
The compound of xenon with zero dipole moment is:
A. \[XeO{F_4}\]
B. \[Xe{O_2}\]
C. \[Xe{O_3}\]
D. \[Xe{F_4}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The zero dipole moment of a compound has symmetrical geometry and also has similar atoms with less distance between the charge separation.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
1. The dipole moment is the product of the magnitude of charge and the distance between the centre of the positive and negative charge.
2. It is expressed as:
\[\mu = Q \times r\]
Where, \[\mu \] =dipole moment
\[Q\] =charge
\[r\] =separation distance
3. The dipole moment is a vector quantity that is depicted on a Lewis structure as a crossed arrow.
4. A cross appears on the positive end while an arrowhead appears on the negative end.
5. The valence electrons of the xenon are eight and the valence electrons of the Fluoride are seven so the total valence electrons of the compound are thirty-six.
6. There are a total of two lone pairs on the xenon and it is attached to the four Fluoride atoms through the bond pairs.
7. The geometry of the xenon tetrafluoride is square planar with a symmetrical structure with an angle of \[{90^ \circ }\].
8. The zero dipole moment of the compound is defined as the two equal bond dipoles that point in the opposite directions and cancel the effect of each other.
9. The individual bond dipoles cancel out and leave the molecule as a nonpolar so there is no net dipole moment.
10. The Lewis dot structure of the xenon tetrafluoride is represented below:
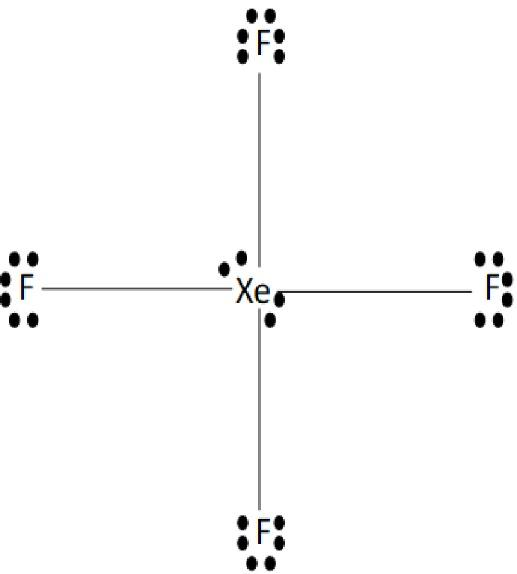
Image: Xenon tetrafluoride
Option (D) is correct.
Additional information:
1. When the same forces of energy are applied at an angle of \[{90^ \circ }\], there is no movement.
2. The direction of the dipole moment is from a less electronegative atom to a more electronegative atom.
Note: The dipole moment arrow represents the direction of the shift of electron density in the molecule with the direction of the crossed arrow opposite the conventional direction of the dipole moment vector.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
1. The dipole moment is the product of the magnitude of charge and the distance between the centre of the positive and negative charge.
2. It is expressed as:
\[\mu = Q \times r\]
Where, \[\mu \] =dipole moment
\[Q\] =charge
\[r\] =separation distance
3. The dipole moment is a vector quantity that is depicted on a Lewis structure as a crossed arrow.
4. A cross appears on the positive end while an arrowhead appears on the negative end.
5. The valence electrons of the xenon are eight and the valence electrons of the Fluoride are seven so the total valence electrons of the compound are thirty-six.
6. There are a total of two lone pairs on the xenon and it is attached to the four Fluoride atoms through the bond pairs.
7. The geometry of the xenon tetrafluoride is square planar with a symmetrical structure with an angle of \[{90^ \circ }\].
8. The zero dipole moment of the compound is defined as the two equal bond dipoles that point in the opposite directions and cancel the effect of each other.
9. The individual bond dipoles cancel out and leave the molecule as a nonpolar so there is no net dipole moment.
10. The Lewis dot structure of the xenon tetrafluoride is represented below:

Image: Xenon tetrafluoride
Option (D) is correct.
Additional information:
1. When the same forces of energy are applied at an angle of \[{90^ \circ }\], there is no movement.
2. The direction of the dipole moment is from a less electronegative atom to a more electronegative atom.
Note: The dipole moment arrow represents the direction of the shift of electron density in the molecule with the direction of the crossed arrow opposite the conventional direction of the dipole moment vector.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




