
The shape of $PC{{l}_{3}}$ molecule is:
A. trigonal bipyramid
B. tetrahedral
C. pyramidal
D. square planar
Answer
240k+ views
Hint: $PC{{l}_{3}}$ is called phosphorus trichloride, which is formed from phosphorus and chlorine. It is actually a very toxic liquid which when reacted with water releases HCl gas. The hybridisation in $PC{{l}_{3}}$is $s{{p}^{3}}$.
Step by step solution:
- Now let’s write the electronic configuration of phosphorus,
The atomic number of phosphorus is 15, so we can write electronic configuration as –
\[1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{3}}\]
- Here, if we have to find the hybridisation, then it is equal to the sum of the number of sigma bonds and the number of lone pairs.
- Here, we can see that all bonds are of (P-Cl) type, we can see from the diagram drawn below that there are three P-Cl single bonds present, so the number of sigma bonds will be 3.
- And we can see here that there are 5 electrons present in valence shell that is $3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{3}}$, so ; two electrons are not participating in pairing , therefore the number of lone pairs will be equal to 1.
- So, we can say that hybridisation in $PC{{l}_{3}}$is $s{{p}^{3}}$.
- Structure of $PC{{l}_{3}}$ is:
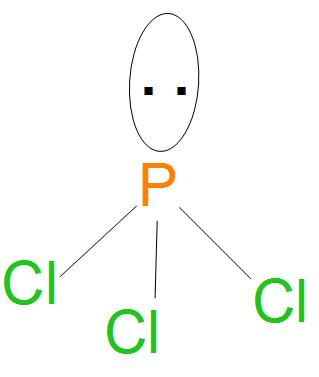
- Hence, from the structure and hybridisation of $PC{{l}_{3}}$ ,we can say that the geometry is pyramidal.
Additional information:
- $PC{{l}_{3}}$ is having a bond angle of approximately .
- $PC{{l}_{3}}$ is found to produce , which are used in many applications, including herbicides, insecticides etc.
- It is also found to be used directly as a reagent in organic synthesis, which is also used to convert many primary as well as secondary alcohols into alkyl chlorides.
Note:
We should not get confused in between $PC{{l}_{3}}$ and $PC{{l}_{5}}$. $PC{{l}_{3}}$ is phosphorus trichloride and is having pyramidal geometry, whereas $PC{{l}_{5}}$ is phosphorus pentachloride that has trigonal bipyramidal geometry.
Step by step solution:
- Now let’s write the electronic configuration of phosphorus,
The atomic number of phosphorus is 15, so we can write electronic configuration as –
\[1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{3}}\]
- Here, if we have to find the hybridisation, then it is equal to the sum of the number of sigma bonds and the number of lone pairs.
- Here, we can see that all bonds are of (P-Cl) type, we can see from the diagram drawn below that there are three P-Cl single bonds present, so the number of sigma bonds will be 3.
- And we can see here that there are 5 electrons present in valence shell that is $3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{3}}$, so ; two electrons are not participating in pairing , therefore the number of lone pairs will be equal to 1.
- So, we can say that hybridisation in $PC{{l}_{3}}$is $s{{p}^{3}}$.
- Structure of $PC{{l}_{3}}$ is:

- Hence, from the structure and hybridisation of $PC{{l}_{3}}$ ,we can say that the geometry is pyramidal.
Additional information:
- $PC{{l}_{3}}$ is having a bond angle of approximately .
- $PC{{l}_{3}}$ is found to produce , which are used in many applications, including herbicides, insecticides etc.
- It is also found to be used directly as a reagent in organic synthesis, which is also used to convert many primary as well as secondary alcohols into alkyl chlorides.
Note:
We should not get confused in between $PC{{l}_{3}}$ and $PC{{l}_{5}}$. $PC{{l}_{3}}$ is phosphorus trichloride and is having pyramidal geometry, whereas $PC{{l}_{5}}$ is phosphorus pentachloride that has trigonal bipyramidal geometry.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques - 2025-26




