
What sequence of reactions would best accomplish the following reaction?
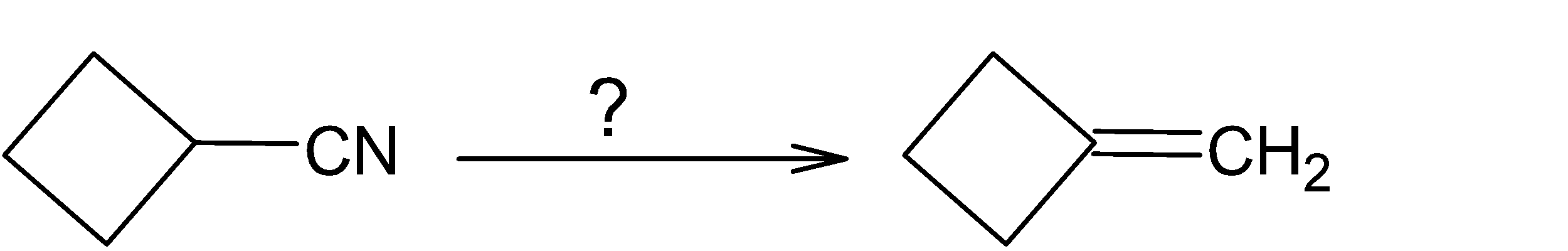
A. (i) $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ in ether; (ii) ${{P}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}$ and heat.
B. (i) $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ in ether; (ii) $3C{{H}_{3}}I$ followed by heating with AgOH.
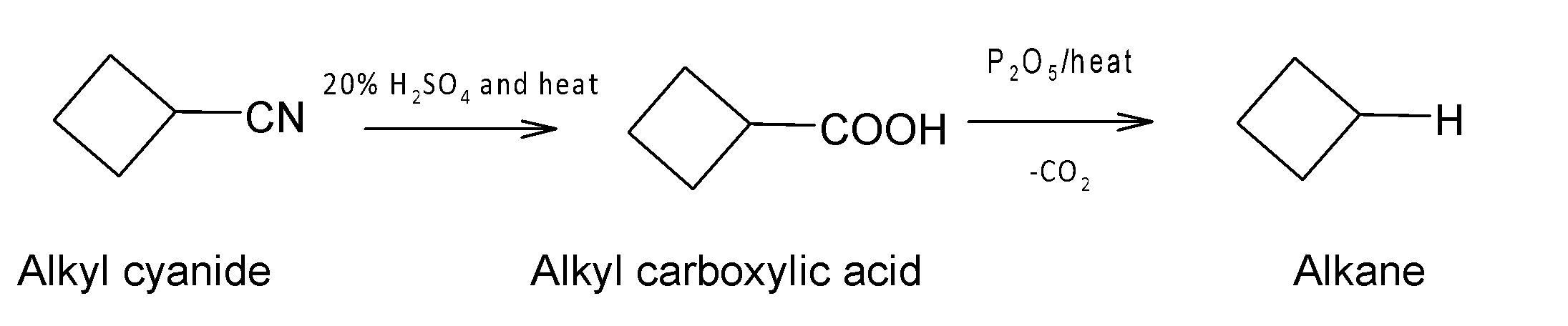
C. (i) $20%{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ and heat; (ii) ${{P}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}$ and heat.
D. ${{H}_{2}}$ and Lindlar catalyst.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Alkyl cyanide can not be converted into alkene by a single step, more than one step is involved. Therefore different reagents are used in this regard. One simple method to solve this problem is to apply the different reagents given in the option, only then we can reach that particular pathway.
Complete step by step solution:
Putting the reagents in the given alkyl cyanide one by one:
(i) Alkyl cyanide compound forms alkyl amine with $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$in ether and presence of ${{P}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}$ heat, alkenes are not formed.
(ii) Here also alkyl amine is formed at the first step. Under the presence of $C{{H}_{3}}I$ AgOH Hoffmann elimination reaction occurs. It is the process of forming tertiary amine and alkenes from the treatment of quaternary ammonium ions with excess $C{{H}_{3}}I$ followed by treating silver oxide, water, and heat. If the alkyl groups contain beta hydrogens, then elimination occurs. Finally, we get the desired product.

(iii) Under the condition $20%{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$and heat a carboxylic acid is formed followed by decarboxylation with the removal of carbon dioxide in the next step.
(iv) ${{H}_{2}}$and Lindlar catalyst can reduce only internal alkyne into cis alkenes but not reduce alkyl cyanide. Therefore, option B is a suitable pathway to synthesize the given alkene.
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: To approach this type of synthesis reaction, one should remember some important reagents and name reactions that will help to guess the product without any broad mechanism. Also, the basic idea of general organic chemistry is mandatory such as inductive effect, acidity, basicity hyperconjugation, resonance, electrophiles, and nucleophiles.
Complete step by step solution:
Putting the reagents in the given alkyl cyanide one by one:
(i) Alkyl cyanide compound forms alkyl amine with $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$in ether and presence of ${{P}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}$ heat, alkenes are not formed.
(ii) Here also alkyl amine is formed at the first step. Under the presence of $C{{H}_{3}}I$ AgOH Hoffmann elimination reaction occurs. It is the process of forming tertiary amine and alkenes from the treatment of quaternary ammonium ions with excess $C{{H}_{3}}I$ followed by treating silver oxide, water, and heat. If the alkyl groups contain beta hydrogens, then elimination occurs. Finally, we get the desired product.

(iii) Under the condition $20%{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$and heat a carboxylic acid is formed followed by decarboxylation with the removal of carbon dioxide in the next step.

(iv) ${{H}_{2}}$and Lindlar catalyst can reduce only internal alkyne into cis alkenes but not reduce alkyl cyanide. Therefore, option B is a suitable pathway to synthesize the given alkene.
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: To approach this type of synthesis reaction, one should remember some important reagents and name reactions that will help to guess the product without any broad mechanism. Also, the basic idea of general organic chemistry is mandatory such as inductive effect, acidity, basicity hyperconjugation, resonance, electrophiles, and nucleophiles.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




