
The correct statement is (are):
Consider the following reaction
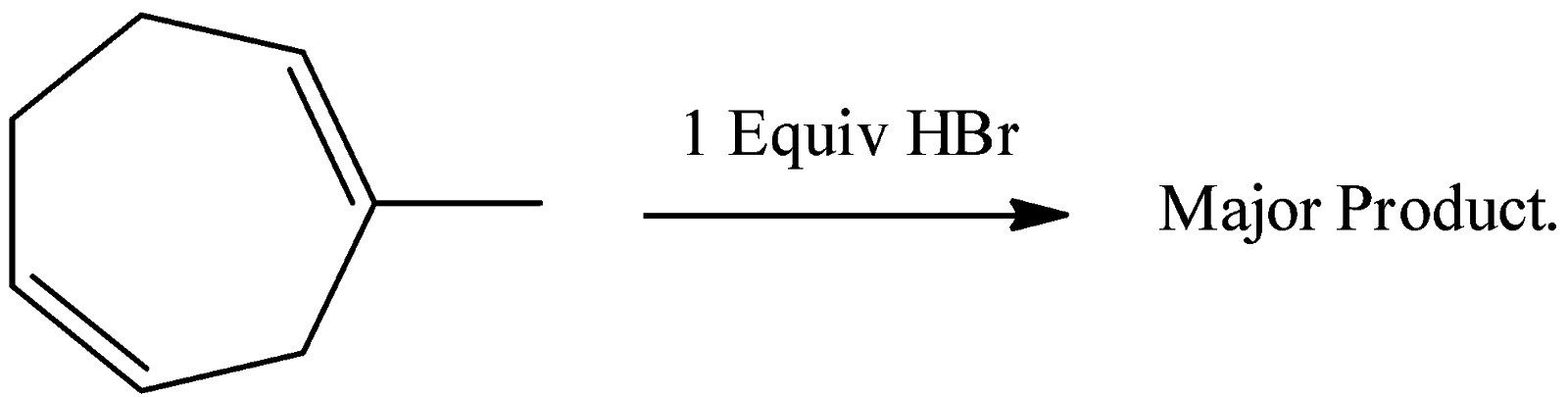
A. the major product is a racemic mixture of
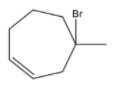
B. the major product is
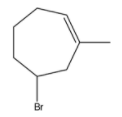
C. If reaction occurs in presence of ROOR, 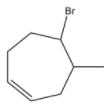
is formed as a major product.
D. Reaction involves rearrangement of free radical intermediate.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The reaction of hydroamination with alkenes will generate a carbocation as an intermediate by the addition of hydrogen cation to one of the double bonds present in the given alkene compound. Hydrobromination of alkenes follows Markonikov’s rule.
Complete step by step solution:
-The name of the given compound in the question is methyl heptadiene.
-The structure of the compound is as follows.
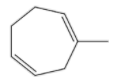
-Now we have to check which product is going to form when methyl heptadiene reacts with hydrogen bromide (HBr).
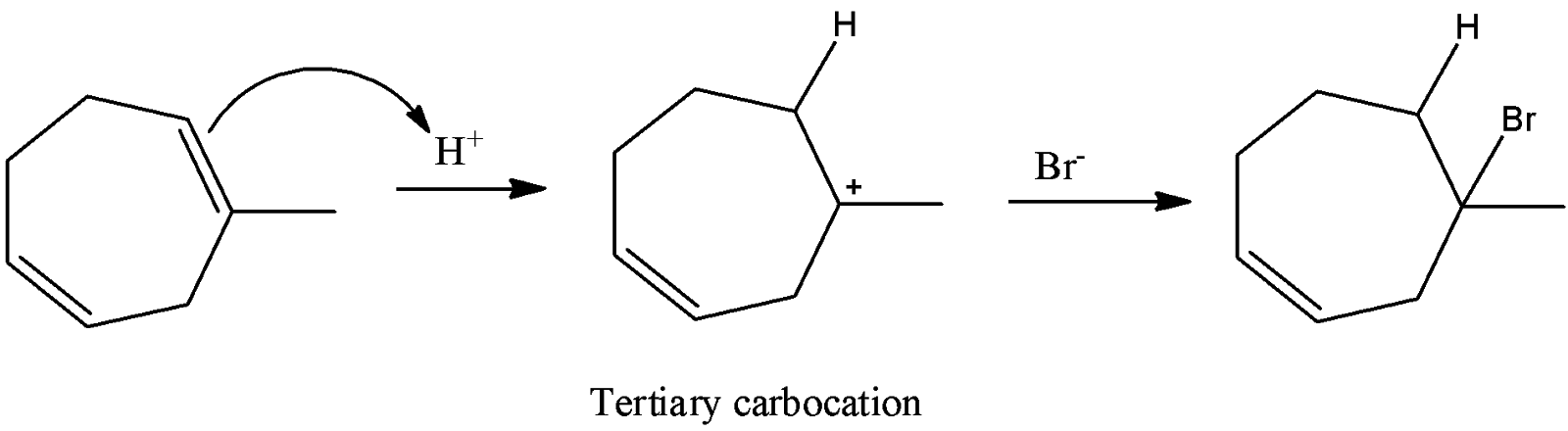
-Methyl heptadiene reacts with H+ ion in the first step and forms a tertiary carbocation due to high stability of the tertiary carbocation through Markonikov’s rule.
-Later the formed tertiary carbocation reacts with bromide ion and forms a racemic mixture of the respective bromide derivative.
-Therefore option A is correct.
- If the double bonds present in conjugation in heptadiene then there is a chance of the formation of the product in option B. So, option B is wrong.
-Coming to option C, If a reaction occurs in presence of ROOR.
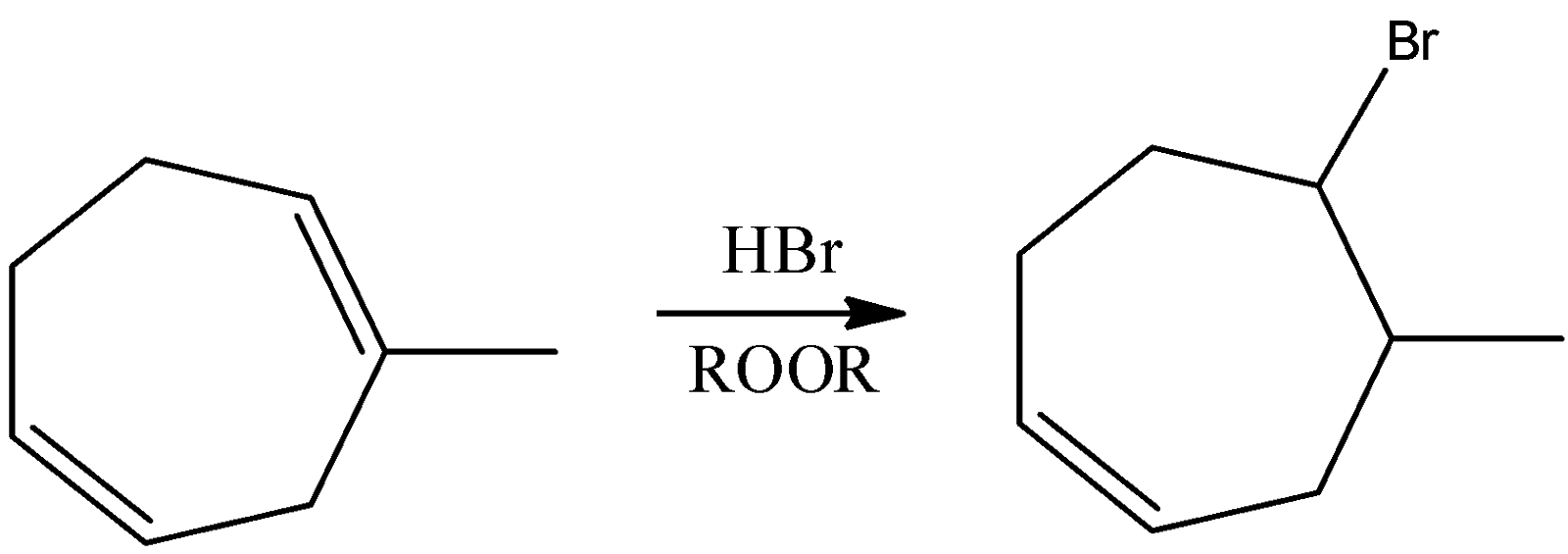
-Due to the presence of ROOR (Peroxide) then the hydroamination proceeds through Anti-Markovnikov's rule and forms a product where Bromine is going to attach to the carbon where more number of hydrogens is present.
-Therefore option C is also correct.
-Coming to option D, Reaction involves rearrangement of free radical intermediate. In the absence of peroxides, the reaction is going to complete without the involvement of the free radicals. Then option D is wrong.
So, the correct options are A and C.
Note: If Hydrobromination is proceeding without the involvement of peroxide then the reaction proceeds through the formation of tertiary carbocation as the intermediate (Markonikov’s rule). If there is a presence of peroxide then the reaction proceeds through Anti-Markovnikov's rule (less substituted product is going to form).
Complete step by step solution:
-The name of the given compound in the question is methyl heptadiene.
-The structure of the compound is as follows.

