
The diagram shows the pattern of the oil dripping on the road, at a constant rate from a moving car.
Which of the following statements is correct?
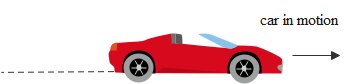
(A) The car moves initially with a constant speed and then slows down
(B) The car accelerates initially and then moves with a constant speed
(C) The car starts from rest and keeps accelerating
(D) The car moves with a constant speed all along
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint We know that in mechanics, acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Accelerations are vector quantities (in that they have magnitude and direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by the orientation of the net force acting on that object. Again, acceleration is in the same direction as the change in velocity, which is negative here. This acceleration can be called a deceleration because it has a direction opposite to the velocity.
Complete step-by step answer
We know that Newton's second law of motion can be formally stated as follows: The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
Initially, the drops are at uniform separation. The rate of dripping being constant, the motion. Then with a constant speed.
Later on, the spacing between the drops keeps decreasing. This means within the same time interval the car covers a lesser distance as the time progresses.
So, later the car slows down.
Hence, the correct answer is Option A.
Note: We know that Newton’s first law states that every object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless compelled to change its state by the action of an external force. This is normally taken as the definition of inertia. In the third law, when two objects interact, they apply forces to each other of equal magnitude and opposite direction.
However, we should know that it is common to use acceleration to mean speeding up and the word deceleration to mean slowing down. Strictly speaking, however, acceleration describes both types of motion. Speeding up might be referred to as positive acceleration and slowing down as negative acceleration.
Complete step-by step answer
We know that Newton's second law of motion can be formally stated as follows: The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
Initially, the drops are at uniform separation. The rate of dripping being constant, the motion. Then with a constant speed.
Later on, the spacing between the drops keeps decreasing. This means within the same time interval the car covers a lesser distance as the time progresses.
So, later the car slows down.
Hence, the correct answer is Option A.
Note: We know that Newton’s first law states that every object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless compelled to change its state by the action of an external force. This is normally taken as the definition of inertia. In the third law, when two objects interact, they apply forces to each other of equal magnitude and opposite direction.
However, we should know that it is common to use acceleration to mean speeding up and the word deceleration to mean slowing down. Strictly speaking, however, acceleration describes both types of motion. Speeding up might be referred to as positive acceleration and slowing down as negative acceleration.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




