
The temperature of the water of a pond is \[0{}^\circ C\] while that of the surrounding atmosphere is \[-20{}^\circ C\] . If the density of ice is \[\rho \] , the coefficient of thermal conductivity is \[\kappa \] and latent heat of melting is \[L\] then the thickness \[Z\] of the ice layer formed increases as a function of time \[t\] as:
(A) \[{{Z}^{2}}=\dfrac{60\kappa }{\rho L}t\]
(B) \[Z=\sqrt{\dfrac{40\kappa }{\rho L}t}\]
(C) \[{{Z}^{2}}=\dfrac{40\kappa }{\rho L}\sqrt{t}\]
(D) \[{{Z}^{2}}=\dfrac{40\kappa }{\rho L}t\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The heat required for the ice layer to be formed will be the latent heat of fusion and it will be provided by the surrounding atmosphere. Since ice formation always occurs in layers, we will begin our solution by taking a thin ice layer of a certain area. This area will be an effective area for heat transaction between the ice layer and the surroundings. Basically the ice will lose heat to the surrounding.
Formula Used:
\[Q=mL\]
\[\dfrac{Q}{t}=\dfrac{\kappa A({{T}_{2}}-{{T}_{1}})}{d}\]
Complete step by step answer:
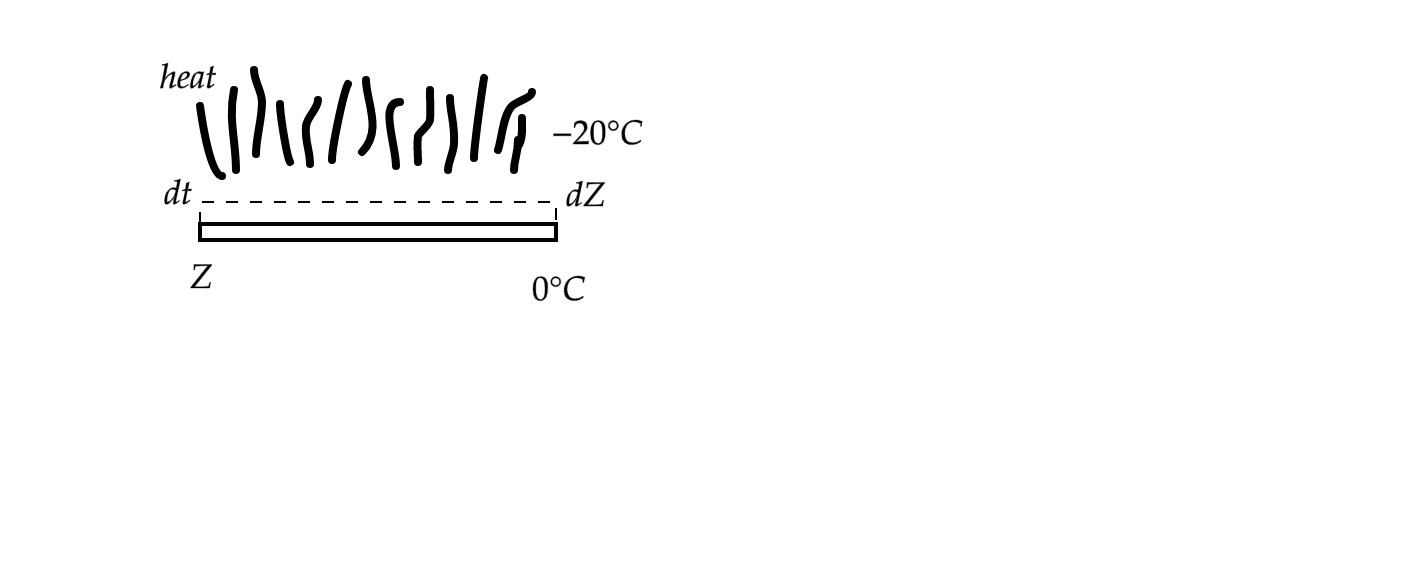
Let the thickness of the ice layer at \[t=0\] being \[Z\] and the effective area of heat exchange being \[A\]
In time \[dt\] , the thickness of the ice layer increases by \[dZ\] (say)
The heat required for ice layer formation is given as,
\[\begin{align}
& Q=mL \\
& \Rightarrow Q=(\rho \times V)\times L \\
& \Rightarrow Q=\rho \times (A\times dZ)\times L \\
\end{align}\]
Now, heat change in the surrounding is given as,
\[Q'=\dfrac{\kappa \times A\times \Delta T}{Z}dt\] where the other symbols have meanings as stated in the question and \[\Delta T\] are the temperature difference.
