
The number of oxygen atoms in an acetamide molecule is
A.$1$
B.$2$
C.$3$
D.$4$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Acetamide is an organic compound that is a colorless hygroscopic solid. Acetamide is the simplest amide of acetic acid also named Acetimidic acid or ethionamide. Therefore to find how many oxygen atoms are present in it, we will have to know about the chemical formula and the structure of acetamide.
Complete answer:Acetamide has mainly originated from acetic acid and the chemical formula of acetamide is ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}NO$. The structure of acetamide consists of a methyl group ($-C{{H}_{3}}$) that is attached to amine ($-N{{H}_{2}}$) and a carbonyl group ($C=O$). The structure of acetamide is given below:
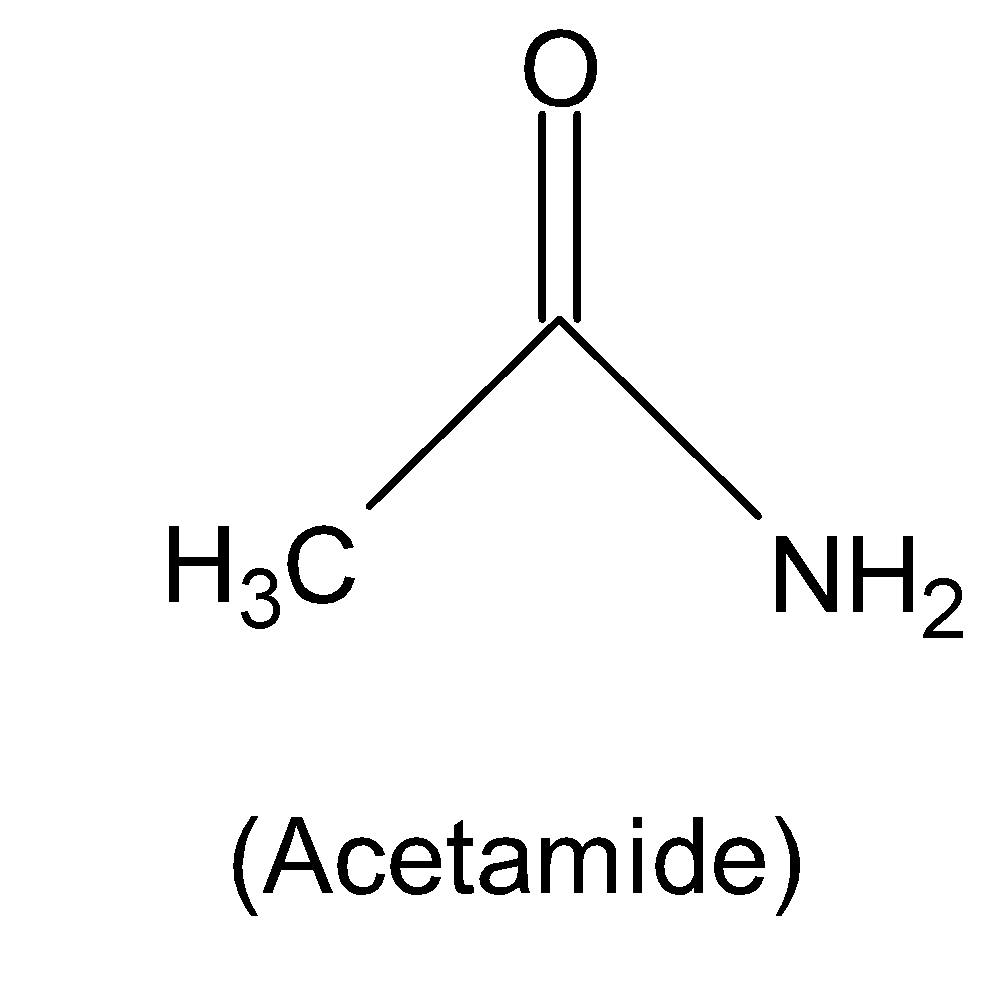
Therefore from the structure of acetamide, we can see that there is only one oxygen and one nitrogen atom present in it.
