
The pans of a physical balance are in equilibrium. Air is blown under the right hand pan, then the right hand pan will:
A. move up
B. move down
C. move erratically
D. remains at the same level
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: To keep the physical balance at equilibrium, the horizontal rod must be in horizontal position, i.e. net torque acting about the balancing point should be zero.
Complete step by step solution:
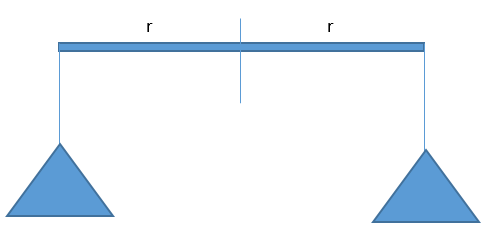
Image: The pans of a physical balance
When the pans of the physical balance is at equilibrium the net torque acting about the point of balance is zero. When the air is blown under the right hand pan then using Bernoulli’s theorem, the pressure above the right hand pan is greater than the pressure under the right hand pan. There is a pressure difference between the upper and lower part of the right hand pan.
Let the pressure difference is \[\Delta P\] and the area of the pan is A. Then the extra unbalancing force acting on the right hand pan is,
\[F = \left( {\Delta P} \right)A\]
Using the formula of torque, the distance between the balancing point and the point of application of force is r.
Then the torque applied due to extra unbalancing force about the balancing point is,
\[\tau = \left( {\Delta P} \right)Ar\]
The direction of the torque is clockwise, i.e. the right hand pan will move down and the left hand pan will move up. Hence, when air is blown under the right hand pan then the right hand pan move down.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: To keep the body at equilibrium the net force acting on the body must be zero. Also, the net moment of the forces about any point on the body must be zero. At static condition the pressure difference due to air is negligible with respect to the width of the pan’s horizontal dimension, so the net force acting on both the pans in upward direction is balanced by the force acting downward.
Complete step by step solution:

Image: The pans of a physical balance
When the pans of the physical balance is at equilibrium the net torque acting about the point of balance is zero. When the air is blown under the right hand pan then using Bernoulli’s theorem, the pressure above the right hand pan is greater than the pressure under the right hand pan. There is a pressure difference between the upper and lower part of the right hand pan.
Let the pressure difference is \[\Delta P\] and the area of the pan is A. Then the extra unbalancing force acting on the right hand pan is,
\[F = \left( {\Delta P} \right)A\]
Using the formula of torque, the distance between the balancing point and the point of application of force is r.
Then the torque applied due to extra unbalancing force about the balancing point is,
\[\tau = \left( {\Delta P} \right)Ar\]
The direction of the torque is clockwise, i.e. the right hand pan will move down and the left hand pan will move up. Hence, when air is blown under the right hand pan then the right hand pan move down.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: To keep the body at equilibrium the net force acting on the body must be zero. Also, the net moment of the forces about any point on the body must be zero. At static condition the pressure difference due to air is negligible with respect to the width of the pan’s horizontal dimension, so the net force acting on both the pans in upward direction is balanced by the force acting downward.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Fluids (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Law of Motion (2025-26)

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