Since the heat change in the surrounding is the heat responsible for ice layer formation, we can say that \[Q=Q'\]
Substituting the values, we get \[\rho \times (A\times dZ)\times L=\dfrac{\kappa \times A\times \Delta T}{Z}dt\]
Since the area is a common factor on both sides, we can cancel it out.
Rearranging the terms, we get \[ZdZ=\dfrac{\kappa \Delta T}{\rho L}dt\]
The temperature difference between the ice layer and the surroundings \[(\Delta T)=0-(-20)=20{}^\circ C\]
Substituting the values in the expression, we get \[ZdZ=\dfrac{20\kappa }{\rho L}dt\]
Integrating both sides, we have
\[\begin{align}
& \int{ZdZ}=\int{\dfrac{20\kappa }{\rho L}dt} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{Z}^{2}}}{2}=\dfrac{20\kappa }{\rho L}t+c \\
& \Rightarrow {{Z}^{2}}=\dfrac{40\kappa }{\rho L}t+c \\
\end{align}\]
Since we just have to establish a relation between the thickness of the ice and the time, we can leave out the constant of integration and say that \[{{Z}^{2}}=\dfrac{40\kappa }{\rho L}t\] .
Hence option (D) is the correct answer.
Note: Sometimes we have to assume quantities which are not provided in the equation but are needed for our solution, for example, in this question, the effective surface area for heat exchange was not mentioned so we assumed it to have a certain value. Most of the time, these assumed values get cancelled at some step of the solution but if they don’t, they can easily be expressed in terms of quantities known to us.
Formula Used:
\[Q=mL\]
\[\dfrac{Q}{t}=\dfrac{\kappa A({{T}_{2}}-{{T}_{1}})}{d}\]
Complete step by step answer:

Let the thickness of the ice layer at \[t=0\] being \[Z\] and the effective area of heat exchange being \[A\]
In time \[dt\] , the thickness of the ice layer increases by \[dZ\] (say)
The heat required for ice layer formation is given as,
\[\begin{align}
& Q=mL \\
& \Rightarrow Q=(\rho \times V)\times L \\
& \Rightarrow Q=\rho \times (A\times dZ)\times L \\
\end{align}\]
Now, heat change in the surrounding is given as,
\[Q'=\dfrac{\kappa \times A\times \Delta T}{Z}dt\] where the other symbols have meanings as stated in the question and \[\Delta T\] are the temperature difference.
Since the heat change in the surrounding is the heat responsible for ice layer formation, we can say that \[Q=Q'\]
Substituting the values, we get \[\rho \times (A\times dZ)\times L=\dfrac{\kappa \times A\times \Delta T}{Z}dt\]
Since the area is a common factor on both sides, we can cancel it out.
Rearranging the terms, we get \[ZdZ=\dfrac{\kappa \Delta T}{\rho L}dt\]
The temperature difference between the ice layer and the surroundings \[(\Delta T)=0-(-20)=20{}^\circ C\]
Substituting the values in the expression, we get \[ZdZ=\dfrac{20\kappa }{\rho L}dt\]
Integrating both sides, we have
\[\begin{align}
& \int{ZdZ}=\int{\dfrac{20\kappa }{\rho L}dt} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{Z}^{2}}}{2}=\dfrac{20\kappa }{\rho L}t+c \\
& \Rightarrow {{Z}^{2}}=\dfrac{40\kappa }{\rho L}t+c \\
\end{align}\]
Since we just have to establish a relation between the thickness of the ice and the time, we can leave out the constant of integration and say that \[{{Z}^{2}}=\dfrac{40\kappa }{\rho L}t\] .
Hence option (D) is the correct answer.
Note: Sometimes we have to assume quantities which are not provided in the equation but are needed for our solution, for example, in this question, the effective surface area for heat exchange was not mentioned so we assumed it to have a certain value. Most of the time, these assumed values get cancelled at some step of the solution but if they don’t, they can easily be expressed in terms of quantities known to us.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




