
The points (2, 5) and (5, 1) are two opposite vertices of a rectangle. If the other two vertices are points on the straight line \[y = 2x + k\] , then find the value of k.
A. 4
B. 3
C. -4
D. -3
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hints First draw the rectangle with the stated information. Then obtain the mid-point of (2, 5) and (5, 1). The given line passes through the mid-point so, substitute the values of x and y as the obtained mid-point and obtain the value of k.
Formula used
The mid-point of a line with end vertices \[(a,b),(c,d)\] is \[\left( {\dfrac{{a + c}}{2},\dfrac{{b + d}}{2}} \right)\] .
Complete step by step solution
The diagram of the given problem is,
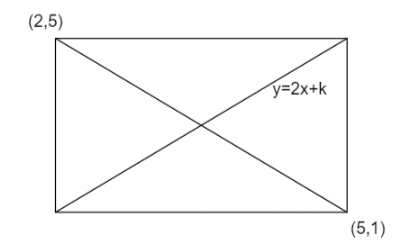
Image: Rectangle
The midpoint of the diagonal with vertices (2, 5) and (5, 1) is
\[\left( {\dfrac{{2 + 5}}{2},\dfrac{{5 + 1}}{2}} \right)\]
\[ = \left( {\dfrac{7}{2},3} \right)\]
From the diagram it is clear that the mid-point is on the given line.
Therefore,
\[3 = 2 \times \dfrac{7}{2} + k\]
\[3 = 7 + k\]
\[k = - 4\]
The correct option is C.
Additional information
The internal angles of a rectangle, which has four sides, are all exactly 90 degrees. At each corner or vertex, the two sides come together at a straight angle. The rectangle differs from a square because its two opposite sides are of equal length.
Note Students sometimes did not understand the fact the given line is the equation of the diagonal line as it is given as -the other two vertices are points of the line \[y = 2x + k\] . But the opposite vertices cannot be the points of a line other than the diagonal, it is clear from the given diagram.
Formula used
The mid-point of a line with end vertices \[(a,b),(c,d)\] is \[\left( {\dfrac{{a + c}}{2},\dfrac{{b + d}}{2}} \right)\] .
Complete step by step solution
The diagram of the given problem is,

Image: Rectangle
The midpoint of the diagonal with vertices (2, 5) and (5, 1) is
\[\left( {\dfrac{{2 + 5}}{2},\dfrac{{5 + 1}}{2}} \right)\]
\[ = \left( {\dfrac{7}{2},3} \right)\]
From the diagram it is clear that the mid-point is on the given line.
Therefore,
\[3 = 2 \times \dfrac{7}{2} + k\]
\[3 = 7 + k\]
\[k = - 4\]
The correct option is C.
Additional information
The internal angles of a rectangle, which has four sides, are all exactly 90 degrees. At each corner or vertex, the two sides come together at a straight angle. The rectangle differs from a square because its two opposite sides are of equal length.
Note Students sometimes did not understand the fact the given line is the equation of the diagonal line as it is given as -the other two vertices are points of the line \[y = 2x + k\] . But the opposite vertices cannot be the points of a line other than the diagonal, it is clear from the given diagram.
Recently Updated Pages
Area vs Volume: Key Differences Explained for Students

Mutually Exclusive vs Independent Events: Key Differences Explained

Square vs Rhombus: Key Differences Explained for Students

Power vs Exponent: Key Differences Explained for Students

Arithmetic Mean Formula Explained Simply

Algebraic Formula: Key Concepts & Easy Examples

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Jan 21 Shift 1 Question Papers with Solutions & Answer Keys – Detailed Day 1 Analysis

JEE Main Marks vs Percentile 2026: Calculate Percentile and Rank Using Marks

JEE Main 2026 Jan 22 Shift 1 Today Paper Live Analysis With Detailed Solutions

JEE Mains 2026 January 21 Shift 2 Question Paper with Solutions PDF - Complete Exam Analysis

JEE Main 2026 Jan 22 Shift 2 Today Paper Live Analysis With Detailed Solutions

Other Pages
Pregnancy Week and Due Date Calculator: Find How Far Along You Are

NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 11 Areas Related to Circles (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes (2025-26)

All Mensuration Formulas with Examples and Quick Revision

Complete List of Class 10 Maths Formulas (Chapterwise)

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Statistics




