
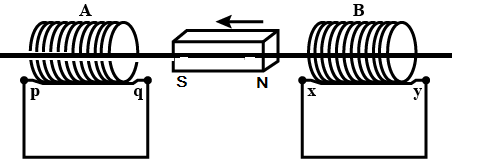
The direction of induced current in the coils A and B in the situation shown in the figure is then:
A) p to q in coil A and x to y in coil B
B) q to p in coil A and x to y in coil B
C) p to q in coil A and y to x in coil B
D) q to p in coil A and y to x in coil B
Answer
239.1k+ views
Hint: A current can be induced in a current loop if it is exposed to a changing magnetic field. Induced current always opposes the cause of it according to Lenz's law.
Complete step by step solution: The direction of the current can be determined by considering Lenz's law, which states that an induced electric current will flow in such a way that it creates a magnetic field that resists change in the field it produces. In other words, if the applied magnetic field continues to increase, the current flowing in the wire will flow in such a way that the magnetic field generated around the wire will decrease the applied magnetic field.
Here in the given figure In coil A, the south pole develops in Q and in coil B also the south pole develops in X. Thus, the current flowing in coil A will be from Q to P and the current flowing in coil B will be from x to y.
Additional Information: In 1831, Michael Faraday conducted several experiments in an attempt to prove that electricity could be produced by magnetism. Within a few weeks, the great experimenter not only explicitly demonstrated this phenomenon, now known as electromagnetic induction.
Note: A current can be induced in conducting loop,If it comes in contact with a changed magnetic field, This change can happen in a variety of ways; You can change the strength of the magnetic field, move the conductor in and out of the field, change the distance between the magnet and the conductor, or change the field of the loop located in a constant magnetic field. Considering how the variant is obtained, the result, the transmitted current, is the same.
Complete step by step solution: The direction of the current can be determined by considering Lenz's law, which states that an induced electric current will flow in such a way that it creates a magnetic field that resists change in the field it produces. In other words, if the applied magnetic field continues to increase, the current flowing in the wire will flow in such a way that the magnetic field generated around the wire will decrease the applied magnetic field.
Here in the given figure In coil A, the south pole develops in Q and in coil B also the south pole develops in X. Thus, the current flowing in coil A will be from Q to P and the current flowing in coil B will be from x to y.
Additional Information: In 1831, Michael Faraday conducted several experiments in an attempt to prove that electricity could be produced by magnetism. Within a few weeks, the great experimenter not only explicitly demonstrated this phenomenon, now known as electromagnetic induction.
Note: A current can be induced in conducting loop,If it comes in contact with a changed magnetic field, This change can happen in a variety of ways; You can change the strength of the magnetic field, move the conductor in and out of the field, change the distance between the magnet and the conductor, or change the field of the loop located in a constant magnetic field. Considering how the variant is obtained, the result, the transmitted current, is the same.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Step-by-Step Guide to Young’s Double Slit Experiment Derivation

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Common Ion Effect: Concept, Applications, and Problem-Solving

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Essential Derivations for CBSE Class 12 Physics: Stepwise & PDF Solutions

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis




