
Reaction of ethyl formate with an excess of \[C{H_3}MgI\] followed by hydrolysis gives:
A. N-propyl alcohol
B. Isopropyl alcohol
C. Acetaldehyde
D. Acetone
Answer
241.2k+ views
Hint: Ethyl formate is an ester compound with chemical formula \[HCOO{C_2}{H_5}\]. Hydrolysis is a reaction which involves the addition of water.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Ethyl formate is an ester compound produced by the reaction of alcohol and formic acid.
A Grignard reagent is a chemical compound with a general formula of \[RMgX\]. Here, R is the alkyl group and X is the halide group. It is an organomagnesium compound. The grignard reagent is formed by the reaction of aryl or alkyl halide with magnesium.
When Grignard reagent reacts with ethyl formate an intermediate product is formed which on hydrolysis leads to isopropyl alcohol.
First, the negative charge of the methyl group of Grignard reagent attacks the central carbon of ethyl formate and the ethyl group is removed, again the negative charge methyl group attack the carbon and an intermediate compound magnesium iodide propan-2-olate. The intermediate compound then undergoes hydrolysis which means the addition of a water molecule which results in the formation of the main product i.e, Isopropyl alcohol.
The reaction of ethyl formate with an excess of \[C{H_3}MgI\] followed by hydrolysis gives Isopropyl alcohol. Therefore, option B is correct.
The reaction mechanism is shown below.
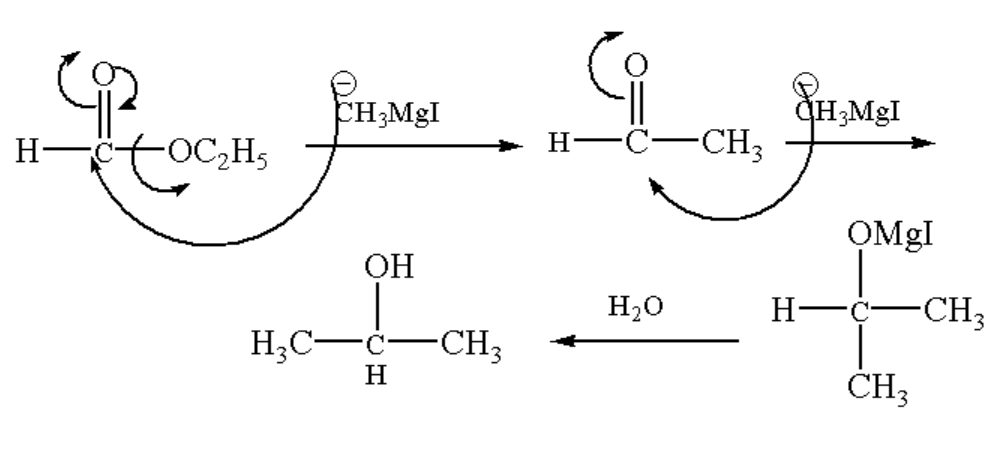
Image: Formation of Isopropyl alcohol
Note: It should be noted that the ester compound needs two equivalent of a Grignard reagent to produce tertiary alcohol. On the other hand aldehyde and ketone requires one equivalent of Grignard reagent to form secondary alcohol and tertiary alcohol respectively.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Ethyl formate is an ester compound produced by the reaction of alcohol and formic acid.
A Grignard reagent is a chemical compound with a general formula of \[RMgX\]. Here, R is the alkyl group and X is the halide group. It is an organomagnesium compound. The grignard reagent is formed by the reaction of aryl or alkyl halide with magnesium.
When Grignard reagent reacts with ethyl formate an intermediate product is formed which on hydrolysis leads to isopropyl alcohol.
First, the negative charge of the methyl group of Grignard reagent attacks the central carbon of ethyl formate and the ethyl group is removed, again the negative charge methyl group attack the carbon and an intermediate compound magnesium iodide propan-2-olate. The intermediate compound then undergoes hydrolysis which means the addition of a water molecule which results in the formation of the main product i.e, Isopropyl alcohol.
The reaction of ethyl formate with an excess of \[C{H_3}MgI\] followed by hydrolysis gives Isopropyl alcohol. Therefore, option B is correct.
The reaction mechanism is shown below.

Image: Formation of Isopropyl alcohol
Note: It should be noted that the ester compound needs two equivalent of a Grignard reagent to produce tertiary alcohol. On the other hand aldehyde and ketone requires one equivalent of Grignard reagent to form secondary alcohol and tertiary alcohol respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




