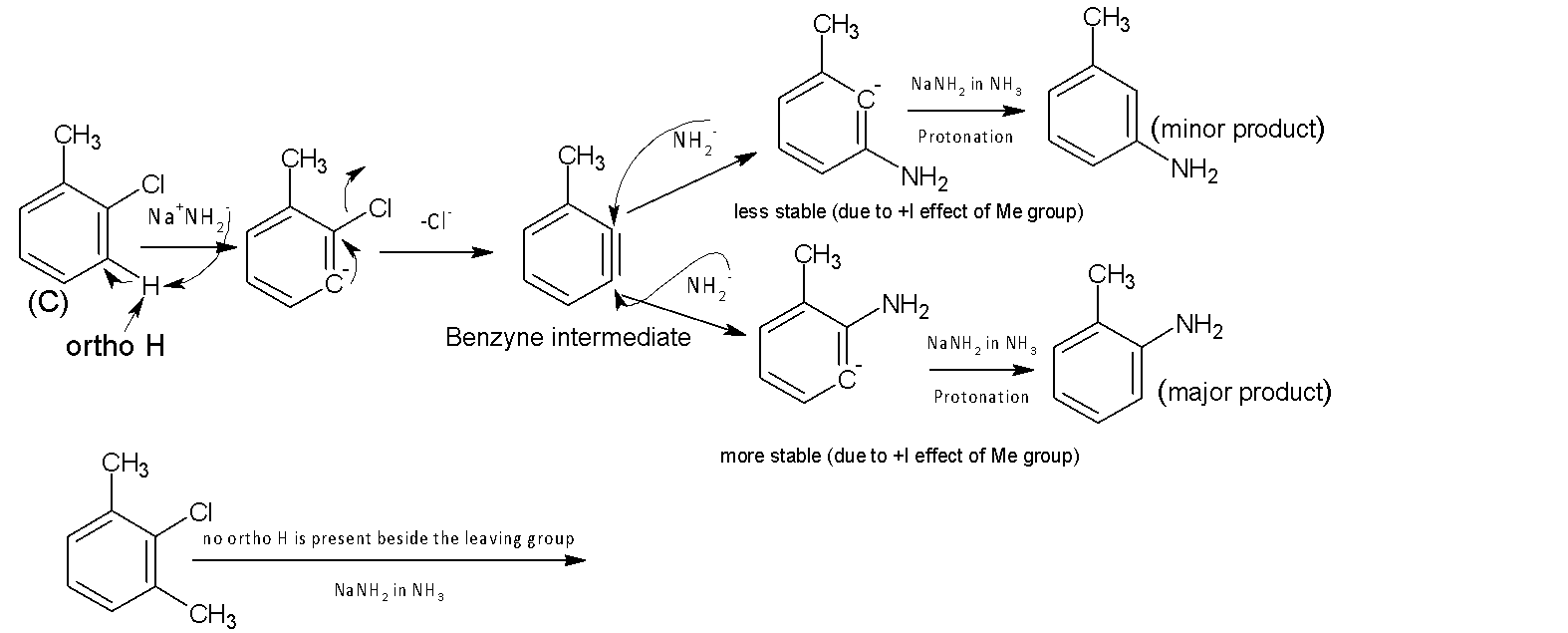
Under the given condition,$NaN{{H}_{2}}$in $N{{H}_{3}}$, compounds (C) undergo an elimination-addition reaction. The reaction starts with the removal of proton ortho to the leaving group $(C{{l}^{-}})$ by $NH_{2}^{-}$( strong base) followed by loss of $C{{l}^{-}}$. Thereby a very unstable benzyne intermediate is formed. In the next step, the corresponding intermediate is attacked by a nucleophile $NH_{2}^{-}$followed by protonation that produces the final product. There is no ortho hydrogen with respect to leaving the group $(C{{l}^{-}})$ in compound (D), so an elimination-addition reaction is not possible. Hence compound (c) is more reactive in elimination-addition reaction than (D) under given conditions.
Mechanism:
Thus, Option (A) is correct.
Note: Benzynes are very reactive and unstable intermediate. Like benzene, it is also an aromatic compound. It has a planar, cyclic and conjugated structure and contains $6\Pi $ electrons according to Huckel’s rule. It consists of one sigma and two pi bonds, where only one pi bond participates in conjugation and another pi bond is perpendicular to the first pi orbital.
Complete step by step solution:
In the case of a given aromatic halide, the elimination reaction is not favoured because an unstable carbanion is formed. A side chain substitution reaction (${{S}_{{{N}^{2}}}}$) is preferred over elimination which $H{{O}^{-}}$acts as a nucleophile. Primary carbon is more reactive than secondary carbon centres in ${{S}_{{{N}^{2}}}}$reaction. Compound (A) has a ${{1}^{{\mathrm O}}}$carbon centre, whereas in (B) has a ${{2}^{{\mathrm O}}}$ carbon centre. Hence (A) is more reactive than (B) under the given conditions.
Mechanism:

Under the given condition,$NaN{{H}_{2}}$in $N{{H}_{3}}$, compounds (C) undergo an elimination-addition reaction. The reaction starts with the removal of proton ortho to the leaving group $(C{{l}^{-}})$ by $NH_{2}^{-}$( strong base) followed by loss of $C{{l}^{-}}$. Thereby a very unstable benzyne intermediate is formed. In the next step, the corresponding intermediate is attacked by a nucleophile $NH_{2}^{-}$followed by protonation that produces the final product. There is no ortho hydrogen with respect to leaving the group $(C{{l}^{-}})$ in compound (D), so an elimination-addition reaction is not possible. Hence compound (c) is more reactive in elimination-addition reaction than (D) under given conditions.
Mechanism:

Thus, Option (A) is correct.
Note: Benzynes are very reactive and unstable intermediate. Like benzene, it is also an aromatic compound. It has a planar, cyclic and conjugated structure and contains $6\Pi $ electrons according to Huckel’s rule. It consists of one sigma and two pi bonds, where only one pi bond participates in conjugation and another pi bond is perpendicular to the first pi orbital.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




