
\[{\rm{Xe}}{{\rm{F}}_{\rm{2}}}\] molecule is
A) Square planar
B) Trigonal bipyramidal
C) Trigonal planar
D) Linear
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We know that xenon forms compounds with smaller electronegative atoms like fluorine and oxygen. Some of the compounds of xenon are \[{\rm{Xe}}{{\rm{F}}_{\rm{2}}}\], \[{\rm{Xe}}{{\rm{F}}_4}\], \[{\rm{Xe}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}}\] etc. Here, we have to identify the shape of \[{\rm{Xe}}{{\rm{F}}_{\rm{2}}}\].
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Let's understand the hybridization of \[{\rm{Xe}}{{\rm{F}}_{\rm{2}}}\]. The configuration of xenon at the ground state is \[5{s^2}5{p^6}\] . The configuration of xenon changes to \[5{s^2}5{p^5}5{d^1}\]at the excited state. Thus, excited state configuration of xenon, that is, \[5s,5{p^y},5{p^x},5{p^z},5{d^z}\] undergoes hybridization to form 5 \[s{p^3}d\] orbitals. Therefore, xenon difluoride has a hybridization of \[s{p^3}d\].
Let's discuss the structure of xenon difluoride. The formation of two sigma bonds F-Xe-F occurs due to the overlap of two half-filled orbitals of fluorine atoms. The three atomic orbitals which contain lone pairs have no participation in bonding. So, the molecule has two bond pairs and three numbers of lone pairs surrounding it. So, the geometry of the molecule is linear in nature. The shape is such that the positions of lone pairs are in equatorial positions. And the measure of the bond angle is \[180^\circ \].
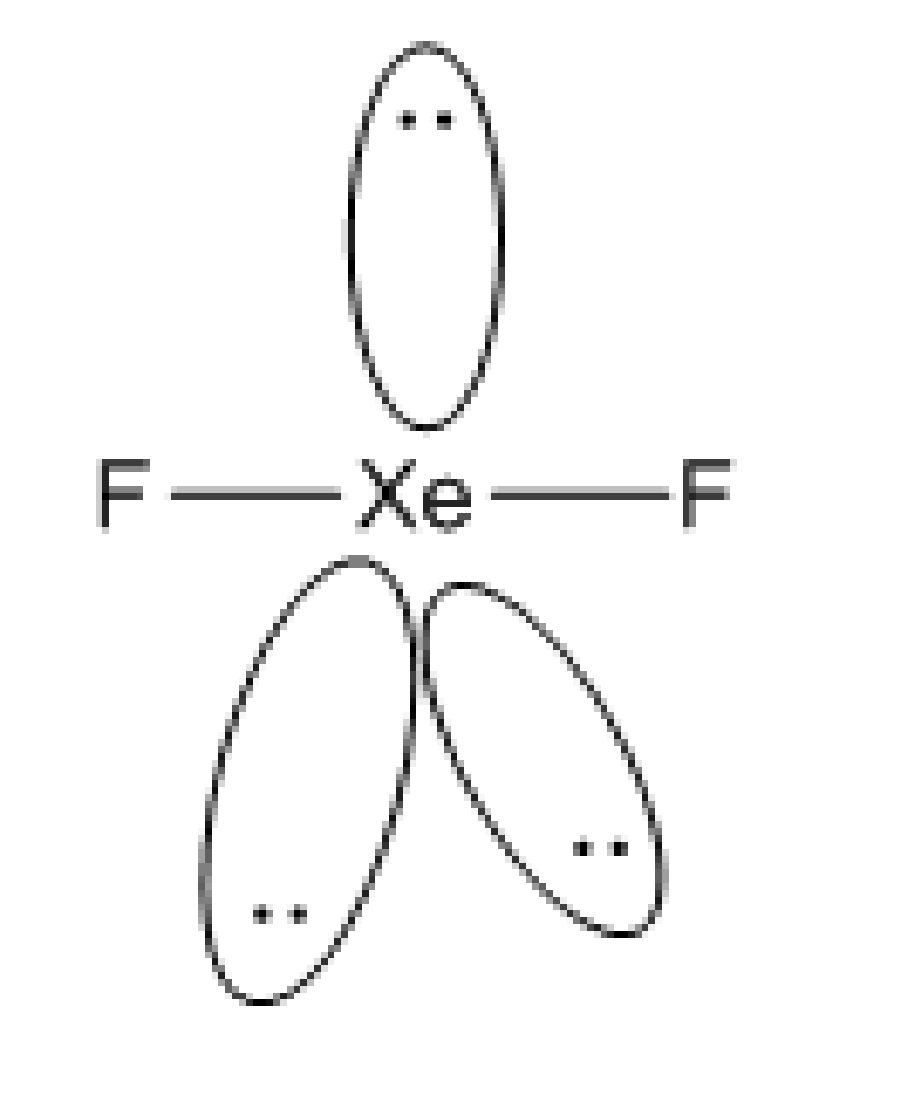
Fig: Structure of \[{\rm{Xe}}{{\rm{F}}_{\rm{2}}}\]
Therefore, the xenon difluoride molecule has a linear shape.
Hence, option D is right.
Note: It is to be noted that only xenon amongst the noble gases forms many compounds. Mostly they are non-reactive in nature because of the fully filled valence shell. The exception in the case of xenon is due to its bigger size which causes weak attraction of the electrons to the nucleus and helps in compound formation.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Let's understand the hybridization of \[{\rm{Xe}}{{\rm{F}}_{\rm{2}}}\]. The configuration of xenon at the ground state is \[5{s^2}5{p^6}\] . The configuration of xenon changes to \[5{s^2}5{p^5}5{d^1}\]at the excited state. Thus, excited state configuration of xenon, that is, \[5s,5{p^y},5{p^x},5{p^z},5{d^z}\] undergoes hybridization to form 5 \[s{p^3}d\] orbitals. Therefore, xenon difluoride has a hybridization of \[s{p^3}d\].
Let's discuss the structure of xenon difluoride. The formation of two sigma bonds F-Xe-F occurs due to the overlap of two half-filled orbitals of fluorine atoms. The three atomic orbitals which contain lone pairs have no participation in bonding. So, the molecule has two bond pairs and three numbers of lone pairs surrounding it. So, the geometry of the molecule is linear in nature. The shape is such that the positions of lone pairs are in equatorial positions. And the measure of the bond angle is \[180^\circ \].

Fig: Structure of \[{\rm{Xe}}{{\rm{F}}_{\rm{2}}}\]
Therefore, the xenon difluoride molecule has a linear shape.
Hence, option D is right.
Note: It is to be noted that only xenon amongst the noble gases forms many compounds. Mostly they are non-reactive in nature because of the fully filled valence shell. The exception in the case of xenon is due to its bigger size which causes weak attraction of the electrons to the nucleus and helps in compound formation.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

JEE Energetics Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