-Now we have to check which product is going to form when methyl heptadiene reacts with hydrogen bromide (HBr).

-Methyl heptadiene reacts with H+ ion in the first step and forms a tertiary carbocation due to high stability of the tertiary carbocation through Markonikov’s rule.
-Later the formed tertiary carbocation reacts with bromide ion and forms a racemic mixture of the respective bromide derivative.
-Therefore option A is correct.
- If the double bonds present in conjugation in heptadiene then there is a chance of the formation of the product in option B. So, option B is wrong.
-Coming to option C, If a reaction occurs in presence of ROOR.

-Due to the presence of ROOR (Peroxide) then the hydroamination proceeds through Anti-Markovnikov's rule and forms a product where Bromine is going to attach to the carbon where more number of hydrogens is present.
-Therefore option C is also correct.
-Coming to option D, Reaction involves rearrangement of free radical intermediate. In the absence of peroxides, the reaction is going to complete without the involvement of the free radicals. Then option D is wrong.
So, the correct options are A and C.
Note: If Hydrobromination is proceeding without the involvement of peroxide then the reaction proceeds through the formation of tertiary carbocation as the intermediate (Markonikov’s rule). If there is a presence of peroxide then the reaction proceeds through Anti-Markovnikov's rule (less substituted product is going to form).
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




