
The number of unpaired electrons in the p-subshell of VI A or $n{{s}^{2}}n{{p}^{4}}$ ${{16}^{th}}$ group of the periodic table is :
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The general electronic configuration of the ${{16}^{th}}$ group element is $n{{s}^{2}}n{{p}^{4}}$. By drawing the electronic configuration diagram and filling up the respective number of electrons in the s and p subshell by using Hund’s Rule, Aufbau principle etc. . We can count the number of unpaired electrons in the p – subshell.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electronic configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule in atomic or molecular orbitals. To calculate an electronic configuration , divide the periodic table into sections to represent the atomic orbitals, the regions where electrons are contained.
An S-block can hold a maximum of two electrons in it . In p-block a maximum of 6 electrons can be placed. Similarly in d- block maximum of 10 electrons can be placed . Now we has been provided with the group number of the element as group 16 , and so in its outer valence orbitals there would be 6 electrons in it. Therefore , the electronic configuration can be written as $n{{s}^{2}}n{{p}^{4}}$ as the sum of electrons in this valence orbitals will be calculated 2+4=6. Now, representing the electronic configuration of this group we have,
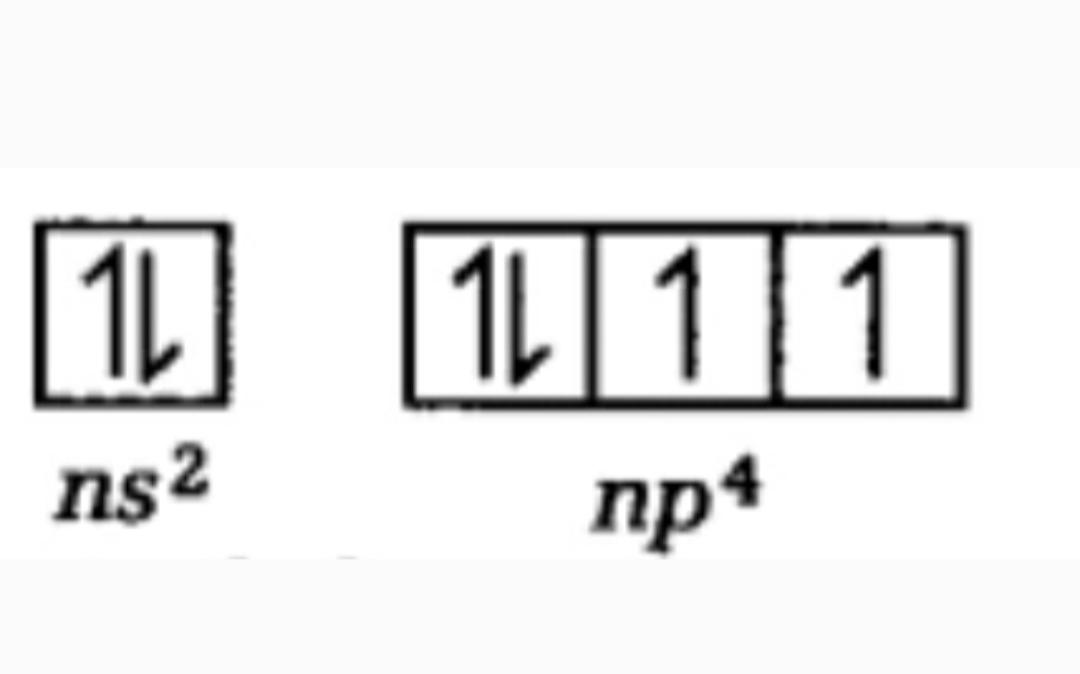
Thus, the number of unpaired electrons in the p subshell is 2.
And thus , the correct answer is option B.
Note: While representing the electrons in the p subshell the rules for electronic configuration representation should be taken in care as sometimes , students represent four electrons of p- subshell as 2 electron pairs but it will not be considered as correct as Hund’s rule and Aufbau principle are violated in this case. So firstly all the boxes need to be half –filled after that fully filling it.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electronic configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule in atomic or molecular orbitals. To calculate an electronic configuration , divide the periodic table into sections to represent the atomic orbitals, the regions where electrons are contained.
An S-block can hold a maximum of two electrons in it . In p-block a maximum of 6 electrons can be placed. Similarly in d- block maximum of 10 electrons can be placed . Now we has been provided with the group number of the element as group 16 , and so in its outer valence orbitals there would be 6 electrons in it. Therefore , the electronic configuration can be written as $n{{s}^{2}}n{{p}^{4}}$ as the sum of electrons in this valence orbitals will be calculated 2+4=6. Now, representing the electronic configuration of this group we have,

Thus, the number of unpaired electrons in the p subshell is 2.
And thus , the correct answer is option B.
Note: While representing the electrons in the p subshell the rules for electronic configuration representation should be taken in care as sometimes , students represent four electrons of p- subshell as 2 electron pairs but it will not be considered as correct as Hund’s rule and Aufbau principle are violated in this case. So firstly all the boxes need to be half –filled after that fully filling it.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




