
Soaps are sodium salts of which of the following?
A. Mineral acids
B. Fatty acids
C. Lactic acids
D. Carbonic acids
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: A soap molecule contains a long chain hydrocarbon which is the tail part and a carboxylate which is a head. When soap is dissolved in water, the sodium and potassium ion freely floats and the negative head is left behind.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Soap is a sodium and potassium salt of long chain fatty acids which are used as a cleaning agent and as a lubricant. The soap formation is done by treating triglycerides with an alkaline solution, for example sodium hydroxide. The animal fats and oil of vegetables are basically triglycerides. This reaction is known as the saponification reaction.
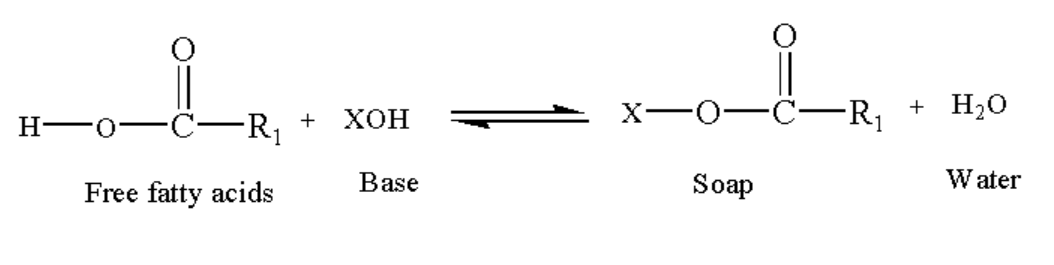
Image: Saponification reaction
The cleansing action of soap is explained by the interaction polar carboxyl group and the nonpolar hydrocarbon chain. The long hydrocarbon chain is a hydrophobic part (water repellent) and the carboxylate head is a hydrophilic part (water loving).
Grease and dirt are non-polar hydrocarbons. When they are dissolved in water, the hydrocarbon tail which is non-polar in nature dissolves in oil and the polar carboxylate head is towards the water. This results in the formation of micelle and dirt gets removed.
When soap is mixed with hard water, the soap is precipitated by the calcium or magnesium ions available in hard water.
Therefore, soaps are sodium salts of fatty acids. Hence, option B is correct.
Note: Soap and detergents both are used as cleansing agents but both are different from each other. Soap is prepared from natural components like fatty acids whereas the detergents are synthetically manufactured.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Soap is a sodium and potassium salt of long chain fatty acids which are used as a cleaning agent and as a lubricant. The soap formation is done by treating triglycerides with an alkaline solution, for example sodium hydroxide. The animal fats and oil of vegetables are basically triglycerides. This reaction is known as the saponification reaction.
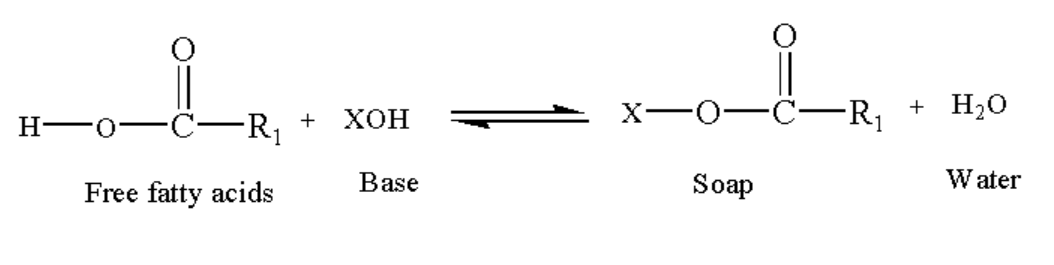
Image: Saponification reaction
The cleansing action of soap is explained by the interaction polar carboxyl group and the nonpolar hydrocarbon chain. The long hydrocarbon chain is a hydrophobic part (water repellent) and the carboxylate head is a hydrophilic part (water loving).
Grease and dirt are non-polar hydrocarbons. When they are dissolved in water, the hydrocarbon tail which is non-polar in nature dissolves in oil and the polar carboxylate head is towards the water. This results in the formation of micelle and dirt gets removed.
When soap is mixed with hard water, the soap is precipitated by the calcium or magnesium ions available in hard water.
Therefore, soaps are sodium salts of fatty acids. Hence, option B is correct.
Note: Soap and detergents both are used as cleansing agents but both are different from each other. Soap is prepared from natural components like fatty acids whereas the detergents are synthetically manufactured.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