Thus, option (A) is correct.
Additional information:
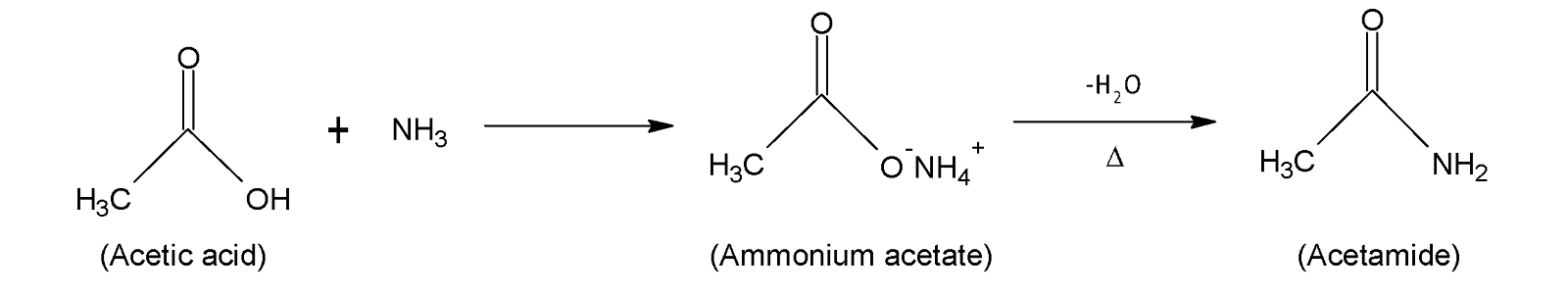
This organic compound belongs to the family of primary carboxylic acid amides that are formed from the formal condensation of ammonia ($-N{{H}_{3}}$) and acetic acid ($C{{H}_{3}}COOH$). At first ammonia solution reacts with glacial acetic acid producing ammonium acetate ($C{{H}_{3}}COON{{H}_{4}}$) which on heating gives ethionamide or acetamide ($C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}$).
Acetamide can also be prepared from partial hydrolysis of acetonitrile ($C{{H}_{3}}CN$) and dry concentrated hydrogen chloride ($HCl$) but on complete hydrolysis carboxylic acid is produced.
Note: As acetamide is formed from a carboxylic acid called acetic acid that’s why it is slightly acidic. It can be used as a solvent for many organic and inorganic chemical reactions. Also, acetamide is used in explosives, stabilizers, plasticizers, and soldering fluxes.
Complete answer:Acetamide has mainly originated from acetic acid and the chemical formula of acetamide is ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}NO$. The structure of acetamide consists of a methyl group ($-C{{H}_{3}}$) that is attached to amine ($-N{{H}_{2}}$) and a carbonyl group ($C=O$). The structure of acetamide is given below:

Therefore from the structure of acetamide, we can see that there is only one oxygen and one nitrogen atom present in it.
Thus, option (A) is correct.
Additional information:
This organic compound belongs to the family of primary carboxylic acid amides that are formed from the formal condensation of ammonia ($-N{{H}_{3}}$) and acetic acid ($C{{H}_{3}}COOH$). At first ammonia solution reacts with glacial acetic acid producing ammonium acetate ($C{{H}_{3}}COON{{H}_{4}}$) which on heating gives ethionamide or acetamide ($C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}$).

Acetamide can also be prepared from partial hydrolysis of acetonitrile ($C{{H}_{3}}CN$) and dry concentrated hydrogen chloride ($HCl$) but on complete hydrolysis carboxylic acid is produced.
Note: As acetamide is formed from a carboxylic acid called acetic acid that’s why it is slightly acidic. It can be used as a solvent for many organic and inorganic chemical reactions. Also, acetamide is used in explosives, stabilizers, plasticizers, and soldering fluxes.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




